Add after example 8
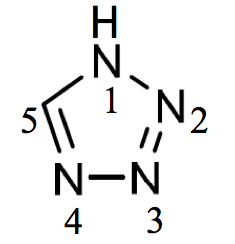
1H-tetrazole (PIN)
(not 1H-1,2,3,4-tetrazole)
Division VIII Chemical Nomenclature and Structure Representation Division
Characters deleted from the printed text or which are modified are marked in red on the original text. Characters added to the corrected text are marked in red too. See separate file of corrections that affect nomenclature
Page xi, P-24.4, title.
For MONOSPIRO RING SYSTEMS ...
read DISPIRO RING SYSTEMS ...
Page xi, P-25.5, title.
For ...COMPONENTS AND PERI-FUSED TOGETHER
read ...COMPONENTS ORTHO- AND PERI-FUSED TOGETHER
Page xix, lines 14-17. [corrected 17 June 2020]
Delete P-76.1
Page xv, P-56.3, title.
For THE SUFFIXES ‘AMIDINE’ AND ‘CARBOXAMIDINE’
read THE SUFFIXES ‘IMIDAMIDE’ AND ‘CARBOXIMIDAMIDE’
Page xv, P-57. [corrected 12 August 2020]
For P-57 SELECTING PREFERED AND PRESELECTED...
read P-57 SELECTING PREFERRED AND PRESELECTED...
Page xv, P-59.2, title.
For EXAMPLES ILLUSTRATING THE METHODOLOGY
read EXAMPLES ILLUSTRATING THE GENERAL METHODOLOGY
Page xvi, Contents P-63.4.
For Hydroperoxides (Peroxols) and Chalcogen ** Analogues
read Hydroperoxides (Peroxols) and Chalcogen Analogues
Page xvii, line 5. [corrected 28 November 2018]
For P-65.5 ACID HALIDES AND PSEUDOHALIDES 796
read P-65.5 ACYL HALIDES AND PSEUDOHALIDES 796
Page xvii, contents. [corrected 16 August 2016]
For P-68 NOMENCLATURE OF ORGANIC COMPOUNDS OF THE GROUPS 13, 14, 15, 16, AND 17 ELEMENTS NOT INCLUDED IN SECTIONS P-62 THROUGH P-67
read P-68 NOMENCLATURE FOR ORGANIC COMPOUNDS OF THE GROUPS 13, 14, 15, 16, AND 17 ELEMENTS NOT INCLUDED IN SECTIONS P-62 THROUGH P-67
Page xvii, P-65.3, title.
For SULFONIC ACIDS AND FUNCTIONAL REPLACEMENT ANALOGUES
read SULFUR, SELENIUM, AND TELLURIUM ACIDS WITH CHALCOGEN ATOMS DIRECTLY LINKED TO A PARENT HYDRIDE
Page xx, Contents P-101.
For ...ALKALOIDS, TEROIDS, TERPENES,...
read ...ALKALOIDS, STEROIDS, TERPENES,...
Page xxiii, CHAPTER P-3, title.
For CHARACTERISTIC (FUNCTIONAL GROUPS)
read CHARACTERISTIC (FUNCTIONAL) AND SUBSTITUENT GROUPS
Page xxiv, Table 7.2.
For ...Radicals of Aamines, Imines...
read ...Radicals of Amines, Imines...
Page xxiv, line 2 on this page. [corrected 7 August 2019]
For Table 7.3 Retained preselected names for the mononuclear...
read Table 7.3 Retained names for the mononuclear...
Page xxix, entry 2 (a), lines 2/3. [corrected 6 May 2020]
For ...hydride and as detachable prefixes...
read ...hydride and as nondetachable prefixes...
Page xxix, Item 2(b), line 1.
For hetero atoms
read heteroatoms [delete space in name]
Page xxxi, changes 6 (d), line 4. [corrected 10 April 2019]
For ...for CH3-CH3-CH2-CH2-CO-NHNH2, not...
read ...for CH3-CH2-CH2-CH2-CO-NHNH2, not...
Page xxxii, entry 7 (f), line 1. [corrected 6 May 2020]
For ...not used in preferred IUPAC names...
read ...not used in IUPAC names...
Page xxxii, entry 7 (g), line 1. [corrected 6 May 2020]
For ...no longer acceptable in preferred IUPAC names...
read ...no longer acceptable in IUPAC names...
Page xxxii, section 7 (g), line 1. [correction deleted 23 December 2020]
Page xxxii, entry 7 (h), line 1. [corrected 6 May 2020]
For ...no longer acceptable in preferred IUPAC names...
read ...no longer acceptable in IUPAC names...
Page xxxiv, preface 9 (b). [corrected 3 June 2020]
For The nomenclature for an a(ba)x heteroacyclic chain does not apply when the 'b' element is nitrogen or carbon; this is a change from the 1993 Guide ('ref.2') where the 'amine' characteristic group present in such a system was not recognized and carbon was not excluded as a 'b' element.
read The nomenclature for an a(ba)x heteroacyclic chain now excludes carbon; and with nitrogen the amine characteristic group is recognized. This is a change from the 1993 Guide ('ref.2').
Page xxxv, entry 11 (d), line 3.
For (refs. 1 and 2)
read (refs. 1, 2 and 4)
Page xxxv, entry 11 (f), lines 6/7.
For (ref. 4)
read (ref. 8)
Page xxxvi, entry 13 line 1. [corrected 6 May 2020]
For 13. Adducts composed solely of...
read 13. Adducts
Adducts composed solely of...
Page xxxvi, entry 14. [corrected 24 April 2019]
Add (d) All locants which form part of the name of all heterocyclic components in spiro ring systems and phane systems are placed in brackets as in fused ring systems. In the previous recommendations (ref. 5 and ref. 8) the locants of the first cited component were not enclosed in brackets.
Page xxxvi, entry 15, line 3.
For ...the first organyl group (alkyl, aryl, etc.) as a separate word before the.....
read ...the last organyl group (alkanediyl, arylene, etc.) as a separate word immediately before the...
Page xxxvi, entry 15, lines 4/5. [corrected 6 May 2020]
For ...(see P-72.2.2.1) rather...
read ...(see P-72.2.2.2) rather...
Page xxxvii, entry 16, lines 3/4. [corrected 6 May 2020]
For ...as substituents on polycyclic ring systems....
read ...as substituents on heterocyclic ring systems....
Page xxxviii, glossary entries 4 and 5. [corrected 11 December 2019]
Reverse the order of these two entries.
Page xxxix, glossary entry 2, line 3. [corrected 31 July 2019]
For ...and –IO2,; or a heteroatomic...
read ...and –IO2; or a heteroatomic...
Page xxxix, glossary entry 5 on this page, line 1. [corrected 6 May 2020]
For ...consisting of two parts, a simple...
read ...consisting of two parts, (1) a simple...
Page xxxix, glossary, entry 5 on this page, line 3. [corrected 19 September 2018]
For ...for example, choromethyl (ClCH2–),...
read ...for example, chloromethyl (ClCH2–),...
Page xl, glossary entry 8. [corrected 14 November 2018]
For Heteroimine
read Heteroimine.
Page xl, glossary entry 8 on this page, line 1. [corrected 6 May 2020]
For ...having a imino group doubly...
read ...having an imino group doubly...
Page xl, glossary entry 12 on this page, lines 1/2. [corrected 6 May 2020]
For ... peripheral atom or a bridgehead atom.
read ... peripheral atom.
Page xli. glossary, entry 7 (now 6). [corrected 12 August 2020]
For An atom in one of the outer rings in a fused ring system that is not a fusion atom or an interior atom.
read Any atom that forms part of the outer perimeter of a fused ring system.
Page xli, glossary entries 6 and 7. [corrected 31 July 2019]
Reverse the order of these two entries
Page xli, glossary entries 12 and 13. [corrected 11 December 2019]
Reverse the order of these two entries.
Page xlii, glossary entry 5 (corrected to 4) on this page, line 3 [corrected 6 May 2020]
For ...(–CH3), hydroxyl (–OH),...
read ...(–CH3), hydroxy (–OH),...
Page 1, P-10, lines 1/4. [corrected 31 July 2019]
For ...atom and no elements from groups 1-12, that can be named using the principles of organic nomenclature, such as substitutive or replacement nomenclature, as described in this book is considered to be an organic compound.
read ...atom is considered to be an organic compound and can be named using the principles of organic nomenclature, such as substitutive or replacement nomenclature, as described in this book.
Page 2, P-11, last line on this page.
For ...monouclear parent hydrides are...
read ...mononuclear parent hydrides are...
Page 3, P-11, paragraph 2 on this page, line 4. [corrected 28.8.2019]
For ...with he IUPAC-IUB Joint Commission...
read ...with he IUPAC-IUBMB Joint Commission...
Page 7, P-12.1, paragraph 3 on this page, line 9. [corrected 16 January 2019]
For Esters, along with acid halides, anhydrides, amine and oxides linked to...
read Esters, along with acid halides, anhydrides, and amine oxides linked to...
Page 7, P-12.1, paragraph 4 on this page, line 12. [corrected 6 May 2020]
For ...illustrate this metholodogy. The...
read ...illustrate this methodology. The...
Page 8, P-12.1, first line on this page.
For ...of organic componds are...
read ...of organic compounds are...
Page 8, P-12.1, paragraph 2 on this page, line 10. [corrected 24 March 2021]
For ...are clearly signaled in these...
read ...are clearly signalled in these...
Page 8, P-12.1, paragraph 3 on this page, line 5. [corrected 6 May 2020]
For ...in these recommendations..
read ...in these recommendations (see P-11).
Page 8, P-12.1, paragraph 4 on this page, lines 2/3.
For ... compounds containing C, B, Si, Ge, Sn, Pb, N, P, As, Sb, Bi, O, S, Se, Te, Po, F, Cl, Br, I, At, and ...
read ... compounds containing B, Si, Ge, Sn, Pb, N, P, As, Sb, Bi, O, S, Se, Te, Po, F, Cl, Br, I, At, and ...
Page 8, P-12.2, paragraph 1 on this page. (corrected 4 December 2019)
Add at the end Although systematic names alumane, gallane, indigane and thallane are preselected names, the names based on these parent hydrides currently do not have PIN status. However such names can be used in general nomenclature.
Page 9, P-12.3, line 3.
For ... or as as alternative ...
read ... or as alternative...
Page 12, P-13.2.2.1, example 2. [corrected 9 October 2024]
For C6H5 -P(O)(OH)2
read C6H5-P(O)(OH)2
for C6H5 -P(≡N)-OH
read C6H5-P(≡N)-OH
Page 12, P-13.2.2.2, example 1. [corrected 11 November 2020]
For C6H5-C{O,Se}H
read C6H5-C{O/Se}H
Page 17, P-13.4.2, title. [corrected 31 July 2019]
For By a change in ending
read By a change of ending
Page 23, P-13.8, line 8. [corrected 6 May 2020]
For removal of all of a side chain in from a carotenoid system
read removal of all of a side chain from a carotenoid system
Page 24, P-13.8.1.2, example 1. [corrected 31 July 2019]
For oxytocin (PIN)
read oxytocin
Page 29, P-14.3.1, lines 5/6 on this page. [corrected 16 January 2019]
For ...three isomers of xylene are still recognized as o-, m-, and p-xylene in general IUPAC nomenclature (see P-22.1.3).
read ...three isomers of xylene and cresol are still recognized as o-, m-, and p-xylene and o-, m-, and p-cresol, respectively in general IUPAC nomenclature (see P-22.1.3 and P-63.1.1.2).
Page 29, P-14.3.1, paragraph 2, line 4. [corrected 23 December 2020]
Add at end The prefixes o-, m-, and p-tolyl are still recognized for general nomenclature (see P-29.6.2.3). No substitution is allowed.
Page 29, P-14.3.1, lines 12/13 on this page. [modified 6 May 2020]
For ...tetrapyrrole nomenclature (ref. 17), and amino acid and peptide (ref. 18).
read ...tetrapyrrole (ref. 17), and amino acid and peptide nomenclature (ref. 18 and P-103.2.1).
Page 30, P-14.3.3 [corrected 28 April 2023}.
Add at end
For omission of locants from a PIN see P-14.3.4.
Page 30, P-14.3.4.1, example 3.
For pentanoyl (PIN)
read pentanoyl (preferred prefix)
Page 30, P-14.3.4.2 (a), example 3. (corrected 27 November 2019)
For trimethylalumane (PIN)
read trimethylalumane
Page 31, P-14.3.4.2 (b), example 1 on this page. [corrected 21 November 2018]
For hydrazinyl (preferred prefix)
read hydrazinyl (preselected prefix)
Page 32, P-14.3.4.3, example on this page. [corrected 21 November 2018]
For choropropanedioic acid (PIN)
read chloropropanedioic acid (PIN)
Page 32, P-14.3.4.4, example 5. [corrected 21 November 2018]
For chloro(silylidene)hydrazine (PIN)
read chloro(silylidene)hydrazine (preselected name)
Page 32, P-14.3.4.4. [corrected 16 June 2021]
Add after example 8

1H-tetrazole (PIN)
(not 1H-1,2,3,4-tetrazole)
Page 32, P-14.3.4.4, example 10.
For ...atom from position ‘2’ to position ‘1’, i.e. ...
read ...atom to the other Si atom, i.e. ...
Page 32, P-14.3.4.4, Note added at end. [modified 18 September 2019]
Add As an exception the locant is not omitted from propan-2-one, butan-2-one, prop-2-enoic acid and prop-2-ynoic acid although unambiguous without the locant.
Page 33, P-14.3.4.5, line 4. [corrected 6 May 2020]
For ...alcohols, and aldehydes, all hydrogen...
read ...alcohols, and to the carbon atoms of formyl groups (aldehydes) all hydrogen...
Page 33, P-14.3.4.5, example 5.
For benzenehexayl (PIN)
read benzenehexayl (preferred prefix)
Page 35, P-14.4 (b), example 3. [corrected 21 November 2018]
For 5H-inden-5-one
read 5H-inden-5-one (PIN)
Page 37, P-14.4 (e), line 2. [corrected 7 November 2018]
For ...and P-31.2.2) and ‘ene’ and ‘yne’ endings);
read ,,,and P-31.2.2) and ‘ene’ and ‘yne’ endings;
Page 37, P-14.4 (e), example 3. [corrected 31 July 2019]
For 2- methylpent-1-en-4-yn-3-ol (PIN)
read 2-methylpent-1-en-4-yn-3-ol (PIN) [delete space from name]
Page 39, P-14.4 (i), example 1 on this page.
Delete this example as it is the same as the next example
Page 42, P-14.5.1, example 4. [corrected 31 July 2019]
For ..., see P-16.5.1.2)]
read ..., see P-16.5.1.2]
Page 44, P-14.5.3, line 3. [corrected 13 January 2021]
For Example:
read Examples:
Page 45, P-14.5.4, example 4 on this page. [corrected 7 November 2018]
For ...the locant set ‘2,3’ is lower than ‘3,2’)
read ...the locant set ‘2,3’ is lower than ‘3,2’]
Page 47, P-14.7.2, line 3. [corrected 10 April 2019]
For ...the addition of a suffix or a prefix describing a structural...
For ...the addition of a suffix describing a structural...
Page 49, P-14.8.1, second paragraph on this page, lines 3/4. [modified 17 June 2020]
For ...connected by long (em) dashes (—) or by a double hyphen (--) without spaces. The proportions...
read ...connected by long (em) dashes (—). The proportions...
Page 52, P-14.8.2, line 3.
For as described in Ref 14;
read as described in Ref 12;
Page 52, P-14.8.2, line 8. [modified 17 June 2020]
For ...by long (em) dashes (—) or a double hyphen (--) without spaces. The proportions...
read ...by long (em) dashes (—). The proportions...
Page 55, P-15.1.2.1, line 7. [corrected 19 September 2018]
For ...IUPAC functonal parent compound...
read ...IUPAC functional parent compound...
Page 57, P-15.1.3, example 1.
For CH4+•
read CH4•+
Page 57, P-15.1.4, title.
For Position of the endings ‘‘ane’’, ‘ene’, and ‘yne’
read Position of the endings ‘ane’, ‘ene’, and ‘yne’
Page 62, P-15.1.8, Type 2b. [corrected 6 May 2020]
For ...that are compulsory prefixes;
read ...that are compulsory prefixes (see Table 5.1);
Page 64, P-15.1.8.2.2, line 9. [corrected 6 May 2020]
For ...and Se and Te analogues.
read ...and Se and Te analogues (see Table 5.1).
Page 65, P-15.1.8.2.3, example 1.
For NH2-O-CH3
read H2N-O-CH3
Page 67, P-15.2.2, line 5.
For ...N-oxides, sulfides, selenides, and tellurides (see P-63.2.5)...
read ...N-oxides, N-sulfides, N-selenides, and N-tellurides (see P-62.5)...
Page 68, P-15.2.3, line 7. [corrected 13 January 2021]
For Example:
read Examples:
Page 69, P-15.3.0, line 1. [corrected 6 May 2020]
For ...identical parent stuctures.
read ...identical parent structures.
Page 71, P-15.3.1.2.1.1, example 1. [corrected 23 December 2020]
For methanediyl
read (not methanediyl)
Page 72, P-15.3.1.2.2.1, example 1.
For ...or twice ‘oxy’ (see P-15.3.1.2.1.1).
read ...or twice ‘oxy’ [see P-15.3.1.2.1.1, P-16.3.6 (b)].
Page 74, P-15.3.1.2.2.3, example 2.
For ethane-1,2- diylbis[azanylylidene(chloromethanylylidene)] (preferred prefix)
read ethane-1,2-diylbis[azanylylidene(chloromethanylylidene)] (preferred prefix) [removed space from name]
Page 74, P-15.3.1.2.2.3, Note lines 5/6. [corrected 6 May 2020]
For ...preferred IUPAC name [oxybis(cycloptopane-1,1-diylmethylene
read ...preferred IUPAC prefix oxybis(cycloptopane-1,1-diylmethylene
Page 75, P-15.3.1.2.2.4, example 4 on this page. [corrected 3 March 2021]
For oxydipropan-1-yl-3-ylidene (preferred prefix)
read oxydi(propan-3-yl-1-ylidene) (preferred prefix)
Page 76, P-15.3.2.1, lines 3/4. [corrected 31 July 2019]
For ...Functionalized parent hydrides, i.e. parent structures substituted by groups expressed by suffixes (see P-15.1.2), are enclosed in parentheses ...
read ...When functionalized parent hydrides, i.e. parent structures substituted by groups expressed by suffixes (see P-15.1.2), have locants, they are enclosed in parentheses...
Page 79, P-15.3.2.1.1, example 1.
For 2-[(4-carboxycyclohexyl)methyl]cyclohexane-1-carboxylic acid (PIN; see P-45.1.2)
read 2-[(4-carboxycyclohexyl)methyl]cyclohexane-1-carboxylic acid (PIN)
for ...lower than ‘4’ (see P-45.1.2)]
read ...lower than ‘4’ (see P-45.2.2)]
Page 80, P-15.3.2.1.1, example 1 on this page.
For [not 3-(1-carboxyethoxy)propanoic acid; the substituent locant ‘2’ is lower than ‘3’ (see P-45.1.2)]
read [not 3-(1-carboxyethoxy)propanoic acid; the substituent locant ‘2’ is lower than ‘3’ (see P-45.2.2)]
Page 82, P-15.3.2.4.1, example 3 on this page.
For N,N ′-oxybis(N-methylmethanamine) (PIN)
read N,N′-oxybis(N-methylmethanamine) (PIN) [delete space from name]
Page 84, P-15.3.2.4.2, example 1 on this page.
For [not [(2-chlorosilyl)ethyl]silane; ...; see P-45.1.1]
read [not [(2-chlorosilyl)ethyl]silane; ...; see P-45.2.1]
Page 86, P-15.3.3.2.1, line 2. [corrected 13 January 2021]
For Example:
read Examples:
Page 88, P-15.3.4.1.2, example (2). [corrected 6 May 2020]
For –CH-CH=N-CH2-CH=
read –CH2-CH=N-CH2-CH=
Page 89, P-15.4.0, paragraph 2, lines 11/12. (corrected 27 November 2019)
For ...(see Table 2.7).
read ...(see Table 2.8).
Page 89, P-15.4.0, 2nd paragraph, line 10. [corrected 5 December 2018]
For ...in certain heterocycles (see Table 2.8) and oxygen...
read ...in certain heterocycles (see Table 2.9) and oxygen...
Page 91, P-15.4.1.4, text after example, line 2. [corrected 30 January 2019]
For ...prefixes is fully discussed in P-73.4.
read ...prefixes is fully discussed in P-72.4 and P-73.4
Page 91, P-15.4.2.2, lines 3/4. [corrected 30 January 2019]
For ...or heterocyclic ring assemblies (see P-28.5), skeletal replacement...
read ...or heterocyclic ring assemblies (see P-28.4), skeletal replacement...
Page 93, P-15.4.3.2.3, example 1.
For (locant 1 is not omitted, in accordance with P-15.4.1.4
read (locant 1 is not omitted, in accordance with P-15.4.3.2.1
Page 93, P-15.4.3.2.4, line 3. [corrected 6 May 2020]
For ...for multiple bonds (see P-31.1.2).
read ...for multiple bonds (see P-31.1.2.2.2).
Page 98, P-15.5.3.4.3, line 2.
For ... described in P-65.1.6 and P-68.3.1...
read ... described in P-66.1.6 and P-68.3.1...
Page 106, P-16.2.4.1 (b) example on this page. [corrected 9 October 2024]
For N1-(2-aminoethyl)-N1,N2,N2 -trimethylethane-1,2-diamine
read N1-(2-aminoethyl)-N1,N2,N2-trimethylethane-1,2-diamine
Page 106, PP-16.2.4.2, line 1.
For No hyphen is placed before a numerical prefix...
read No hyphen is placed after a numerical prefix...
Page 107, P-16.3.3 (a), line 2. [corrected 1 May 2019]
For ...‘dithioic acid’ described in P-16.3.6;
read ...‘dithioic acid’ described in P-16.3.5(b)
Page 108, P-16.3.3 (a), example 8. [corrected 30 January 2019]
Delete dipropanoic acid (see P-15.3.1.2)
Page 108, P-16.3.3 (d), line 1. [corrected 1 May 2019]
For ...systematic names other than those than those described in P-16.3.4(c), P-16.3.4(d) and P-16.3.4(e).
read ...systematic names other than those described in P-16.3.4(c), P-16.3.4(d) and P-16.3.4(e).
Page 109, P-16.3.3 (d), line 1. [corrected 6 May 2020]
For diacetic acid (see (15.3.2.1; see also P-15.6.1.4)
read diacetic acid (see P-15.3.2.1; see also P-15.6.1.4)
Page 109, P-16.3.4 (c), example 4. [corrected 31 July 2019]
For see P-68.262
read see P-68.6.2.
Page 109, P-16.3.4 (d), line 1.
For ...substituent groups amd functionalized parent...
read ...substituent groups and functionalized parent...
Page 109, P-16.3.4 (d), lines 2/3. [corrected 30 January 2019]
For ...containing 12 to 19 atoms (see P-16.4.1.1)
read ...containing 12 to 19 atoms (see P-15.1.2);
Page 109, P-16.3.4 (e). [corrected 1 May 2019]
For (e) functionalized parent hydrides;
read (e) functionalized parent hydrides with locants;
Page 109, P-16.3.3 (e), line 2. [corrected 13 January 2021]
For Example:
read Examples:
Page 109, P-16.3.4 (c), example 1. [corrected 6 May 2020]
For di(dodecyl) ( preferred prefix; see P-68.2.6.1)
read di(dodecyl) (preferred prefix; see P-68.2.6.1) [delete space after opening parenthesis]
Page 110, P-16.3.5, lines 1/2. [corrected 11 November 2020]
For The numerical prefixes ‘bis’, ‘tris’, ‘tetrakis’, etc . are used to indicate a a multiplicity of:
read The numerical prefixes ‘bis’, ‘tris’, ‘tetrakis’, etc. are used to indicate a multiplicity of:
Page 110, P-16.3.5 (c), example 2. [corrected 6 May 2020]
For ...whereas 'dinitrilium' might be might be interpreted as two 'nitrile' suffixes...
read ...whereas 'dinitrilium' might be interpreted as two 'nitrile' suffixes...
Page 111, P-16.3.6 (a), examples, line 3. [corrected 30 January 2019]
For defines the –SSH group; see P-63.3.1)
read defines the –SSH group; see P-63.4.2.2)
Page 111, P-16.3.6 (a), example 1. [corrected 6 May 2020]
For ...defines two –SH Groups, see...
read ...defines two –SH groups, see...
Page 111, P-16.3.6 (a), examples, line 6. [corrected 30 January 2019]
For the –SSSH group; see P-68.3.1.3)
read the –SSSH group; see P-68.4.1)
Page 111, P-16.3.6 (a), example 3. [corrected 12 August 2020]
For bis(λ4-sulfanyl) (prefered prefix; ...
read bis(λ4-sulfanyl) (preferred prefix; ...
Page 112, P-16.3.6 (b), example 3 on this page.
For ...whereas disulfonyl is...
read ...whereas disulfinyl is...
Page 112, P-16.3.6 (c), example 1, line 4.
For ...a five membered ring...
read ...a five-membered ring...
Page 112, P-16.3.6 (c), example 2.
For ...atoms, see P-23.2.3.2.2)
read ...atoms, see P-22.2.3.2.2)
Page 112, P-16.3.6 (c), example 3.
For bis(1,2-oxazol-3-yl) [PIN, but di(isoxazol-3-yl, see P-16.3.2 above, or di(1,2-oxazol-3-yl) might be ...
read bis(1,2-oxazol-3-yl) [preferred prefix, but di(isoxazol-3-yl), see P-16.3.2; whereas di(1,2-oxazol-3-yl) might be ...
Page 112, P-16.3.6 (d),
For Example:
read Examples:
Page 112, P-16.3.6 (d), example 1.
For bis(benzo[a]anthracen-1-yl) [PIN, describes two...
read bis(benzo[a]anthracen-1-yl) [preferred prefix, describes two...
Page 113, P-16.5, contents list. [corrected 30 March 2022]
Add P-16.5.4 Multiple types of enclosing marks
Page 114, P-16.5.1.1, line 2.
For ...after the multiplicative multiplicative prefixes...
read ...after the multiplicative prefixes...
Page 114, P-16.5.1.1, example 1. [corrected 6 May 2020]
For ...would describes the structure Cl-SiH2-CH3]
read ...would describe the structure Cl-SiH2-CH3]
Page 115, P-16.5.1.2, example 1.
For ...not cited, see P-14.3.4.3)
read ...not cited, see P-14.3.4.6)
Page 115, P-16.5.1.2, example 3. [corrected 6 May 2020]
For ...see P-63.3.3.2.2)
read ...see P-68.3.1.3.2.2)
Page 116, P-16.5.1.3, example 5 on this page. [modified 6 May 2020]
Add ethyldi(isopropyl)silane
Page 116, P-16.5.1.3.1 (formerly P-16.5.1.3), example 6. [corrected 10 June 2021]
For ethyl(methyl)(propyl)silanecarboxylic acid
read ethyl(methyl)(propyl)silanecarboxylic acid (PIN)
Page 116, P-16.5.1.3.1 (formerly P-16.5.1.3), example 7. [corrected 10 June 2021]
For methyl(phenyl)phosphinic acid
read methyl(phenyl)phosphinic acid (PIN)
Page 116, P-16.5.1.3.1 (formerly P-16.5.1.3), example 8. [corrected 10 June 2021]
For cyclopropyl(phenyl)methanol
read cyclopropyl(phenyl)methanol (PIN)
Page 116, P-16.5.1.3.2 (extension to P-16.5.1.3), example 1. [corrected 10 June 2021]
For bromo(nitro)(phenyl)acetic acid
read bromo(nitro)(phenyl)acetic acid (PIN)
Page 116, P-16.5.1.3.2 (extension to P-16.5.1.3), example 2. [corrected 10 June 2021]
For diethyl ethyl(methyl)propanedioate
read diethyl ethyl(methyl)propanedioate (PIN)
Page 116, P-16.5.1.3.2 (extension to P-16.5.1.3), example 3. [corrected 10 June 2021]
For bromo(chloro)acetic acid
read bromo(chloro)acetic acid (PIN)
Page 116, P-16.5.1.3.2 (extension to P-16.5.1.3), example 4. [corrected 10 June 2021]
For cyclopropyl(fluoro)acetonitrile
read cyclopropyl(fluoro)acetonitrile (PIN)
Page 117, P-16.5.1.5, example 1. [corrected 6 May 2020]
For [N-(2-chloroethyl)propan-1-amine (PIN)]
read N-(2-chloroethyl)propan-1-amine (PIN)
Page 117, P-16.5.1.5, example 2. [corrected 6 May 2020]
For [N-ethyl-N-propylbutan-1-amine (PIN)]
read N-ethyl-N-propylbutan-1-amine (PIN)
Page 117, P-16.5.1.5, example 3. [corrected 6 May 2020]
For [N-ethyl-N-methylbutan-1-amine (PIN)]
read N-ethyl-N-methylbutan-1-amine (PIN)
Page 118, P-16.5.1.12, line 1. [corrected 6 May 2020]
For ...are used to enclosing multiple dots and...
read ...are used to enclose multiple dots and...
Page 118, P-16.5.2.3, example 1. [corrected 6 May 2020]
For [cyclodeca-1,3,5,7,9-pentaene (PIN)]
read cyclodeca-1,3,5,7,9-pentaene (PIN)
Page 119, P-16.5.4.. [corrected 30 March 2022]
For P-16.5.4 When multiple types...
read P-16.5.4 Multiple types of enclosing marks
When multiple types...
Page 120, P-16.4.1, line 7. [corrected 6 May 2020]
For ... The (1S) descriptor forces...
read ... The (2S) descriptor forces...
Page 121, P-16.6.1, example 1. [corrected 6 May 2020]
For [1,2-xylene (PIN)]
read 1,2-xylene (PIN)
Page 121, P-16.6.1, example 2. [corrected 6 May 2020]
For [1,4-dinitrosobenzene (PIN)]
read 1,4-dinitrosobenzene (PIN)
Page 121, P-16.6.4, example 2.
For ‘E’ and ‘Z’ (P-93.4.2.1.1); ‘cis’, and ‘trans’ (P-93.5.2.2.2); ‘r’, ‘c’, and ‘t’ (P-93.5.1.3); ‘r’and ‘s’ (P-93.5.1.1.2)
read ‘E’ and ‘Z’ (P-93.4.2.1.1); ‘cis’, and ‘trans’ (P-93.4.2.1.1); ‘r’, ‘c’, and ‘t’ (P-93.5.1.3)
Page 121, P-16.6.4, example 3.
For ‘R’ and ‘S’ (P-93.1.1); ‘R*’ (spoken R-star), ‘S*’ (spoken S-star), ‘r’, ‘s’ (P-93.1.2.1), ‘rel’ (P-93.1.2.1)
read ‘R’ and ‘S’ (P-93.1.1); ‘R*’ (spoken R-star), ‘S*’ (spoken S-star), ‘r’, ‘s’ (P-93.5.1.1), ‘rel’ (P-93.1.2.1)
Page 121, P-16.6.2, example 2. [corrected 6 May 2020]
For O-ethyl hexaneselenoate (PIN, P-65.6.3.3.1)
read O-ethyl hexaneselenoate (PIN, P-65.6.3.3.7.1)
Page 122, P-16.7.1, example 6. [corrected 21 November 2018]
For sulfanyl (PIN, P-29.3.1)
read sulfanyl (preselected prefix, P-29.3.1)
Page 123, P-16.7.2 (b), example.
For 2,4,6-tetrasilaundecan-11-yl (PIN)
read 2,4,6-tetrasilaundecan-11-yl (preferred prefix)
Page 123, P-16.7.2 (g), line 4.
For ...vowel [see P-16.8.1(f) for an...
read ...vowel [see P-16.7.1 (f) for an...
Page 124, P-16.8.1, example 2.
For phenylphosphononitridic acid (PIN, P-67.1.2.4.1)
read phenylphosphononitridic acid (PIN, P-67.1.2.4.1.1)
Page 124, P-16.9.1 line 3. [corrected 6 May 2020]
For ...amidrazones (see P-66.4.2), and hydrazidines (see P-66.4.3)
read ...hydrazonamides (amidrazones) (see P-66.4.2), and hydrazonohydrazides (hydrazidines) (see P-66.4.3)
Page 125, P-16.9.2, box line 3. [corrected 6 May 2020]
For ...di(amidrazones), di(hydrazonohydrazides,...
read ...di(amidrazones), di(hydrazonohydrazides),...
Page 125, P-16.9.2, box line 2. [corrected 16 January 2019]
For ...symmetrical geminal diamines, diimines,...
read ...symmetrical diamines, diimines,...
Page 125, P-16.9.2, lines 2/3 in the box.
For ...di(imidamides), (diamidines), di(hydrazonamides)...
read ...di(imidamides), di(amidines), di(hydrazonamides)...
Page 125, P-16.9.2, box line 4. [corrected 12 August 2020]
For ...imidohydrazides, poylimidopolycarbonic and inorganic...
read ...imidohydrazides, polyimidopolycarbonic and inorganic...
Page 125, P-16.9.2, example 3. [corrected 6 May 2020]
For N1,N5-dimethylpentanediamide (PIN)
read N1,N5-dimethylpentanediamide (PIN, see P-66.1.1.3.1.1)
Page 125, P-16.9.2, example 4.
For N4,2-dimethylpentane-2,4-diamine (see P-62.2)
read N4,2-dimethylpentane-2,4-diamine (PIN, see P-62.2.4.1.2)
Page 126, P-16.9.2, example 1 on this page. [corrected 6 May 2020]
For 1,3-diimidodicarbonic acid (PIN)
read 1,3-diimidodicarbonic acid (PIN, P-65.2.3.1.2.1)
Page 126, P-16.9.3, example 1. [corrected 6 May 2020]
For N3-ethyl-N′3-methylhexane-3,3-diamine (PIN)
read N3-ethyl-N′3-methylhexane-3,3-diamine (PIN, P-62.2.4.1.2)
Page 126, P-16.9.3, example 2. [modified 30 January 2019]
For (PIN, P-66.4.1.4.2)
read (PIN, P-66.4.1.1 and P-66.4.1.4.2)
Page 127, P-16.9.3, example 4 on this page.
For N3-ethyl- N1,N′3-dimethyl(hexane-1,3,3,6-tetrayltetraamine)
read N3-ethyl-N1,N′3-dimethyl(hexane-1,3,3,6-tetrayltetraamine) [delete space from name]
Page 128, P-16.9.3, example 1 on this page. [modified 30 January 2019]
For N1, N1, N′3-triethyl-N′1, N3, N3-trimethylnapthalene-1,3-dicarboximidamide (PIN, P-66.4.1.4.2)
read N1,N1,N′3-triethyl-N′1,N3,N3-trimethylnapthalene-1,3-dicarboximidamide (PIN, P-66.4.1.4.1) [delete spaces from name]
Replace structure with:
Page 129, P-16.9.5 (a), example 3.
For cyclopenta[1,2-b:5,1-b′]bis([1,4]oxathiine) (PIN, P-25.7.1)
read cyclopenta[1,2-b:5,1-b′]bis([1,4]oxathiine) (PIN, P-25.3.7.1)
Page 129, P-16.9.5 (c), example. [corrected 23 December 2020]
For naphtho[2′,1′:2,3]-5α-androstane (PIN, P-101.5.1.1)
read naphtho[2′,1′:2,3]-5α-androstane (P-101.5.1.1)
Page 132, P-21.1.1.1, structure 2. (corrected 27 November 2019)
For aluminane (PIN)
read aluminane
Page 133, P-21.1.2.1, 1st paragraph, line 3. [corrected 5 December 2018]
For ...to the name of the hydride (ref. 10).
read ...to the name of the hydride (ref. 13).
Page 134, P-21.2.2, example 1. [corrected 8 May 2019]
For hydrazine (retained, preselected name, see P-12.2)
read hydrazine (retained, preselected name, see P-12.3)
Page 135, P-21.2.3.1, line 11. [corrected 6 May 2020]
For ...(see P-62) are preferred because of the ...
read ...(see P-62) should be used because of the ...
Page 140, Table 2.2, title. [corrected 23 January 2019]
For Retained names of mancude* heteromonocyclic parent hydrides
read Retained names of mancude heteromonocyclic parent hydrides
Page 142, P-22.2.1, Table 2.3, structure 4. [corrected 26 June 2019]
For selenomorpholine (Se instead of O) PIN)
read selenomorpholine (Se instead of O) (PIN)
Page 143, P-22.2.2, title.
For ...hydrides with 3 through 10 membered rings...
read ...hydrides with 3- through 10-membered rings...
Page 143, P-22.2.2.1.1, line 11.
For ...name for =N-N= componds (see...
read ...name for =N-N= compounds (see...
Page 144, P-22.22.1.1, Table 2.5.
For irene/irine
read irene/irine1
for irane/iridine
read irane/iridine2
for etane/etidine
read etane/etidine2
for olane/olidine
read olane/olidine2
add footnote 1 see P-22.2.2.1.5.1
add footnote 2 see P-22.2.2.1.5.2
Page 146, P-22.2.2.1.4, line 2.
For ...with a bonding order of three...
read ...with a bonding number of three...
Page 146, P-22.2.2.1.5.1, line 2.
For ...containing only nitrogen; otherwise...
read ...containing only nitrogen heteroatoms; otherwise...
Page 148, after P-22.2.2.1.6 [corrected 16 June 2021]
Add:
P-22.2.2.1.7 Omission of locants
All locants are omitted for parent Hantzsch-Widman names if there is only one heteroatom or if there is no ambiguity if locants are omitted.
Examples:
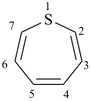
thiepine
(not 1-thiepine)
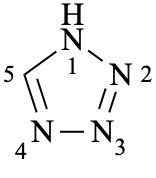
1H-tetrazole
(not 1H-1,2,3,4-tetrazole)
Page 151, P-22.2.4, example 4. [corrected 9 October 2024]
For 2H-1,4,8,11-oxatriazacyclotetradecine
1-oxa-4,8,11-triazacyclotetradeca-3,5,7,9,11,13- hexaene (PIN)
read 2H-1,4,8,11-oxatriazacyclotetradecine
1-oxa-4,8,11-triazacyclotetradeca-3,5,7,9,11,13-hexaene (PIN)
Page 153, P-22.2.6, example 1 on this page. [corrected 30 January 2019]
For cycloheptasiloxane (see P-22.2.5)
read cycloheptasiloxane
for 1,3,5,7,9,11,13-heptaoxa-2,4,6,8,10,12,14-heptasilacyclotetradecane (preselected name, see P-12.2)
read 1,3,5,7,9,11,13-heptaoxa-2,4,6,8,10,12,14-heptasilacyclotetradecane (preselected name, see P-12.2, P-22.2.3.2.3)
Page 155, P-23, line 3. [corrected 27 May 2020]
For P-23.2 Naming and numbering von Baeyer hydrocarbons
read P-23.2 Naming and numbering of von Baeyer hydrocarbons
Page 158, P-23.2.5.1, line 2 on this page.
For ...for example e.g. [2.2.1.02,6]...
read ...for example [2.2.1.02,6]...
Page 162, P-23.2.6.2.5, line 1 on this page. [corrected 13 January 2021]
For Example:
read Examples:
Page 163, P-23.2.6.3, example 2 on this page. [modified 1 December 2021]
For ...versus 2; see P-25-3.2.3.2(a) and P-44.2.2.2.3(b)]
read ...versus 2; see P-25.3.2.3.2(a) and P-44.2.2.2.3(b)]
Page 165, P-23.4, line 7. [corrected 27 May 2020]
For ...described in P-15.4.2.2, in which...
read ...described in P-22.2.5, in which...
Page 166, P-23.5.1, line 17. [corrected 18 September 2019]
For ...derivatives see P-52.1.7.
read...derivatives see P-52.1.6.2.
Page 167, P-23.5.2, line 4. [corrected 13 January 2021]
For Example:
read Examples:
Page 168, P-23.5.3, example. [corrected 21 November 2018]
For tetracyclo[5.5.1.13,11.15,9]hexasiloxane (a hexasilasesquioxane)
read tetracyclo[5.5.1.13,11.15,9]hexasiloxane (preselected name, P-12.2) (a hexasilasesquioxane)
for 2,4,6,8,10,12,13,14,15-nonaoxa-1,3,5,7,9,11-hexasilatetracyclo[5.5.1.13,11.15,9]pentadecane (preselected name, P-12.2)
read 2,4,6,8,10,12,13,14,15-nonaoxa-1,3,5,7,9,11-hexasilatetracyclo[5.5.1.13,11.15,9]pentadecane
Page 169, P-23.7, line 3.
For ...prismane is not longer recommended.
read ...prismane is no longer recommended.
Page 170, P-24.0, line 4/5 on this page. [corrected 8 May 2019]
For No other modifications have been made to the 1999 publication (ref. 8).
read Also in P-24.5.3, P-24.6, P-24.7 and P-24.8.4 some modifications on the usage of brackets have been made to SP-4, SP-5 and SP-7 of the 1999 publications (ref. 8).
Page 173, P-24.2.3, example. [corrected 23 January 2019]
For (the importance of superscripts is illustrated by this example and the second example in P-24.2.2; ...
read (the importance of superscripts is illustrated by this example and the third example in P-24.2.2; ...
Page 174, P-24.2.3.1. line 3. [corrected 13 January 2021]
For Example:
read Examples:
Page 176, P-24.2.4.1.1, line 4. [corrected 27 May 2020]
For ...above (P-24.2). Heteroatoms...
read ...above (P-24.2.1, P-24.2.2, P-24.2.3). Heteroatoms...
Page 177, P-24.2.4.2, line 2. [corrected 27 May 2020]
For ...described in P-24.2 using the...
read ...described above using the...
Page 177, P-24.2.4.2, line 8. [corrected 30 January 2019]
For PIN names for organic derivatives see P-52.1.5.
read PIN names for organic derivatives see P-52.1.6.
Page 178, P-24.2.4.3 (1) (b), line 2. [corrected 27 May 2020]
For ...for example, Si before O).
read ...for example, Si before O.
Page 183, P-24.4.2, example on this page, explanation. [corrected 11 November 2020]
For ...is lower than ‘1,2′,2′′,5′ ’ in (II) or ‘1′,1′′,2,6′ ’ in in (III).
read ...is lower than ‘1,2′,2′′,5′ ’ in (II) or ‘1′,1′′,2,6′ ’ in (III).
Page 187, P-24.5.3, example 3 and 4 on this page, note line 3. [corrected 31 July 2019]
For ...(see P-16.5.2.2).
read ...(see P-16.5.2.2). The use of brackets in the name of the first cited component is a change from SP-4 of ref. 8.
Page 188, P-24.5.4, line 2. [corrected 5 December 2018]
For ...nomenclature, P-24.5.2 and P-24.5.3 are applied to...
read ...nomenclature, P-24.5.1 and P-24.5.3 are applied to...
Page 190, P-24.6.1, example 1, note line 3. [corrected 31 July 2019]
For ...(see P-16.5.2.2).
read ...(see P-16.5.2.2). The use of brackets in the name of the first cited component is a change from SP-4 of ref. 8.
Page 191, P-24.7.2, example (1), note line 3. [corrected 31 July 2019]
For ...(see P-16.5.2.2).
read ...(see P-16.5.2.2). The use of brackets in the name of the first cited component is a change from SP-4 of ref. 8.
Page 192, P-24.7.2, example (3) explanation line 4.
For ...where 4′ is lower than 5′)
read ...where 4′ is lower than 5′.
Page 192, P-24.7.2, example (4) explanation line 1
For ...locant’ 3′’ in (I)...
read ...locant ‘3′’ in (I)...
explanation line 2
For ...central ring component)
read ...central ring component.
Page 193, P-24.7.3, example explanation line 2.
For ..‘1,1′′,2′,2′′′,6′,8′ ’ in (IV)]
read ..‘1,1′′,2′,2′′′,6′,8′ ’ in (IV).
Page 194, P-24.7.4.1, example 1.
For trispiro{bis(cyclohexane)-1,4′:1′′,6′-furo[3,4-d][1,3]oxathiole-2′,14′′′-[7]oxadispiro[5.1.58.26]pentadecane} (PIN)
read trispiro[bis(cyclohexane)-1,4′:1′′,6′-furo[3,4-d][1,3]oxathiole-2′,14′′′-[7]oxadispiro[5.1.58.26]pentadecane] (PIN)
for pentaspiro[tetracyclohexane-1,2′(5′H):1′′′,5′:1′′′′,4′′(6′′H):1′′′′′6′′-furan-3′(4′H),2′′-furo[3,4-d][1,3]oxathiole] (the CAS index name)
read pentaspiro[tetracyclohexane-1,2′(5′H):1′′′,5′:1′′′′,4′′(6′′H):1′′′′′,6′′-furan-3′(4′H),2′′-furo[3,4-d][1,3]oxathiole] (the CAS index name; note that multiple primes are not divided into groups of three)
Page 194, P-24.7.4.1, example 2. [modified 24.8.2017]
For 1λ5,3λ5,5λ5,7λ5-tetraspiro[tetraspiro[2,4,6,8,9,10-hexathia-1,3,5,7-tetraphosphaadamantane-1,2′:3,2′′:5,2′′′:7,2′′′ ′-tetrakis([1,3,2]oxathiaphosphetane)]-4′,7′′′ ′′, 4′′,7′′′ ′′′,:4′′′,7′′′ ′′′ ′,4′′′ ′,7′′′ ′′′ ′′-tetrakis(pyrano[2,3-c]acridine)} [PIN, see SP-7.4(b)]
read 1λ5,3λ5,5λ5,7λ5-tetraspiro[tetraspiro[2,4,6,8,9,10-hexathia-1,3,5,7-tetraphosphaadamantane-1,2′:3,2′′:5,2′′′:7,2′′′ ′-tetrakis([1,3,2]oxathiaphosphetane)-4′,7′′′ ′′:4′′,7′′′ ′′′: 4′′′,7′′′ ′′′ ′:4′′′ ′,7′′′ ′′′ ′′-tetrakis(pyrano[2,3-c]acridine)] [PIN, see SP-7.4(b)]
for
octaspiro[2,4,6,8,9,10-hexathia-1,3,5,7-tetraphosphatricyclo[3.3.1.13,7]decane-1,2′λ5:3,2′′λ5:5,2′′′λ5:7,2′′′′λ5-tetrakis[1,3,2]oxathiaphosphetane- 4′,7′′′ ′′:4′′,7′′′ ′′′:=4′′′,7′′′ ′′′ ′:4′′′,7′′′ ′′′ ′′-tetrakis[7H]pyrano[2,3-c]acridine] (the CAS index name)
read octaspiro[2,4,6,8,9,10-hexathia-1,3,5,7-tetraphosphatricyclo[3.3.1.13,7]decane-1,2′λ5:3,2′′λ5:5,2′′′λ5:7,2′′′′λ5-tetrakis[1,3,2]oxathiaphosphetane-4′,7′′′′′:4′′,7′′′′′′:4′′′,7′′′′′′′:4′′′′,7′′′′′′′′-tetrakis[7H]pyrano[2,3-c]acridine] (the CAS index name; note that multiple primes are not divided into groups of three) [delete spaces from name]
Page 197, P-24.8.1.4, line 3.
For ...The rules for...
read ...the rules for...
Page 199, P-24.8.3, line 2.
For ..prefix spiroter- before..
read ..prefix ‘spiroter’ before..
Page 200, P-24.8.4.1, example 1 and 3, note line 3. [corrected 31 July 2019]
For ...(see P-16.5.2.2).
read ...(see P-16.5.2.2). The use of brackets in the name of the first cited component is a change from SP-4 of ref. 8.
Page 200, P-24.8.4.1, example 2, note 2, line 3. [modified 31 July 2019]
For ...(see P-16.5.2.2).
read ...(see P-16.5.2.2). The use of brackets in the name of the first cited component is a change from SP-4 of ref. 8.
Page 201, P-24.8.4.2, example, note line 3. [corrected 31 July 2019]
For ...(see P-16.4.2.2).
read ...(see P-16.5.2.2). The use of brackets in the name of the first cited component is a change from SP-4 of ref. 8.
Page 203, P-25, title. [corrected 8 May 2019]
For FUSED AND BRIDGED FUSED SYSTEMS
read FUSED AND BRIDGED FUSED RING SYSTEMS
Page 204, P-25.0, line 6. [corrected 12 August 2020]
For ...involved. Positions common to two or more rings are termed 'angular' positions. The...
read ...involved. Atoms common to two or more rings are termed 'fusion' atoms. The...
Page 204, P-25.0, example 1, Explanation, line 2. [corrected 7 November 2018]
For ...benzene rings (one bond and two atoms in common.
read ...benzene rings (one bond and two atoms in common).
Page 204, P-25.0, example 2, Explanation, line 2/3. [corrected 7 November 2018]
For ...a benzene ring (two bonds and three atoms in common.
read ...a benzene ring (two bonds and three atoms in common).
Page 210, P-25.1.2.6, example, right structure Note. [modified 27 May 2020]
For phenanthro[3,4-c]phenanthrene, ref. 1)
read phenanthro[3,4-c]phenanthrene, ref. 22.
Page 210, P-25.1.2.7, lines 1/2.
For ...a five membered ring...
read ...a five-membered ring ...
Page 213, Table 2.8, entries (18), (19) and (20). Correction deleted [11 November 2020]
Page 216, P-25.2.2.2, example 5 in the left column move to end of column 2. [corrected 30 January 2019]
Move X = SiH silanthrene (PIN)
Page 216, P-25.2.2.3, line 5.
For ...described in Section 25.3.3.
read ...described in P-25.3.3.
Page 220, P-25.3.1.2.1, line 1.
For nomenclature principles.
read principles.
Page 221, P-25.3.1.3, lime above example. [corrected 13 January 2021]
For Example:
read Examples:
Page 221, P-25.3.1.3, example, right version. [corrected 3 October 2018]
Replace the structure with:
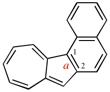
Page 222, P-25.3.1.3, example 1 on this page, right version. [corrected 3 October 2018]
Replace the structure with:
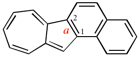
Page 223, P-25.3.2.1.1, line 4. [corrected 5 December 2018]
For ...in the 1993 Guide (see R-2.4.1.1, ref. 2)...
read ...in the 1993 Guide (see R-2.3.1.2, ref. 2)...
Page 225, P-25.3.2.2.2, example 5. [corrected 27 May 2020]
For (from 1,4,8,11-oxatriazacyclotetradecine, PIN)
read (from 1,4,8,11-oxatriazacyclotetradecine, see P-25.2.2.1.2, P-25.3.2.1.2)
Page 226, P-25.3.2.3.1, last line of text.
For ...for three to eight membered rings...
read ...for three- to eight-membered rings...
Page 233, P-25.3.2.4 (j), line 3. [corrected 13 January 2021]
For Example:
read Examples:
Page 236, P-25.3.3.1.1, example on this page.
For ...phenanthro[3,4-c]phenanthrene, ref. 22)
read ...phenanthro[3,4-c]phenanthrene, ref. 22.
Page 236, P-25.3.3.1.2 (b), line 4. [corrected 13 January 2021]
For Example:
read Examples:
Page 240, P-25.3.3.3.1, example 3.
Replace left-hand formula with:
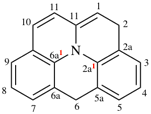
Page 241, P-25.3.3.3.2, example Note.
For ...but still used in in CAS index nomenclature.
read ...but still used in CAS index nomenclature.
Page 242, P-25.3.4.1.3, box line 2. [corrected 27 May 2020]
For ...multiple occurences of a parent...
read ...multiple occurrences of a parent...
Page 243, P-25.3.4.1.3, at top of this page.
Add: Examples:
Page 245, P-25.3.4.2.1 (d), example.
For (not benzo[c]phenanthreno[2,1-m]picene
read (not benzo[c]phenanthreno[2,1-m]picene)
Page 249, P-25.3.4.2.3.3, example. [corrected 3 October 2018]
Replace the structure with:
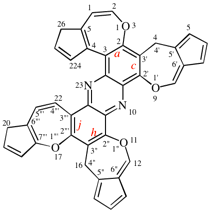
Page 252, P-25.3.4.2.4 (c), example 1 on this page. [corrected 3 October 2018]
Replace the structure with:
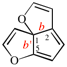
Page 252, P-25.3.4.2.4 (d), example. [corrected 3 October 2018]
Replace the structure with:
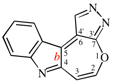
Page 252, P-25.3.4.2.4 (e), example. [corrected 3 October 2018]
Replace the structure with:
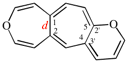
Page 252, P-25.3.4.2.4 (f), example. [corrected 3 October 2018]
Replace the structure with:
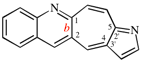
Page 253, P-25.3.4.2.4 (g), example 1. [corrected 3 October 2018]
Replace the structure with:
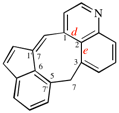
Page 253, P-25.3.5, line 3. [corrected 11 September 2019]
For ...unit (a ‘benzoheterocycle, see P-25.2.2.4)...
read ...unit (a ‘benzoheterocycle’, see P-25.2.2.4)...
Page 253, P-25.3.5, lines 5/6.
For ...this approach is not be used...
read ...this approach is not used...
Page 254, P-25.3.5.4, example 2. [modified 27 May 2020]
For (not [1]benzofuro[5′,4′:3,4]cyclopenta[1,2-b]pyridine; pridine is senior to furan; indene...
read (not 10H-[1]benzofuro[5′,4′:3,4]cyclopenta[1,2-b]pyridine; pyridine is senior to furan; indene...
Page 255, P-25.3.6.1, example 1. [corrected 3 October 2018]
Replace the structure with:
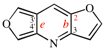
Page 255, P-25.3.6.1, example 2. [corrected 3 October 2018]
Replace the structure with:
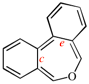
Page 256, P-25.3.6.1, example 1 on this page. [corrected 3 October 2018]
Replace the structure with:
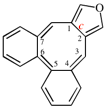
Page 256, P-25.3.6.1, example 2 on this page. [corrected 3 October 2018]
Replace the structure with:
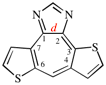
Page 257, P-25.3.6.2, example. [corrected 3 October 2018]
Replace the structure with:
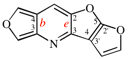
Page 258, P-25.3.7.1, example 1. [corrected 3 October 2018]
Replace the structure with:
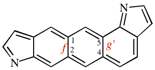
Page 260, P-25.3.7.2, lines 1/2, on this page.
For ...interparent component(s) are cited next to the prefix for the interparent component.
read ...interparent component(s) are cited in front of the prefix for the interparent component.
Page 260, P-25.3.7.2, example 1. [corrected 3 October 2018]
Replace the structure with:
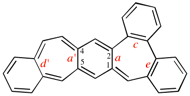
Page 260, P-25.3.7.2, example 2. [corrected 3 October 2018]
Replace the structure with:
Page 261, P-25.3.7.3, example left. [corrected 3 October 2018]
Replace the structure with:
Page 261, P-25.3.7.3, example right. [corrected 3 October 2018]
Replace the structure with:
Page 261, P-25.3.8.1, example 1. [corrected 3 October 2018]
Replace the structure with:
Page 261, P-25.3.8.1, example 3. [corrected 3 October 2018]
Replace the structure with:
Page 261, P-25.3.8.1, example 4. [corrected 3 October 2018]
Replace the structure with:
Page 261, P-25.3.8.1, example 5. [corrected 3 October 2018]
Replace the structure with:
Page 262, P-25.3.8.4, example 1. [corrected 3 October 2018]
Replace the structure with:
Page 262, P-25.3.8.4, example 2. [corrected 3 October 2018]
Replace the structure with:
Page 263, P-25.4, line 7. [corrected 27 May 2020]
For P-25.4.3 Naming bridged fused systems
read P-25.4.3 Naming bridged fused ring systems
Page 264, P-25.4.1.6, title.
For Bivalent bridge.
read Divalent bridge.
Page 264, P-25.4.1.7, line 3.
For ...two simple bivalent bridges.
read ...two simple divalent bridges.
Page 265, P-25.4.2.1, title.
For Bivalent bridges.
read Divalent bridges.
Page 265, P-25.4.2.1.1, line 1.
For A bivalent acyclic hydrocarbon bridge...
read A divalent acyclic hydrocarbon bridge...
Page 266, P-25.4.2.1.2, line 1.
For A bivalent monocyclic hydrocarbon bridge...
read A divalent monocyclic hydrocarbon bridge...
Page 266, P-25.4.2.1.2, line 11. [corrected 27 May 2020]
For ...completed name (see P-25.4.3.4.1).
read ...completed name (see P-25.4.3.4).
Page 266, P-25.4.2.1.3, line 1.
For Bivalent cyclic hydrocarbon bridges...
read Divalent cyclic hydrocarbon bridges...
Page 266, P-25.4.2.1.3, example 2. [corrected 7 November 2018]
For (not [1,3]epibenzeno; benzeno is) the name of a fusion prefix)
read (not [1,3]epibenzeno; benzeno is the name of a fusion prefix)
Page 267, P-25.4.2.1.4, line 1.
For A bivalent acyclic homogeneous heteroatom bridge...
read A divalent acyclic homogeneous heteroatom bridge...
Page 268, P-25.4.2.1.4, example 6 on this page. (corrected 4 December 2019)
For biimino (see ref. 1, R-9.2.1.4)
read biimino (see ref. 1, B-15.1)
Page 268, P-25.4.2.1.4, example 7 on this page.
For azo see ref. 1, B-15.2
read azo (see ref. 1, B-15.1)
Page 268, P-25.4.2.1.4, example 9 on this page. [corrected 5 December 2018]
For azimino (see ref. 1, B-15.2)
read azimino (see ref. 1, B-15.1)
Page 268, P-25.4.2.1.5, line 1.
For A bivalent heterocyclic bridge...
read A divalent heterocyclic bridge...
Page 268, P-25.4.2.1.5, line 9. [corrected 27 May 2020]
For ...the bridge itself (see P-25.4.3.4.1). For numbering...
read ...the bridge itself (see P-25.7.1). For numbering...
Page 270, P-25.4.2.2.1, example 3 on this page. [corrected 5 December 2018]
For epiazanetriyl, ref. 4, FR-8.3.1 (d)
read epiazanetriyl [ref. 4, FR-8.3.2 (a)]
Page 270, P-25.4.2.2.1, example 4 on this page. [corrected 5 December 2018]
For (epiphosphanylylidene) [ref. 4, FR-8.3.1 (d)]
read (epiphosphanylylidene) [ref. 4, FR-8.3.2 (a)]
Page 270, P-25.4.2.2.1, example 5 on this page. [modified 23 January 2019]
For [not phosphanetriyl, ref. 4, FR-8.3.1 (d); (nor phosphanidyne)
read [not phosphanetriyl, ref. 4, FR-8.3.2 (a); nor phosphanidyne]
Page 271, P-25.4.2.3.2.
Add at the end of the text:
If an acyclic bridge component requires internal numbering it is numbered in the direction implied by the bridge name
Page 273, P-25.4.3.2.1, title.
For Bivalent symmetric bridges
read Divalent symmetric bridge
Page 273, P-25.4.3.2.1, line 1 and 2.
For ...to which bivalent symmetric bridges...
read ...to which divalent symmetric bridges...
Page 273, P-25.4.3.2.1, line 4. [corrected 13 January 2021]
For Example:
read Examples:
Page 276, P-25.4.3.4.2 (a), line 2. [corrected 13 January 2021]
For Examples:
read Example:
Page 276, P-25.4.3.4.2 (a), example explanation. [corrected 27 May 2020]
For Explanation: the correct name has three rings in the fused system; the incorrect name has only two rings in the fused system)
read Explanation: the correct name has three rings in the fused ring system; the incorrect name has only two rings in the fused ring system.
Page 277, P-25.4.3.4.2 (d), example 1. [modified 11 September 2019]
For ...(II); the the locant set ‘1,2,4□ for the heteroatoms...
read ...(II); the locant set ‘1,2,4’ for the heteroatoms...
Page 278, P-25.4.3.4.2 (d), example 1 on this page, line 4. [corrected 11 September 2019]
For...[see P-25-3.2.3.2(a) and...
read...[see P-25.3.2.3.2(a) and...
Page 279, P-25.4.3.4.2 (h), line 1.
For ...maximum of bivalent bridges;...
read ...maximum of divalent bridges;...
Page 280, P-25.4.3.4.2 (h), line 1 on this page. [corrected 26 June 2019]
For (the PIN has...
read [the PIN has...
Page 280, P-25.4.2.3.2 (i), example 1. [corrected 23 January 2019]
For 5,14-(metheno)-2,3,4-(epiprop[2]ene[1,3]diyl[1]ylidene)dicyclopenta[f,f ′]pentaleno=[1,2-a:6,5-a′]dipentalene; PIN; the single bond of...
read 5,14-(metheno)-2,3,4-(epiprop[2]ene[1,3]diyl[1]ylidene)dicyclopenta[f,f ′]pentaleno[1,2-a:6,5-a′]dipentalene (PIN); the single bond of...
Page 288, P-25.6, paragraph after example 3, line 2.
For ...with a bonding order of three...
read ...with a bonding number of three...
Page 295, P-25.8.1, lines 6/7 on this page. [corrected 27 May 2020]
For ...heteroatoms including at least least one nitrogen atom...
read ...heteroatoms including at least one nitrogen atom...
Page 299, P-26.1.1, lines 8/9.
For ...those of The cyclic components...
read ...those of the cyclic components...
Page 300, P-26.2.1, line 1. [corrected 27 May 2020]
For ...skeletal name consist of the term...
read ...skeletal name consists of the term...
Page 300, P-26.2.1, line 6.
For ...represent, onvention, carbon...
read ...represent, by convention, carbon...
Page 301, P-26.2.1, 1st paragraph on this page, line 5. [corrected 5 December 2018]
For ...in order of increasing value (see P-14.3.4).
read ...in order of increasing value (see P-14.3.5).
Page 302, P-26.2.2.2.2 (a) (1). [corrected 14 November 2018]
For ...such as ‘1,1′-spirobi[indene] (PIN)
read ...such as ‘1,1′-spirobi[indene]’ (PIN)
Page 306, P-26.4.1.3, line 9. [corrected 13 January 2021]
For Example:
read Examples:
Page 309, P-26.4.2.2, example 1.
For ...senior quinoline amplificants; the locant sets ‘4,2’ and ‘2,4’, respectively, when...
read ...senior quinoline amplificants, ‘4,2’ and ‘2,4’, respectively, when...
for ...‘3’ (see P-26.2.2.3)}
read ...‘3’ (see P-26.3.2.2)}
Page 309, P-26.4.2.2, example 1. [corrected 31 July 2019]
Add Note: The use of brackets in the name of the third amplificant is a change from PHI-3.2 of ref. 5.
Page 311, P-26.4.2.2, example 2 on this page. [corrected 5 December 2018]
For...superatoms ‘3,’ and ‘5’, respectively (see P-26.4.1.3)]
read...superatoms ‘3’, and ‘5’, respectively (see P-26.3.2)]
Page 311, P-26.4.2.3, example 1.
For ...to the lowest locant of the simplified parent sleleton, ‘1’ (see P-26.3.2.2)]
read ...to the lower locant of the simplified parent sleleton, ‘4’ (see P-26.3.2.2)]
Page 314, P-26.4.2.4, example 1 on this page.
For ...attachment locants set ‘(2,5)(2,5)5,2)’ in the PIN compared in the...
read ...attachment locants set ‘(2,5)(2,5)(5,2)’ in the PIN compared in the...
for ...order of the increasing value of their corresponding is lower than...
read ...order of the increasing value of their corresponding superatom locant it is lower than...
for ...the corresponding set of attachment locants, ‘(2,5)(5,2)5,2)’]
read
...the corresponding set of attachment locants, ‘(2,5)(5,2)(5,2)’]
Page 314, P-26.4.3.3, example 1. [corrected 5 December 2018]
For [not 12,13,2,2,44,45,46-heptachloro-1(1,4),4(1,3)- dibenzenacycloheptaphane; the
amplificant with the lower attachment locant set is not assigned to the superatom with the lowest locant (see P-26-4.3.3)]
read [not 12,13,2,2,44,45,46-heptachloro-1(1,4),4(1,3)-dibenzenacycloheptaphane; tamplificant with the lower attachment locant set is not assigned to the superatom with the lowest locant (see P-26.4.2.2)] [delete space in name]
Page 315, P-26.4.3.3, example 1 on this page. [corrected 5 December 2018]
For ... is lower than the locant set ‘1,1,4,4,4’ (see P-26.4.3.3)]
read ... is lower than the locant set ‘1,1,4,4,4’]
Page 315, P-26.4.3.3, example 2 on this page. [corrected 23 January 2019]
For ...is lower than ‘14,16,45,46 ’ (see P-26.4.3.3)]
read ...is lower than ‘14,16,45,46 ’]
Page 316, P-26.5.1, example 2. [corrected 31 July 2019]
Add Note: The use of brackets in the name of the first amplificant is a change from PHI-4.2 of ref. 5.
Page 319, P-26.5.4.1, example 1.
For [not 3-oxa-6-thia-1,7(1,3)-dibenzenacyclododecaphane; the locant set...
read [not 3-oxa-6-thia-1,7(1,3)-dibenzenacyclododecaphane (II); the locant set...
Page 320, P-26.5.4.2, line 3.
For ... B > Al > Ga > Tl (see P-15.4), first with regard to...
read ... B > Al > Ga > In > Tl (see P-15.4), first with regard to...
Page 320, P-26.5.4.2, example 1.
Replace structure with:
Page 322, P-26.6, line 4/5. [corrected 5 December 2018]
For ...developed in Section P-31.6 and P-31.2.3.3.4.
read ...developed in Section P-31.1.6 and P-31.2.3.3.4.
Page 324, P-27.3, lines 7-9.
For ...The numberings associated with trivial names is different, as it is based on principles such as, like ‘most reactive bond’.
read ...The numbering associated with a trivial name may be different if it is based on principles such as ‘most reactive bond’.
Page 326, P-27.3 line 3 on this page. [corrected 9 January 2019]
For ... with Cs and C1 point...
read ...with Cs and C1 point...
Page 327, P-27.4.1, line 9. [modified 11 November 2020]
For ...the letter ‘a’ (b’, ‘c’, etc. if more...
read ...the letter ‘a’, (‘b’, ‘c’, etc. if more...
Page 330, P-27.4.5, line 1.
For When more than operation...
read When more than one operation...
Page 332, P-27.6, line 4. [corrected 27 May 2020]
For P-27.6.1 Fullerenes ortho fused to organic rings or ring systems
read P-27.6.1 Fullerenes and modified fullerenes ortho fused to organic rings or ring systems
Page 332, P-27.6.1, last line on this page and start of next.
For ...The fullerene or modified fullerene locants are always unprimed, and unprimed, and primes are...
read ...The fullerene or modified fullerene locants are always unprimed, and primes are...
Page 337, P-27.6.2, example 1 on this page. [corrected 9 January 2019]
For7,20:8.10:11,13:14,16:17,19-pentaetheno-1,2,3,4,5,6,9,12,15,18-decanor(C60- Ih)[5,6]fullerene (PIN)
read 7,20:8.10:11,13:14,16:17,19-pentaetheno-1,2,3,4,5,6,9,12,15,18-decanor(C60-Ih)[5,6]fullerene (PIN) [delete space from name]
Page 338, P-27.6.3, 2nd pragraph, line 3. [corrected 5 December 2018]
For ...as described in P-24.6.
read ...as described in P-24.5.
Page 338, P-27.7 (1), line 1. [corrected 23 January 2019]
For ...axis (Cn; n >1) and...
read ...axis (Cn; n >1) and...
Page 338, P-27.7 (2), line 1. [corrected 23 January 2019]
For ...axis (Cn; n >1) but...
read ...axis (Cn; n >1) but...
Page 338, P-27.7, title. (corrected 4 December 2019)
For OTHER ASPECTS OF FULLERENCE NOMENCLATURE
read OTHER ASPECTS OF FULLERENE NOMENCLATURE
Page 340, P-28.2.1, example 2. [corrected 23 January 2019]
For (1) 1,1′-biphenyl
read (2) 1,1′-biphenyl
Page 343, P-28.3.1, line 11. [corrected 5 December 2018]
For ...assembly (ref. 25). Locants...
read ...assembly (ref. 26). Locants...
Page 343, P-28.3.1, lines 2/3 in the box.
For The new system, composed of primary and composite locants as described...
read The new system, which uses composite locants composed of primary locants and superscript numbers attached to them as described...
Page 346, P-28.4.2, example 1.
For ...the locant set 2,3′ is lower than 3,2′]
read ...the locant set 2,3′ is lower than 2′,3]
Page 347, P-28.6, line 4. [corrected 9 April 2025]
For ...the longest chain, the maximum number of substituents...
read ...the longest chain, the lowest attachment locants in the order of citation, the maximum number of substituents...
Page 348, P-28.6, example 3. [corrected 23 January 2019]
For ...nor 22,24,25,26-tetraphenyl-11,21:23,31- terphenyl;
read ...nor 22,24,25,26-tetraphenyl-11,21:23,31-terphenyl; [remove space in name]
Page 348, P-28.6, example 3. [corrected 23 January 2019]
For ...; the locant set 1,1′:2′,1′′ is 1 lower than either ...)
read ...; the locant set 1,1′:2′,1′′ is lower than either ...)
Page 349, P-28.7, lines 9/10.
For ...the endings ‘ene’ or ‘yne’ (introduction of double bonds in saturated systems)...
read ...the endings ‘ene’ or ‘yne’ (introduction of multiple bonds in saturated systems)...
Page 350, P-29.1.2, line 11. [corrected 19 September 2018]
For ...as prefixes, often called ‘substitutent prefixes’.
read ...as prefixes, often called ‘substituent prefixes’.
Page 351, P-29.1.3, line 5. [corrected 5 December 2018]
For ...in multiplicative nomenclature (see P-15.3.2.3), are...
read ...in multiplicative nomenclature (see P-15.3.2), are...
Page 357, P-29.3.2.2, example 5.
For 2,5,8,11-tetraoxatetradecan-14-yl (PIN)
read 2,5,8,11-tetraoxatetradecan-14-yl (preferred prefix)
Page 359 P-29.3.4.1, example 5.
For (C60-Ih)[5,6]fulleren-1(9H)-yl (preferred prefix)
read (C60-Ih)[5,6]fulleren-1(9H)-yl (preferred prefix)
Page 362, P-29.4.1, example 1. [corrected 5 December 2018]
For pentan-2-yl (preferred prefix, see P-29.2.2)
read pentan-2-yl [preferred prefix, see P-29.2 (2)]
Page 366, P-29.6.1, example 2.
For 2-[(4-bromophenyl)methyl]pyridine(PIN)
read 2-[(4-bromophenyl)methyl]pyridine (PIN) [insert space].
Page 367, P-29.6.2, title. [corrected 27 May 2020]
For P-29.6.2 Retained prefixes that are not preferred prefixes
read P-29.6.2 Retained prefixes that are not used as preferred prefixes
Page 368, P-29.6.2.2, examples 1 and 2.
Delete extraneous line between structures
Page 369, P-29.6.2.3, example 2 on this page.
For 2-anthryl (also 1- and 9- isomers)
read 2-anthryl (also 1- and 9-isomers) [delete space before isomers]
Page 369, P-29.6.2.3, example 3 on this page.
For 3-furyl (also 2- isomer)
read 3-furyl (also 2-isomer) [delete space before isomers]
Page 369, P-29.6.2.3, example 7 on this page.
For 2-piperidyl (also 1-, 3-, and 4- isomers)
read 2-piperidyl (also 1-, 3-, and 4-isomers) [delete space before isomers]
for piperidin-2-yl (also 1-, 3-, and 4-isomers; (preferred prefixes)
read piperidin-2-yl (also 1-, 3-, and 4-isomers; preferred prefixes)
Page 369, P-29.6.2.3, example 8 on this page.
For 2-pyridyl (also 3- and 4- isomers)
read 2-pyridyl (also 3- and 4-isomers) [delete space before isomers]
Page 370, P-29.6.2.3, example 1 on this page.
For 2-quinolyl (also 3-, 4-, 5-, 6-, 7-, and 8- isomers)
read 2-quinolyl (also 3-, 4-, 5-, 6-, 7-, and 8-isomers) [delete space before isomers]
for quinolin-2-yl (also 3-, 4-, 5-, 6-, 7-, and 8- isomers; preferred prefixes)
read quinolin-2-yl (also 3-, 4-, 5-, 6-, 7-, and 8-isomers; preferred prefixes) [delete space before isomers]
Page 370, P-29.6.2.3, example 3 on this page.
For 2-methylphenyl (also 3- and 4- isomers; preferred prefixes)
read 2-methylphenyl (also 3- and 4- isomers; preferred prefixes) [delete space before isomers]
Page 370, P-29.6.3, example 1. [corrected 23 December 2020]
For phenethyl
read (not phenethyl)
Page 370, P-29.6.3, example 2. [corrected 23 December 2020]
For benzhydryl
read (not benzhydryl)
Page 370, P-29.6.3, example 3. [corrected 23 December 2020]
For isobutyl
read (not isobutyl)
Page 370, P-29.6.3, example 4. [corrected 23 December 2020]
For sec-butyl
read (not sec-butyl)
Page 370, P-29.6.3, example 5. [corrected 23 December 2020]
For isopentyl
read (not isopentyl)
Page 371, P-29.6.3, example 1 on this page. [corrected 23 December 2020]
For tert-pentyl
read (not tert-pentyl)
Page 371, P-29.6.3, example 2 on this page. [corrected 23 December 2020]
For neopentyl
read (not neopentyl)
Page 371, P-29.6.3, example 3 on this page. [corrected 23 December 2020]
For furfuryl (2-isomer only)
read [not furfuryl (2-isomer only)]
Page 371, P-29.6.3, example 4 on this page. [corrected 23 December 2020]
For thenyl (2-isomer only)
read [not thenyl (2-isomer only)]
Page 373. P-31.0, line 4. [corrected 26 January 2022]
For ...also called ‘mancude’ compounds (an acronym for MAximum Number of nonCUmulated DoublE bonds)....
read ...also called ‘mancude’ compounds (an acronym for MAximum number of NonCUmulated DoublE bonds)....
Page 373, P-31.1.1.1, lines 2-4. [corrected 27 May 2020]
For ...Hantzsch-Widman names (see P-31.1.1.3), or retained names denoting partial hydrogenation as indicated later (see P-31.1.1.3)] is denoted by...
read ...Hantzsch-Widman names (see P-22.2.2.1.1), or retained names denoting partial hydrogenation as indicated later (see P-31.2.3.3.1)] is denoted by...
Page 374, P-31.1.1.3, line 7.
For P-31.1.5 Spiro compounds monocyclic rings
read P-31.1.5 Spiro compounds
Page 376, P-31.1.2.2.2, lines 1/2. (corrected 30 October 2019)
For ...by skeletal replacement (‘a) nomenclature.
read ...by skeletal replacement (‘a’) nomenclature.
Page 381, P-31.1.4.2 (2), example 1.
Replace diagram of (III) and (IV) with:
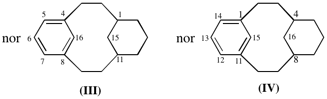
Page 381, P-31.1.4.2 (2), example 2. [corrected 6 February 2019]
For tricyclo[9.3.1.14,8]hexadeca-1(14),4(16)5,7,11(15),12-hexaene (IV
read tricyclo[9.3.1.14,8]hexadeca-1(14),4(16),5,7,11(15),12-hexaene (IV);
Page 382, P-31.1.4.2 (3), example.
For ...the locant set ‘3,11,(18)’ is lower than ‘3,11,(19)’]
read ...the locant set ‘3,11,18’ is lower than ‘3,11,19’]
Page 384, P-31.1.5.1.3, example 2.
For 1,4,7-trithiaspiro[4.5]dec-9-ene (PIN
read 1,4,7-trithiaspiro[4.5]dec-9-ene (PIN)
Page 384, P-31.1.5.1.2 (1), line 1.
For locants are assigned to multiple bonds as a set;
read lower locants are assigned to multiple bonds as a set;
Page 385, P-31.1.5.2.1, Note, line 3.
For ...compounds (ref. 4)
read ...compounds (ref. 8).
Page 388, P-31.1.7.1, box lines 4/5. [modified 27 May 2020]
For ...for spiro compouns in the1999 publication on nomenclature of spiro cpounds (ref. 4)
read ...for spiro compounds in the 1999 publication on nomenclature of spiro compounds (ref. 8)
Page 389, P-31.1.7.2, example 3. [corrected 9 October 2024]
For [11,21:24,31-tercyclohexane]-11(21),22,32- triene (PIN)
read [11,21:24,31-tercyclohexane]-11(21),22,32-triene (PIN)
Page 393, P-31.2.3.3.1, title. [corrected 27 May 2020]
For P-31.2.3.3.1 Retained names of partially saturated mancude compounds
read P-31.2.3.3.1 Retained names of partially saturated polycyclic mancude compounds
Page 397, P-31.2.3.3.5.1 (a), line 9. [corrected 5 December 2018]
For ...nomenclature is preferred (see Chapter P-5).
read ...nomenclature is preferred (see P-54.3).
Page 399, P-31.2.4.1, example 2. [corrected 11 November 2020]
For 1,2-didehydrobenzene (PIN)
read 1,2-didehydrobenzene (PIN) (numbering shown)
Page 400, P-32, contents.
For P-32.3 Retained names
read P-32.3 Retained names for substituent groups derived from unsaturated acyclic parent hydrides
add P-32.4 Retained names for substituent groups derived from partially saturated polycyclic parent hydrides
Page 400, P-32.1.1 (2), line 3. [corrected 5 December 2018]
For ...Section 29.
read ...Section P-29.
Page 401, P-32.1.1, example 7.
Replace structure with:
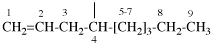
Page 402, P-32.1.1, example 6 on this page. (modified 30 October 2019)
For (1) distibenyl (preselected prefix; see-12.2)
read (1) distibenyl (preselected prefix; see P-12.2)
replace the structure with:
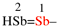
Page 403, P-32.2, line 3.
For ...the order of seniority (see P-24.2 and also P-59.1.10) for...
read ...the order of seniority (see P-44.2 and also P-59.1.10) for...
Page 404, P-32.2.3, line 4. [corrected 27 May 2020]
For ...valence suffixes, added hydrogen atom, and...
read ...valence suffixes, ‘added indicated hydrogen’ atom, and...
Page 405, P-32.3, line 12.
For 2-phenylethenyl’
read 2-phenylethenyl.
Page 405, P-32.4, Table 3.2 first structure, line 2.
For (also 1-, 4-, and 5- isomers
read (also 1-, 4-, and 5-isomers) [remove space in name]
Page 406, P-34.4, Table 3.2 structure 1 on this page line 4-5.
For (also 1-, 3-, 4-, 5-, 6-,and 7-isomers
read (also 1-, 3-, 4-, 5-, 6-, and 7-isomers)
Page 406, P-34.4, Table 3.2 structure 1 on this page.
For indolin-2-yl (also 1-, 3-, 4-, 5-, 6-, and 7- isomers)
read indolin-2-yl (also 1-, 3-, 4-, 5-, 6-, and 7-isomers) [delete space before isomers]
Page 406, P-34.4, Table 3.2 structure 2 on this page.
For isoindolin-2-yl (also 1-, 4-, and 5- isomers)
read isoindolin-2-yl (also 1-, 4-, and 5-isomers) [delete space before isomers]
for 2,3-dihydro-1H-isoindolin-2-yl (preferred prefix) (also 1-, 4-, and 5-isomers)
read 2,3-dihydro-1H-isoindolin-2-yl (preferred prefix) (also 1-, 4-, and 5-isomers)
Page 406, P-34.4, Table 3.2 structure 3 on this page.
Replace text with:
chroman-2-yl (also 3-, 4-, 5-, 6-, 7-, and 8-isomers)
3,4-dihydro-2H-chromen-2-yl (also 3-, 4-, 5-, 6-, 7-, and 8-isomers)
3,4-dihydro-2H-1-benzopyran-2-yl (also 3-, 4-, 5-, 6-, 7-, and 8-isomers) (preferred prefixes)
thiochroman-2-yl (S instead of O) (also 3-, 4-, 5-, 6-, 7-, and 8-isomers)
3,4-dihydro-2H-thiochromen-2-yl (also 3-, 4-, 5-, 6-, 7-, and 8-isomers)
3,4-dihydro-2H-1-benzothiopyran-2-yl (also 3-, 4-, 5-, 6-, 7-, and 8-isomers; preferred prefixes)
selenochroman-2-yl (Se instead of O) (also 3-, 4-, 5-, 6-, 7-, and 8-isomers)
3,4-dihydro-2H-selenochromen-2-yl (also 3-, 4-, 5-, 6-, 7-, and 8-isomers)
3,4-dihydro-2H-1-benzoselenopyran-2-yl (also 3-, 4-, 5-, 6-, 7-, and 8-isomers; preferred prefixes)
tellurochroman-2-yl (S instead of O) (also 3-, 4-, 5-, 6-, 7-, and 8-isomers)
3,4-dihydro-2H-tellurochromen-2-yl (also 3-, 4-, 5-, 6-, 7-, and 8-isomers)
3,4-dihydro-2H-1-benzotelluropyran-2-yl (also 3-, 4-, 5-, 6-, 7-, and 8-isomers; preferred prefixes) [remove spaces before isomer]
Page 406, P-34.4, Table 3.2 structure 4 on this page.
Replace text with:
isochroman-3-yl (also 3-, 4-, 5-, 6-, 7-, and 8-isomers)
3,4-dihydro-2H-isochromen-3-yl (also 3-, 4-, 5-, 6-, 7-, and 8-isomers)
3,4-dihydro-2H-2-benzopyran-3-yl (also 3-, 4-, 5-, 6-, 7-, and 8-isomers) (preferred prefixes)
isothiochroman-3-yl (S instead of O) (also 3-, 4-, 5-, 6-, 7-, and 8-isomers)
3,4-dihydro-2H-isothiochromen-3-yl (also 3-, 4-, 5-, 6-, 7-, and 8-isomers)
3,4-dihydro-2H-2-benzothiopyran-3-yl (also 3-, 4-, 5-, 6-, 7-, and 8-isomers; preferred prefixes)
isoselenochroman-3-yl (Se instead of O) (also 3-, 4-, 5-, 6-, 7-, and 8-isomers)
3,4-dihydro-2H-isoselenochromen-3-yl (also 3-, 4-, 5-, 6-, 7-, and 8-isomers)
3,4-dihydro-2H-2-benzoisoselenopyran-3-yl (also 3-, 4-, 5-, 6-, 7-, and 8-isomers; preferred prefixes)
isotellurochroman-3-yl (Te instead of O) (also 3-, 4-, 5-, 6-, 7-, and 8-isomers)
3,4-dihydro-2H-isotellurochromen-3-yl (also 3-, 4-, 5-, 6-, 7-, and 8-isomers)
3,4-dihydro-2H-2-benzotelluropyran-3-yl (also 3-, 4-, 5-, 6-, 7-, and 8-isomers; preferred prefixes) [remove spaces before isomer]
Page 407, P-33.1. line 2. [corrected 27 May 2020]
For ...that are use to denote radicals...
read ...that are used to denote radicals...
Page 407, P-33.1, lines 2/3.
Delete Suffixes describing characteristic groups are divided into ‘functional suffixes’ and ‘cumulative suffixes’.
Page 408, P-33.1, under ethan-1-yl-2-ylidene.
For (preferred prefix; the suffix -ylidene describes loss the of two hydrogen atoms)
read (preferred prefix; the suffix -ylidene describes the loss of two hydrogen atoms)
Page 412, P-33.2.2 (7). [corrected 6 February 2019]
Add Examples: before structures.
Page 412, P-33.2.2 (7), second structure. [corrected 24 February 2021]
For propanehydroxamic acid
read propanohydroxamic acid
Page 412, P-33.2.2 (7), fourth structure. [corrected 24 February 2021]
For propanehydroximic acid
read propanohydroximic acid
Page 413, P-33.3, example 3.
For ethan-2-id-1-yl (preferred prefix)
read ethan-2-id-1-yl (PIN)
Page 413, P-34.0, contents.
For P-34.1 Functional parent compounds
read P-34.1 Retained functional parent compounds
delete P-34.3 Parent structures and corresponding prefixes
Page 414, P-34.0, lines 6/7 on this page.
Delete Names of substituent groups are discussed in P-34.3, Chapter 6, Chapter 10.
Page 414, P-34.1, line 8. [corrected 27 May 2020]
For ...they are discussed in P-34.1.2
read ...they are discussed in P-34.1.4
Page 414, P-34.1, line 14. [corrected 27 May 2020]
For P-34.1.4 Inorganic functional parent compouinds
read P-34.1.4 Inorganic functional parent compounds
Page 414, P-34.1.1.1, example 4. [corrected 27 May 2020]
For carbonic acid (PIN) (see P-65.2)
read carbonic acid (PIN) (see P-65.2.1)
Page 415, P-34.1.1.1, example 4 on this page.
For (substitution allowed; see P-65.1.6.1.1)
read (substitution allowed; see P-65.1.6.1)
Page 415, P-34.1.1.4, example. [corrected 27 May 2020]
For ...groups listed in P-15.1.8.2; see also P-63.2.3)
read ...groups listed in P-15.1.8.2.2; see also P-63.2.3)
Page 416, P-34.1.1.5, title. [corrected 19 September 2018]
For P-34.1.1.5 Nitrogeneous compounds
read P-34.1.1.5 Nitrogenous compounds
Page 416, P-34.1.1.5, example 1. [corrected 27 May 2020]
For ...(PIN); full substitution, see...
read ...(PIN); (full substitution, see...
Page 416, P-34.1.1.5, example 6. [corrected 24 October 2018]
Replace the structure with:
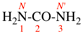
Page 416, P-34.1.2, line 1. [corrected 27 May 2020]
For Retained name (PIN)
read Retained name (PIN) or preselected name
Page 416, P-34.1.2, example 3. [corrected 9 January 2019]
For ...on the α -methoxy group...
read ...on the α-methoxy group... [remove space from name]
Page 417, P-34.1.2, example 7 on this page. [corrected 5 December 2018]
For oxamic acid (substitution allowed; see P-65.1.6.1.1)
read oxamic acid (substitution allowed; see P-65.1.6.1)
Page 418, P-34.2.1.1, example 2. [corrected 9 January 2019]
For benzoyl (preferred prefix) (full substitution P-65.1.7.2)
read benzoyl (preferred prefix) (full substitution, see P-65.1.7.2)
Page 418, P-34.2.1.2, title. [corrected 27 May 2020]
For P-34.2.1.3 Nitrogeneus substituent group names
read P-34.2.1.3 Nitrogenous substituent group names
Page 419, P-34.2.1.3, example 8 on this page. (corrected 30 October 2019)
For formazan-1,3-5-triyl (preferred prefix)
read formazan-1,3,5-triyl (preferred prefix)
Page 419, P-34.2.1.3, example 9 on this page. [modified 23 December 2020]
For (not guanidino)
read guanidino
Page 419, P-34.2.1.3, example 12. [corrected 5 December 2018]
For oxalylbis(azanediyl) (preferred prefix) (see P-66.1.1.4.5,2)
read oxalylbis(azanediyl) (preferred prefix) (see P-66.1.1.4.5.2)
Page 420, P-34.2.2, example 2. [corrected 7 November 2018]
For (phenylamino)
read phenylamino
Page 420, P-34.2.2, example 3. [corrected 7 November 2018]
For (phenylcarbonyl)
read phenylcarbonyl
Page 422, P-35.1, (2) lines 1/2. [corrected 6 February 2019]
For ...groups from oxo acids for example...
read ...groups from oxoacids for example... [remove space from name]
Page 423, P-35.2.2, example 1. [corrected 6 February 2019]
For (not mercapto-)
read (not mercapto)
Page 424, P-35.2.2, example 11 on this page.
For >NH
read –HN–
Page 424, P-35.2.2, first box.
For Systematic names based on the parent hydride azane are preferred IUPAC names in order to...
read The systematic name based on the parent hydride azane is the preferred IUPAC name for –HN– in order to...
Page 424, P-35.2.2, second box.
For Systematic names based on the parent hydride azane are preferred IUPAC names in order to...
read The systematic name based on the parent hydride azane is the preferred IUPAC name for –N= in order to...
Page 425, P-35.2.3, example 2. [corrected 5 December 2018]
For [preselected prefix; see P-67.1.4.1.1 (b)]
read (preselected prefix; see P-67.1.4.1.1.2)
Page 428, P-41, line 3.
For (classes 21 through 44).
read (classes 21 through 43)
Page 429, Table 4.1, 7e.
For ‘oxo acids’
read ‘oxoacids’ [remove space in name]
Page 429, P-41, Table 4.1, 16, line 3. [corrected 5 December 2018]
For See classes 8, 9, and 11, on lactones, lactams, anhydrides, imides.
read See classes 8, 9, 11, and 13, on lactones, lactams, anhydrides, and imides.
Page 430, P-41, Table 4.1.
For entries 42 to 44
renumber as 41 to 43
Page 431, P-41, example 1.
For 2-carboxyethyl (PIN)
read 2-carboxyethyl (preferred prefix)
Page 431, P-41, example 9. [corrected 21 November 2018]
For methoxy(methylsulfanyl)methane
read methoxy(methylsulfanyl)methane (PIN)
Page 431, P-41, example 10. [corrected 21 November 2018]
For (methyldiselanyl)(methylsulfanyl)methane
read (methyldiselanyl)(methylsulfanyl)methane (PIN)
Page 432, P-42.2, title. [corrected 14 November 2018]
For CLASS 7b
read CLASS 7b.
Page 434, P-42.4, (e) [corrected 3 June 2020]
For (e) maximum number of acidic groups (-OH) groups);
read (e) maximum number of acidic groups (-OH groups);
Page 434, P-42.4, example 2. [corrected 13 February 2019]
For (HO)2P-[P-(OH)-O]n-P(OH)2
read (HO)2P-[P-(OH)-O-]nP(OH)2
Page 438, P-43.1, Table 4.3, line 7 on this page. [modified 3 January 2020]
For carbo(dithoperox)imidic aci
read carbo(dithoperoxo)imidic acid
Page 442, P-43.1, Table 4.4, entry number 5, line 2 on this page.
For Sulfonimidic acids modified by replacement with S, Se, and Te
read Sulfonimidic acids modified by replacement with S, Se, or Te
Page 446, P-44, line 1. [corrected 13 February 2019]
For A parent structure is defined (P-15.1) as a...
read A parent structure is defined (P-15.1.1 and P-15.1.2) as a...
Page 449, P-44.1.2.1, example 2. (corrected 27 November 2019)
For triethylalumane (PIN)
read triethylalumane
Page 405, P-32.3, line 6. [corrected 18 May 2023]
For ...are the preferred IUPAC names.
read ...are the preferred prefixes.
Page 405, P-32.3, line 8. [corrected 18 May 2023]
For ...preferred IUPAC name. It is...
read ... preferred prefix. It is...
Page 405, P-32.3, line 9. [corrected 18 May 2023]
For ...The preferred IUPAC name is prop-1-en-2-yl.
read ... The preferred prefix is prop-1-en-2-yl.
Page 405, P-32.3, line 11. [corrected 18 May 2023]
For ...The preferred IUPAC name is ..
read ... The preferred prefix is...
Page 451, P-44.1.2.1, example 4. [corrected 13 February 2019]
For [O > S; see P-44.3); senior parent cannot be chosen by P-44.1.2)
read [O > S (see P-44.3; senior parent cannot be chosen by P-44.1.2)]
Page 452, P-44.1.2.2, example 5.
For 2-hydrazinylpyridine (PI
read 2-hydrazinylpyridine (PIN)
Page 453, P-44.1.5, line 2.
For ...with different bonding orders, isotopically...
read ...with different bonding numbers, isotopically...
Page 453, P-44.2.1.1, line 3.
For haracteristic group...
read characteristic
Page 461, P-44.2.2.2 (2), left structure
Replace the structure with:
Page 462, P-44.2.2.2.1.2, example 2. [corrected 13 February 2019]
For ...spiro fusions ‘4,,6’ is lower that ‘4,7’]
read ...spiro fusions ‘4,6’ is lower that ‘4,7’]
Page 464, P-44.2.2.2.2.1, Examples, line 1. [corrected 13 February 2019]
For ...according to the criteria in P-44.2.2.2.2):
read ...according to the criteria (a) in P-44.2.2.2.2):
Page 468, P-44.2.2.2.2.7, example II (note).
For [the heteroatom locant set ‘2,3’ is lower than ‘2’5’]
read [the heteroatom locant set ‘2,3’ is lower than ‘2,5’]
Page 468, P-44.2.2.2.2.8, line 3. [corrected 3 June 2020]
For ...order: F > Cl > B > I > O > S > Se ...
read ...order: F > Cl > Br > I > O > S > Se ...
Page 469, P-44.2.2.2.3, line 1. [corrected 13 February 2019]
For Seniority criteria for fused ring systems are applied succesively ...
read Seniority criteria for fused ring systems given below are applied succesively ...
Page 471, P-44.2.2.2.4 (c).
For ... in the fused ring system;
read ... in the fused ring system before bridging;
Page 473, P-44.2.2.2.4.4, line 2. [corrected 14 November 2018]
For ... before bridging according to P-44-2.2.3. [criterion (d) ...
read ... before bridging according to P-44.2.2.3 [criterion (d) ...
Page 473, P-44.2.2.2.4.5, line 1.
For The senior bridged ring system...
read The senior bridged fused ring system...
Page 473, P-44.2.2.2.4.5, example.. [corrected 3 January 2020]
For ...bridge attachments ‘1,3’ is lower than ‘1’4'’]
read ...bridge attachments ‘1,3’ is lower than ‘1,4’]
Page 479, P-44.2.2.2.6, line 3.
For ... for linear acyclic phanes ...
read ... for linear (acyclic) phanes ...
Page 479, P-44.2.2.2.6 (b), line 2. [corrected 5 December 2018]
For ... P-44.2.1.2 through P-44.2.8;
read ... P-44.2.1.2 through P-44.2.1.8;
Page 480, P-44.2.2.2.6.1, line 2.
For ...by P-44.2.1. through P-44.2.1.8 [criterion (a)...
read ...by P-44.2.1.2 through P-44.2.1.8 [criterion (a)...
Page 482, P-44.2.2.2.6.2, example (1), first structure.
Replace the structure with:
Page 484, P-44.2.2.2.6.4, second structure.. [corrected 3 January 2020]
For (the locant set ‘1,7’ for the pyridine amplificant is lower than the set ‘1,8’)
read (the locant set ‘1,7’ for the pyridina amplificant is lower than the set ‘1,8’)
Page 485, P-44.2.2.2.6.6, example explanation. [modified 3 June 2020]
For ...amplificants in order of occurence in the name ‘1,7,9,3,5’ is lower than the locant set ‘1,9,7,3,5’]
read ...amplificants in order of occurrence in the name ‘1,7,9,3,5,11’ is lower than the locant set ‘1,9,7,3,5,11’]
Page 487, P-44.2.2.2.7, example.
For criteria for phane nomenclature (see P-51.4) are met for the PIN]
read [criteria for phane nomenclature (see P-51.4) are met for the PIN]
Page 487, P-44.2.2.2.7, example explanation. [corrected 3 June 2020]
For ...phane nomenclature (see P-51.4) are met...
read ...phane nomenclature (see P-52.2.5.1) are met...
Page 488, P-44.2.2.2.7, criterion (g).
For ...greated number...
read ...greater number...
Page 488, P-44.2.2.2.7, last line.
For ...found in P-4.44.
read ...found in P-44.4.
Page 487, P-44.2.2.2.7, line 2.
For ... criteria for rings and ring systems given in P-44.2.1.2. Phane...
read ... criteria for rings and ring systems given in P-44.2.1. Phane...
Page 487, P-44.2.2.2.7, second paragraph, line 3.
For (a) rings containing any heterocycle;
read (a) rings containing any heteroatom;
Page 489, P-44.2.2.2.7.6, line 2.
For ...[criterion (f) in P-44.2.2.2.7.5].
read ... [criterion (f) in P-44.2.2.2.7].
Page 491, P-44.3.2, box line 4.. [corrected 3 January 2020]
For unsaturation is now the second
read unsaturation is now the second criterion.
Page 492, P-44.3.2 (7), line 6. [corrected 13 February 2019]
For[five heteroatoms in each chain; and sixteen skeletal atoms greater than five]
read [five heteroatoms in each chain; and fifteen skeletal atoms greater than five]
Page 494, P-44.4.1.1, example (3).
For [(one double bond greater than zero]
read [one double bond greater than zero]
Page 495, P-44.4.1.2, example (2). [modified 3 June 2020]
Add [two double bonds are senior to one double bond and one triple bond]
Page 496, P-44.4.1.2, example (3). [corrected 3 June 2020]
For [four double bonds greater than three]
read [four double bonds are greater than three]
Page 498, P-44.4.1.3.2 (1). [corrected 13 February 2019]
For [the locant ‘1’ for the nonstandard bonding number is lower than ‘2’]
read [the locant ‘1’ for the atom with the nonstandard bonding number is lower than ‘2’]
Page 498, P-44.4.1.3.2 (2). [corrected 13 February 2019]
For [the locant ‘1’ for the nonstandard bonding number is lower than ‘2’]
read [the locant ‘1’ for the atom with the nonstandard bonding number is lower than ‘2’]
Page 498, P-44.4.1.3.2, example (3). [modified 13 February 2019]
For 1λ6,2λ4,3-trithiane(PIN)
read 1λ6,2λ4,3-trithiane (PIN) [add space after name]
for [the locant sets ‘1,2’ for the nonstandard bonding number are the same, ...]
read [the locant sets ‘1,2’ for the atoms with the nonstandard bonding number are the same, ...]
Page 501, P-44.4.1.6, example (1).. [corrected 3 January 2020]
For [the heteroatom locant set ‘1,2,3,4,5,7’ is lower than ‘1,2,3,4,6,7’]
read [the heteroatom locant set ‘1,2,3,4,5,7,6,8’ is lower than ‘1,2,3,4,6,7,5,8’]
Page 505, P-44.4.1.9, example.
For pyridin-2-yl (PIN)
read pyridin-2-yl (preferred prefix)
for pyridin-3-yl (PIN)
read pyridin-3-yl (preferred prefix)
Page 510, P-44.4.1.11.4, example 1.
For [4-2H is senior to5-2H]
read [4-2H is senior to 5-2H] [add space after to]
Page 513, P-44.4.1.12.2, line 2. [corrected 21 October 2020]
For ...of the chiral centers, the principal chain...
read ...of the chirality centers, the principal chain...
Page 515, P-45.0, line 9. [modified 3 June 2020]
For P-45.3 Criteria related only to nonstandard bonding order
read P-45.3 Criteria related only to substituents with nonstandard bonding numbers, other criteria being equal
Page 515, P-45.1.1, line 6. [corrected 29 January 2020]
For ...for its use are met (see P-51.2.3).
read ...for its use are met (see P-51.3.1).
Pag 515, P-45, line10. [corrected 3 June 2020]
For P-45.4 Criteria related only to isotopic modification
read P-45.4 Criteria related only to isotopic modification of substituents
Page 516, P-45.1.2, line 4. [corrected 13 January 2021]
For Example:
read Examples:
Page 518, P-45.2.1, example (2), lines 3/4. [corrected 13 February 2019]
For ... two (one simple and one compound) substituents vs. one complex substituent]
read ... two (one simple and one complex) substituents vs. one complex substituent]
Page 518, P-45.2.1, example (4).
For [not 3-{5-[(3-dimethyamino)-2-methyl-3-oxopropyl]-2-methylphenyl}-N,2-dimethylpropanamide; the PIN name has...
read [not 3-{5-[(3-dimethyamino)-2-methyl-3-oxopropyl]-2-methylphenyl}-N,2-dimethylpropanamide; the PIN parent structure has...
Page 519, P-45.2.1 , example (5). [corrected 13 February 2019]
For ... two simple substituents vs. one simple]
read ... two simple substituents vs. one compound]
Page 519, P-45.2.1, example (6). [modified 13 February 2019]
For 1,1-dimethyl-3-[(λ4-thian-3-ylsulfanyl)methyl]- λ4-thiane (PIN)
read 1,1-dimethyl-3-[(λ4-thian-3-ylsulfanyl)methyl]-λ4-thiane (PIN) [delete space from name]
for ... substituents, two simple substituents vs. one complex substituent]
read ... substituents, three (two simple and one complex) substituents vs. one complex substituent]
Page 519, P-45.2.1 , example (8). [corrected 7 November 2018]
For ... four simple substituents vs. three (two simple and one compound substituent]
read ... four simple substituents vs. three (two simple and one compound) substituents]
Page 521, P-45.2.1 , example (13). [corrected 13 February 2019]
For ... two simple substituents vs. one simple]
read ... two simple substituents vs. one simple or one compound substituent]
Page 521, P-45.2.1, example (15).
For 5-(81Br)bromo -3-[1-(81Br)bromopropyl]-4-methylhexanoic acid (PIN)
read 5-(81Br)bromo-3-[1-(81Br)bromopropyl]-4-methylhexanoic acid (PIN). [Deleted space from name]
Page 529, P-45.4, lines 1/2.
For The following criteria are relative only to substituents with nonstandard bonding numbers applied...
read The following criteria are relative only to substituents with isotopic modification applied...
Page 531, P-45.4.2 (formerly P-45.4.5), new example. [modified 3 June 2020]
For 2-[(13C)methyloxy]-N-{2-[methyl(18O)oxy]ethyl}ethan-1-amine
read 2-[(13C)methyloxy]-N-{2-[methyl(18O)oxy]ethyl}ethan-1-amine (PIN)
Page 531, P-45.4.3 (formerly P-45.4.6), new example. [modified 3 June 2020]
For 4-([2-13C]ethyl)-2-[2-([2-14C]ethyl)pentyl]heptan-1-ol
read 4-([2-13C]ethyl)-2-[2-([2-14C]ethyl)pentyl]heptan-1-ol (PIN)
Page 532, P-45.5 (was P-45.5.1), example (1). [corrected 3 March 2021]
For ‘bromo’ in the PIN is earlier alphabetically than ‘dibromo’.
read in both names the locant set is ‘1,2,4’, and the locants appear in the name in the same order set ‘1,4,2’ so
no decision can be made by P-45.2.2 or P-45.2.3; but ‘bromo’ in the PIN is earlier alphabetically than ‘dibromo’.]
Page 538, P-45.6.3.
For examples:
read Example:
Page 539, P-45.6.4, example 2.
For (1S,6S)-3-{[(4R,5S)-5-hydroxy-4-methylcyclohex-1-en-1-yl]amino}-6- methylcyclohex-3-en-1-ol (PIN)
read (1S,6S)-3-{[(4R,5S)-5-hydroxy-4-methylcyclohex-1-en-1-yl]amino}-6-methylcyclohex-3-en-1-ol (PIN) [remove space from name]
Page 541, P-46.1, line 3. [corrected 5 December 2018]
For ...illustrated in P-46.1.1 through P-46.1.11.
read ...illustrated in P-46.1.1 through P-46.1.13.
Page 543, P-46.1.4, example 2 left. [corrected 3 January 2020]
For (preferred prefix; a compound) substituent group)
read (preferred prefix; a compound substituent group)
Page 545, P-46.1.8, example 2. [corrected 3 June 2020]
For ...prefix, see P-70.3.1)
read ...prefix, see P-70.3.1, P-71.5)
Page 546, P-46.1.9, line 3. [corrected 13 February 2019]
For ... applicable to both methods (1) and 2b) in P-46.0; ...
read ... applicable to both methods (1) and (2) in P-46.0; ...
Page 546, P-46.1.10, line 3. [corrected 13 February 2019]
For ... the principal substituent chain has the higher bonding number ...
read ... the principal substituent chain has (an) atom(s) of the higher bonding number ...
Page 548, P-46.1.12, 2nd paragraph, line 2. [corrected 13 February 2019]
For ... substituent groups with the highest bonding number.
read ... substituent groups with (an) atom(s) of the highest bonding number.
Page 548, P-46.1.12, example 1 left, [corrected 3 January 2020]
For (preferred prefix; a a compound substituent group)
read (preferred prefix; a compound substituent group)
Page 548, P-46.1.12, example 1 right. [corrected 9 October 2024]
For [not 3-hydroxy-1-(1- hydroxyethyl)propyl
read [not 3-hydroxy-1-(1-hydroxyethyl)propyl
Page 549, P-46.1.13, example 1, left version. [corrected 7 November 2018]
For (preferred prefix; (a compound substituent group)
read (preferred prefix; a compound substituent group)
Page 549, P-46.1.13, example 2, left version. [corrected 7 November 2018]
For (preferred prefix; (a compound substituent group)
read (preferred prefix; a compound substituent group)
Page 549, P-46.1.13, example 2, right version.
For (a complex substituent group)
read (a compound substituent group)
Page 550, P-46.2.1, example 1 on this page. [corrected 13 February 2019]
For (2) 1-(1-18O)hydroxy-3-hydroxypropan-2-yl (preferred prefix)
read (2) 1-(18O)hydroxy-3-hydroxypropan-2-yl (preferred prefix)
Page 550, P-46.3.1, example.
Replace structures by:
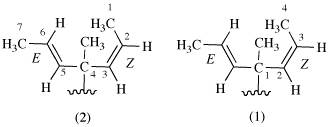
Page 550, P-46.3.1, Note, lines 3/4. [corrected 21 October 2020]
For ...creates a chiral center at C-4 (method 2) or C-1 (method 1)...
read ...creates a chirality center at C-4 (method 2) or C-1 (method 1)...
Page 550, P-46.3.1, line 3. [corrected 24 March 2021]
For Example:
read Examples:
Page 551, P-46.3.2, title. [corrected 21 October 2020]
For ...The principal substituent chain contains the greater number of (R)-chiral centers....
read ...The principal substituent chain contains the greater number of (R)-chirality centers....
Page 551, P-46.3.2, Note, lines 3/4. [corrected 21 October 2020]
For ...creates a chiral center at C-5 (method 2) or C-1 (method 1) and...
read ...creates a chirality center at C-5 (method 2) or C-1 (method 1) and...
Page 554, P-51.1.3, example. [corrected 29 January 2020]
For ...(PIN; a skeletal (a) replacement name)
read ...(PIN; a skeletal (‘a’) replacement name)
Page 554, P-51.1.4, example.
For [1-[(ethylsulfanyl)methyl]-1′-methyl-1,1′-[silanediylbis(methylene)]bis(silane)
read 1-[(ethylsulfanyl)methyl]-1′-methyl-1,1′-[silanediylbis(methylene)]bis(silane)
Page 555, P-51.2.1, last example on this page. [corrected 20 February 2019]
For acetic propanoic anhydride (PIN; P-65.7.1)
read acetic propanoic anhydride (PIN; P-65.7.2)
Page 556, P-51.2.1, example 1 on this page. [corrected 20 February 2019]
For Acid halides, pseudohalides [derived from class 7(d) acids]
read Acid halides, pseudohalides [derived from class 7(c) acids]
Page 556, P-51.2.1, example 3 on this page. [corrected 20 February 2019]
For Acid hydrazides [derived from class 7(d) acids]
read Acid hydrazides [derived from class 7(c) acids]
Page 559, P-51.3.2, line 3. [corrected 20 February 2019]
For ... are formed using phane nomenclature when four rings are present, ...
read ... are formed using phane nomenclature when four or more rings are present, ...
Page 561, P-51.3.2.1, example 1 on this page, last line of text. [corrected 7 April 2021]
For ...alpabetically than ‘diphenyltriphenylmethyl’)]
read ...alphabetically than ‘diphenyltriphenylmethyl’)]
Page 562, P-51.3.2.2, example 1. [corrected 20 February 2019]
For 2,4,6-trioxa...heptaphane (PIN, a phane name, see P-51.4)
read 2,4,6-trioxa...heptaphane (PIN, a phane name, see P-51.4, P-52.2.5)
Page 562, P-51.3.2.2, example 2. [corrected 20 February 2019]
For ... (PIN; a phane name, see P-51.4)
read ... (PIN; a phane name, see P-51.4, P-52.2.5)
Page 563, P-51.3.3, example 1. [corrected 20 February 2019]
For ...is lower than ‘4’ (see P-44.2.2)]
read ...is lower than ‘4’ (see P-14.3.5, P-45.2.2)]
Page 563, P-51.3.3, last line. [corrected 5 December 2018]
For More examples are found in P-15.3, and in P-44, P-45, P-46, and P-47.
read More examples are found in P-15.3, and in P-44, P-45, and P-46.
Page 564, P-51.4.1.1, second paragraph, last two lines. [corrected 20 February 2019]
For ...three units (see seventh example below).
read ...three units (see example 11 below).
Page 564, P-51.4.1.2, example 1. [corrected 3 June 2020]
For 3-phospha-2,5,7-trisilaoctane [PIN, skeletal replacement (‘a’) name)
read 3-phospha-2,5,7-trisilaoctane [PIN, skeletal replacement (‘a’) name]
Page 564, P-51.4.1.2, example 2. [corrected 29 January 2020]
For a multiplicative name]
read (a multiplicative name)
for a substitutive name]
read (a substitutive name)
Page 566, P-51.4.1.2, lines 3/4 of explanation. [corrected 3 June 2020]
For ...in one of the ester organyl parts of the ester ...
read ...in one of the organyl parts of the ester ...
Page 568, P-51.4.2.1, 1st box, line 3/4. [corrected 20 February 2019]
For ... from previous recommendations even though such organometallic compounds involving those elements are only preselected at this time.
read ... from previous recommendations even though the names of such organometallic compounds involving those elements are not PINs at this time.
Page 568, P-51.4.2.1 second box line 4
For ...for the Hantzsch-Widman.
read ...for the Hantzsch-Widman system.
Page 576, P-52.1.7, example 2. [corrected 3 June 2020]
For 1,3,4a,6,8-pentaaza-2,4,5,7,8a-pentaboranaphthalene
read 1,3,4a,6,8-pentaaza-2,4,5,7,8a-pentaboranaphthalene (numbering shown)
Page 576, P-52.2.1.2, line 5. [corrected 5 December 2018]
For ...names (see P-32.1.3.1).
read ...names (see P-31.1.3.1).
Page 578, P-52.2.4.1, title.
For Five membered ring requirement.
read Five-membered ring requirement
Page 578, P-52.2.4.1, box, line 1. [corrected 20 February 2019]
For ...in the 1999 publication on...
read ...in the 1998 publication on...
Page 579, P-52.2.4.3, example. [corrected 29 January 2020]
Replace the structures with:
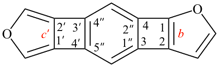
Page 580, P-52.2.4.3, example on this page. [modified 29 January 2020]
For benzo[1′′,2′′:3,4;4′′,5′′:3′,4′]dicyclobuta[1,2-c:1′,2′-c′]difuran(PIN)
read benzo[1′′,2′′:3,4;4′′,5′′:3′,4′]dicyclobuta[1,2-c:1′,2′-c′]difuran (PIN) [add space]
Replace the structures with:
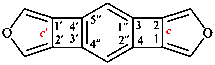
Page 580, P-52.2.4.4.1.1, example 2. [corrected 20 February 2019]
For 10-azacyclobuta[1,7]indeno[5,6-b]anthracene (PIN
read 10-azacyclobuta[1,7]indeno[5,6-b]anthracene (PIN)
Page 581, P-52.2.4.4.1.2, Explanation, line 6. [corrected 7 November 2018]
For ... which is not allowed, see P-25.3.5).
read ... which is not allowed, see P-25.3.5.
Page 582, P-52.2.4.4.2.1, example on this page. [corrected 29 January 2020]
For 5H,12H-2,3,4a,7a,9,10,11a,14a-octaazadicyclopenta[ij:i′j′ ]benzo[1,2-f :4,5-f′ ]diazulene (PIN)
read 5H,12H-2,3,4a,7a,9,10,11a,14a-octaazadicyclopenta[ij:i′j′]benzo[1,2-f:4,5-f′]diazulene (PIN) [delete spaces in name]
Page 584, P-52.2.5.2.1, 2nd paragraph, lines 2/3. [corrected 20 February 2019]
For ... > bridged fused system > non fused bridged systems. ...
read ... > bridged fused system > non-fused bridged systems. ...
Page 589, P-52.2.6.2, Example 1. [corrected 29 January 2020]
For Cyclopenta[cd]di-as-indaceno[3,4,5,6-fghij:3′4′5′6′-lmnoa]fluoranthene (I) (PIN)
read cyclopenta[cd]di-as-indaceno[3,4,5,6-fghij:3′,4′,5′,6′-lmnoa]fluoranthene (I) (PIN)
Page 590, P-52.2.6.2, Example 2, explanation. [corrected 3 June 2020]
For ...fullerene fragment is a norfullerene name because...
read ...fullerene fragment is a systematic bridged fused ring name because...
Page 591, P-52.2.6.2, Example 4, explanation. [corrected 29 January 2020]
For ...it has 15 rings].
read ...it has 15 rings.
Page 592, P-52.2.6.3, Example 2, explanation. [corrected 29 January 2020]
For ...and 21 rings).
read ...and 21 rings.
Page 593, P-52.2.6.4, Example 1, explanation. [corrected 29 January 2020]
For ...and 22 rings).
read ...and 22 rings.
Page 596, P-52.2.8, Example 1. [corrected 29 January 2020]
For chain has greater number of skeletal atoms)
read (chain has greater number of skeletal atoms)
Page 598, P-54.4, box line 1. [corrected 29 January 2020]
For ...‘hydro’ and dehydro’ are...
read ...‘hydro’ and ‘dehydro’ are...
Page 600, P-54.4.3, line 1. [corrected 20 February 2019]
For Fused ring systems and monocyclic mancude ring assemblies...
read Fused ring systems and mancude ring assemblies...
Page 602, P-54.4.3.2, line 6. [corrected 3 June 2020]
For ...1H-2-benzopyran (an their chalcogen analogues)...
read ...1H-2-benzopyran (and their chalcogen analogues)...
Page 602, P-54.4.4, box line 1.
For ...the prefix dehydro’ is detachable...
read ...the prefix ‘dehydro’ is detachable...
Page 602, P-54.4.4, box, line 3. [corrected 5 December 2018]
For ... see also P-15.1.3.2, P-32.1, P-58.2), ...
read ... see also P-15.1.5.2, P-32.1, P-58.2), ...
Page 602, P-54.4.4, box line 4.
For ...was aphabetized...
read ...was alphabetized...
Page 603, P-55, second paragraph, line 4. [corrected 5 December 2018]
For This issue is discussed in P-15.1.3.
read This issue is discussed in P-15.1.8.
Page 603, P-56.1, line 1.
For ...the suffix ‘peroxol to provide...
read ...the suffix ‘peroxol’ to provide...
Page 604, P-56.2, line 6. [corrected 29 January 2020]
For Example:
read Examples:
Page 605, P-56.4, example 1. [corrected 23 December 2020]
For methanediyl
read (not methanediyl)
Page 605, P-56.4, example 9. [corrected 23 December 2020]
For stibinediyl
read (not stibinediyl)
Page 605, P-56.4, example 10. [corrected 23 December 2020]
For stibinylidene
read (not stibinylidene)
Page 606, P-57, title. [corrected 3 June 2020]
For P-57 SELECTING PREFERED AND PRESELECTED PREFIXES FOR SUBSTITUENT GROUPS
read P-57 SELECTING PREFERRED AND PRESELECTED PREFIXES FOR SUBSTITUENT GROUPS
Page 606, P-57.1, title. [corrected 28 November 2018]
For P-57.1 SUBSTITUENT PREFIXES DERIVED FROM PARENT HYDRIDES
read P-57.1 PREFIXES DERIVED FROM PARENT HYDRIDES
Page 606, P-57.1.1.1, line 2. [corrected 19 September 2018]
For ...from mononuclear hydrides carbon, silanium, germanium, tin and lead...
read ...from mononuclear hydrides carbon, silicon, germanium, tin and lead...
Page 607, P-57.1.3, line 2. [corrected 5 December 2018]
For ...only for general nomenclature (P-19.6.2.3)
read ...only for general nomenclature (P-29.6.2.3).
Page 607, P-57.1.3, line 5. [corrected 14 November 2018]
For ... is allowed (see P-29.6.2.2)
read ... is allowed (see P-29.6.2.2).
Page 607, P-57.1.5.1, line1/3. [corrected 20 February 2019]
For Preferred prefixes derived ... derived from cyclic compounds other that cycloalokanes ... described above in P-56.1.1.1.
read Preferred prefixes derived ... derived from cyclic compounds other than cycloalokanes ... described above in P-57.1.1.1.
Page 608, P-57.1.5.2, structure 2.
For 1,4-phenylene (also 1,2- and 1,3- isomers)
read 1,4-phenylene (also 1,2- and 1,3-isomers) [delete space before isomers]
Page 608, P-57.1.5.3, structure 2.
For 2-anthryl (also 1- and 9- isomers)
read 2-anthryl (also 1- and 9-isomers) [delete space before isomers]
Page 608, P-57.1.5.3, structure 3. [modified 7 November 2018]
For 3-furyl (also 2- isomer)
read 3-furyl (also 2-isomer) [delete space before isomer]
for (also 2-isomer; (preferred prefixes)
read (also 2-isomer; preferred prefixes)
Page 609, P-57.1.5.3, structure 1 on this page.
For 2-naphthyl (also 1- isomer)
read 2-naphthyl (also 1-isomer) [delete space before isomer]
Page 609, P-57.1.5.3, structure 2 on this page.
For 9-phenanthryl (also 1-, 2-, 3-, and 4- isomers)
read 9-phenanthryl (also 1-, 2-, 3-, and 4-isomers) [delete space before isomers]
for phenanthren-9-yl (also 1-, 2-, 3-, and 4- isomers, preferred prefixes)
read phenanthren-9-yl (also 1-, 2-, 3-, and 4-isomers, preferred prefixes)
Page 609, P-57.1.5.3, structure 3 on this page.
For 2-piperidyl (also 3-, 4-, isomers)
read 2-piperidyl (also 3- and 4-isomers) [delete space before isomers]
for piperidin-2-yl (also 3-, 4-isomers; preferred prefixes)
read piperidin-2-yl (also 3- and 4-isomers; preferred prefixes)
Page 609, P-57.1.5.3, structure 4 on this page.
For 2-pyridyl (also 3- and 4- isomers)
read 2-pyridyl (also 3- and 4-isomers) [delete space before isomers]
for pyridin-2-yl (also 3-, 4-, isomers; preferred prefixes)
read pyridin-2-yl (also 3- and 4-isomers; preferred prefixes) [delete space before isomers]
Page 609, P-57.1.5.3, structure 5 on this page.
For 2-quinolyl (also 3-, 4-, 5-, 6-, 7-, and 8- isomers)
read 2-quinolyl (also 3-, 4-, 5-, 6-, 7-, and 8-isomers) [delete space before isomers]
for quinolin-2-yl (also 3-, 4-, 5-, 6-, 7-, and 8- isomers; preferred prefixes)
read quinolin-2-yl (also 3-, 4-, 5-, 6-, 7-, and 8-isomers; preferred prefixes) [delete space before isomers]
Page 609, P-57.1.5.3, structure 7 on this page.
For 2-methylphenyl (also 3- and 4- isomers; preferred prefixes)
read 2-methylphenyl (also 3- and 4-isomers; preferred prefixes) [delete space before isomers]
Page 611, P-57.1.6.2 (1), example. [modified 3 June 2020]
For hept-2-en-4-yl (alkanyl type; see P-29.1 method (2)
read hept-2-en-4-yl [alkanyl type; see P-29.2 method (2)]
for 1-propylbut-2-en-1-yl (alkyl type; see P-29.1 method (1)
read 1-propylbut-2-en-1-yl [alkyl type; see P-29.2 method (1)]
Page 612, P-57.2, line 4. [corrected 5 December 2018]
For ...prefixes derived from parent hydrides (see P-56.1.1).
read ...prefixes derived from parent hydrides (see P-57.1.1).
Page 612, P-57.3, line 4. [corrected 5 December 2018]
For ...in P-34.1.1.5. Retained prefixes...
read ...in P-34.2. Retained prefixes...
Page 612, P-57.3, example 2. [corrected 5 December 2018]
For ...; see P-62.2.1.1.3)
read ...; see P-63.2.2.2)
Page 613, P-57.4, last explanation on this page, line 1. [corrected 26 January 2022]
For ...involves a choice is between a ‘methyl’ group...
read ...involves a choice between a ‘methyl’ group...
Page 614, P-57.4, example 3 on this page, Explanation, line 4. [corrected 5 December 2018]
For ... two-part prefix ‘cyclohexylcarbonyl’ (see P-65.4.1), resulting...
read ... two-part prefix ‘cyclohexylcarbonyl’ (see P-65.1.7.4.2), resulting...
Page 615, P-58.1, example 1. [corrected 5 December 2018]
For ...preferred IUPAC name has more prefixes (see P-45.1.1]
read ...preferred IUPAC name has more substituents (see P-45.2.1)]
Page 615, P-58.1, example 2. [modified 3 June 2020]
For [not 2-[(4-chloro-1,3-oxazol-5-yl)methyl]-1,3-oxazole;
the preferred IUPAC name has more prefixes (see P-45.1.1]
read [not 2-[(4-chloro-1,3-oxazol-5-yl)methyl]-1,3-oxazole;
the preferred IUPAC name has more substituents (see P-45.2.1)]
Page 615, P-58.2.1.2, lines 1/2. [corrected 12 August 2020]
For ...cited at the lowest nonangular positions (see P-25.0)...
read ...cited, if possible, at the lowest nonfusion peripheral atom (see P-25.0)...
Page 615, P-58.2.1.1, line 2. [corrected 5 December 2018]
For ...bridged fused ring systems (see P-25.7.1.3.2), spiro...
read ...bridged fused ring systems (see P-25.7.1.3.3), spiro...
Page 616, P-58.2.1.2, examples 1. [corrected 21 November 2018]
For 1H-pyrrole
read 1H-pyrrole (PIN)
Page 616, P-58.2.1.2, examples 2. [corrected 21 November 2018]
For 2H-1-benzopyran
read 2H-1-benzopyran (PIN)
Page 616, P-58.2.1.2, examples 3. [corrected 21 November 2018]
For 2H,5H-pyrano[2,3-b]pyran
read 2H,5H-pyrano[2,3-b]pyran (PIN)
Page 616, P-58.2.1.2, examples 7. [corrected 21 November 2018]
For 2,3-dihydro-1H-indene
read 2,3-dihydro-1H-indene (PIN)
Page 617, P-58.2.1.2, example 2 on this page. [corrected 21 November 2018]
For hexahydro-2H,5H-pyrano[2,3-b]pyrano(PIN)
read hexahydro-2H,5H-pyrano[2,3-b]pyrano (PIN) [insert space after name]
Page 617, P-58.2.1.2, example 3 on this page. [corrected 21 November 2018]
For 3a,5-dihydro-4H-indene
read 3a,5-dihydro-4H-indene (PIN)
Page 618, P-58.2.2.2, line 2. [corrected 12 August 2020]
For ...to ring atoms, angular or nonangular, with the lowest locants...
read ...to peripheral ring atoms with the lowest locants...
Page 618, P-58.2.2.2, example 7. [corrected 21 November 2018]
For 3,4-dihydroquinolin-2(1H)-ylidene
read 3,4-dihydroquinolin-2(1H)-ylidene (preferred prefix)
Page 618, P-58.2.2.2, example 8. [corrected 21 November 2018]
For 5,6,7,8-tetrahydronaphthalen-2(4aH)-one
read 5,6,7,8-tetrahydronaphthalen-2(4aH)-one (PIN)
Page 619, P-58.2.2.2, example 1 on this page. [corrected 21 November 2018]
For 1,3,4,5-tetrahydronaphthalen-4a(2H)-carboxylic acid
read 1,3,4,5-tetrahydronaphthalen-4a(2H)-carboxylic acid (PIN)
Page 620, P-58.2.3.1, line 4. [corrected 21 November 2018]
For ...principal characteristic groups groups or free valences.
read ...principal characteristic groups or free valences.
Page 620, P-58.2.3.1.1, line 3. [corrected 12 August 2020]
For ...hydrogen atoms are placed at angular or nonangular positions that will accommodate...
read ...hydrogen atoms are placed at peripheral atoms that will accommodate...
Page 620, P-58.2.3.1.1, example 4. [corrected 21 November 2018]
For 1,4-dihydro-3aH-indene-3a-carboxylic acid
read 1,4-dihydro-3aH-indene-3a-carboxylic acid (PIN)
Page 621, P-58.2.3.1.1, example 2 on this page. [corrected 21 November 2018]
For 2,3,7,8-tetra-4H,6H-benzo[1,2-b:5,4-b‘]dipyran-4,6-dione
read 2,3,7,8-tetrahydro-4H,6H-benzo[1,2-b:5,4-b′]dipyran-4,6-dione (PIN)
Page 621, P-58.2.3.1.2, lines 3/4. [corrected 12 August 2020]
For ...assigned to the lowest nonangular positions consistent...
read ...assigned to the lowest nonfusion peripheral atoms consistent...
Page 622, P-58.2.3.1.3 (1), lines 1/2. [corrected 12 August 2020]
For ...assigned to a nonangular position having the lowest locants...
read ...assigned to a nonfusion peripheral atom having the lowest locants...
Page 623, P-58.2.3.1.3, example 2, explanation line 2. [corrected 3 June 2020]
For ...principal characteristic goups to be accommodated...
read ...principal characteristic groups to be accommodated...
Page 623, P-58.2.3.1.3, structure 3. [corrected 9 January 2019]
For
9,10,12,13,14,21,22,23,24,25,26,27,32,33,34,34a-hexadecahydro- 3H-23,27-epoxypyrido[2,1-c][1,4]oxaazacyclohentriacontine-1,5,11,28,29(4H,6H,31H)-pentone (PIN)
read 9,10,12,13,14,21,22,23,24,25,26,27,32,33,34,34a-hexadecahydro-3H-23,27-epoxypyrido[2,1-c][1,4]oxaazacyclohentriacontine-1,5,11,28,29(4H,6H,31H)-pentone (PIN) [remove space from name]
Page 625, P-58.2.4, example 2.
For 4-iminonaphthalen-1(4H)-one (PIN
read 4-iminonaphthalen-1(4H)-one (PIN)
Page 626, P-58.2..5, example 4. [modified 3 June 2020]
For (detachable but nonalphabetizeable hydro prefixes do not having precedence
read (detachable but nonalphabetized hydro prefixes do not have precedence...
Page 627, P-58.3.1, lines 4-5. [corrected 20 February 2019]
For ...For boron chains, see P-68. For chains involving chalcogen atoms, see P-68.
read ...For boron chains, see P-68.1.1.2. For chains involving chalcogen atoms, see P-68.4.
Page 627, P-58.3.2, line 1 and line 4. [corrected 20 February 2019]
For...of an acyclic homogeneous heterocyclic chain...
read ...of a homogeneous heteroatomic chain...
Page 627, P-58.3.2, example 6. [corrected 5 December 2018]
For (not hydrazinone; (see P-61.5.2)
read (not hydrazinone; see P-61.6)
Page 628, P-58.3.2, example on this page. [corrected 3 June 2020]
For ...chalcogen atom (see P-65.6.3.4.2 and P-68.4.2.4]
read ...chalcogen atom (see P-65.6.3.4.2 and P-68.4.2.4)]
Page 628, P-59.1.1 (1). [corrected 3 June 2020]
For (1) 'functional class nomenclature', for compounds such as esters, and acid halides (see P-15.2 and P-51.2 for preferred IUPAC names and for general nomenclature;
read (1) 'functional class nomenclature', for compounds such as esters and acid halides (see P-15.2 and P-51.2 for preferred IUPAC names and for general nomenclature);
Page 629, P-59.1.3, line 9.
For ...from standard bonding order and isotopic...
read ...from standard bonding number and isotopic...
Page 629, P-59.1.5, line 1. [corrected 20 February 2019]
For Determine affixes and/or prefixes, in...
read Determine suffixes and/or prefixes, in...
Page 629, P-59.1.6, line 4. [corrected 5 December 2018]
For ...preferred IUPAC name or in general nomenclature, and P-15.8 for their...
read ...preferred IUPAC name or in general nomenclature, and P-15.1.8 for their...
Page 629, P-59.1.9, line 2. [corrected 5 December 2018]
For ...suffixes and prefixes (see P-33 and P-36),...
read ...suffixes and prefixes (see P-33 and P-35),...
Page 630, Table 5.1. [corrected 20 February 2019]
For –BrO
read –BrO1
Page 630, Table 5.1. [corrected 20 February 2019]
For –BrO2
read –BrO21
Page 630, Table 5.1, after line 4 on the left column. [corrected 20 February 2019]
Add –BrO31 perbromyl
Page 631, P-59.1.9, third paragraph, line 3/4 on this page. [corrected 5 December 2018]
For ...the seniority order of classes (see P-41.2, and P-42 and P-43, ...
read ...the seniority order of classes (see P-41, P-42 and P-43, ...
Page 631, P-59.1.9, fourth paragraph, lines 1/2 on this page. [corrected 20 February 2019]
For ...prefixes, if any, as described in Appendix 1) begins...
read ...prefixes, if any) begins...
Page 631, P-59.1.9, fifth paragraph, line 1/2 on this page. [corrected 5 December 2018]
For (compound substituent, see P-35, P-36, and P-46),...
read (compound substituent, see P-29.4, P-35.3, and P-46),...
Page 631, P-59.1.10, box line 3
For ...replacement (’a’) nomenclature...
read ...replacement (‘a’) nomenclature...
Page 632, P-59.2, title.
For P-59.2 EXAMPLES ILLUSTRATING THE GENERAL METHODOLOGY
read P-59.2 EXAMPLES ILLUSTRATING THE GENERAL METHODOLOGY
Page 632, P-59.2, lines 2/3. [corrected 3 June 2020]
For P-59.2.2 Seniority of heteroatoms over principal characteristic groups
read P-59.2.2 Seniority of heteroatoms over suffixes
Page 632, P-59.2, lines 6/7. [corrected 3 June 2020]
For P-59.2.4 Seniority of hydro/dehydro prefixes over detachable prefixes
read P-59.2.4 Seniority of ‘ene’ and ‘yne’ endings and hydro prefixes over detachable prefixes.
Page 638, P-59.2.1.7, example, line 4 on this page.
For Substituent –CH2[CH2]5-CHO
read Substituent –CH2-[CH2]5-CHO
Page 640, P-59.2.2.1, example (cont’d) [modified 29 January 2020]
Move 3,6,9,12-tetraoxapentadecane into column 3.
Page 641, P-59.2.3.1. [corrected 19 September 2018]
For Functionalized parent hydri
read Functionalized parent hydride:
Page 642, P-59.2.3.2, box, line3. [corrected 5 December 2018]
For ...detachable prefixes (see P-14.4; see also P-15.1.3.2, P-31.2, P-58.2), which is...
read ...detachable prefixes (see P-14.4; see also P-15.1.5.2, P-31.2, P-58.2), which is...
Page 643, P-59.2.3.3, Example 1. [corrected 20 February 2019]
For Saturation prefix 2 –H dihydro
read Saturation prefix 4 –H tetrahydro
Page 643, P-59.2.3.3, Example 2, last line. [corrected 21 November 2018]
For 3,4-dihydoroquinolin-2(1H)-ylidene (PIN)
read 3,4-dihydoroquinolin-2(1H)-ylidene (preferred prefix)
Page 645, P-59.2.3.3, Example 4, Explanation. [corrected 29 January 2020]
For See P-58.2.5
read See P-58.2.2
Page 648, P-6, line 8. [corrected 24 June 2020]
For P-65 Acids and derivatives
read P-65 Acids, acyl halides and pseudohalides, salts, esters, and anhydrides
Page 648, P-6, line 9. [corrected 24 June 2020]
For P-66 Amides, hydrazides, nitriles, aldehydes
read P-66 Amides, imides, hydrazides, nitriles, and aldehydes
Page 648, P-6, line 10. [corrected 24 June 2020]
For P-67 Oxoacids used as parents for organic compounds
read P-67 Mononuclear and polynuclear noncarbon acids and their functional replacement analogues as functional parents for naming organic compounds
Page 648, P-6, line 11. [corrected 24 June 2020]
For P-68 Nomenclature of other classes of compounds
read P-68 Nomenclature for organic compounds of the group 13, 14, 15, 16, and 17 elements not included in sections P-62 through P-67
Page 648, P-6, line 12. [corrected 24 June 2020]
For P-69 Organometallic compounds
read P-69 Nomenclature for organometallic compounds
Page 649, P-60.2, paragraph 5 on this page, line 3. (corrected 4 March 2020)
For ...names. The abbreviation ‘PIN’ is placed after preferred IUPAC names’. ...
read ...names’. The abbreviation ‘PIN’ is placed after names that are ‘preferred IUPAC names’. ...
Page 650, P-61.0, last line on this page. [corrected 12 December 2018]
For ...determined first (see for example, P-62.4)
read ...determined first (see P-41)
Page 650, P-61.1, title. [corrected 28 November 2018]
For P-61.1 GENERAL METHODOLOGY
read P-61.1 GENERAL METHODOLOGY
Page 651, P-61.1, 1st box, line 3. [corrected 27 February 2019]
For ... such, have seniority over suffixes for numbering.’
read ... such, have seniority over suffixes for numbering.
Page 653, P-61.2.3, second paragraph, line 2/3. [corrected 12 December 2018]
For ...as prescribed in P-15.1.8.2.2. There...
read ...as prescribed in P-31.1.3.4. There...
Page 654, P-61.2.3, example 1 on this page.
Delete (not p-vinylstyrene; substitution of styrene is not allowed: see P-22.1.3)
Page 654, P-61.2.3, examples 2 and 3 on this page. [corrected 12 December 2018]
For ...see P-52.2.9)
read ...see P-52.2.8)
Page 657, P-61.3.1, last example on page
For ...dodecane (PIN
read ...dodecane (PIN)
Page 660, P-61.3.2.1, example 4. [corrected 21 November 2018]
For chlorodiphosphane (PIN; diphosphane is a preselected name see P-12.2)
read chlorodiphosphanes (preselected name; diphosphane is a preselected name; see P-12.2)
Page 660, P-61.3.2.2, line 2. [corrected 12 December 2018]
For ...described in P-41.1.
read ...described in P-41.
Page 660, P-61.3.2.2, line 4. [corrected 12 December 2018]
For ...described in P-61.3.1 and P-61.3.2. Similarly...
read ...described in P-61.3.1. Similarly...
Page 661, P-61.3.2.2, example 1. [corrected 12 December 2018]
For (PIN; see P-67.1.2.6)
read (PIN; see P-68.5.3)
Page 661, P-61.4, title. [corrected 28 November 2018]
For P-61.4 DIAZO COMPOUNDS
read P-61.4 DIAZO COMPOUNDS
Page 661, P-61.4, line 3. [corrected 12 December 2018]
For ...(see also P-74.2.2.2.5).
read ...(see also P-74.2.2.2.3).
Page 663, P-61.5.1, example 3 on this page. [corrected 21 November 2018]
For 1-methyl-2-nitrosodiphosphane
read 1-methyl-2-nitrosodiphosphane (PIN)
Page 663, P-61.6, Note line 2. [corrected 11 December 2019]
For ...a substitutent prefix...
read ...a substituent prefix...
Page 663, P-61.6, line 1/2. [corrected 12 December 2018]
For ...(see P-64.1.3). In...
read ...(see P-64.1.2.2, P-64.4). In...
Page 664, P-61.7, line 4. [corrected 12 December 2018]
For ...(see also P-74.2.2.4).
read ...(see also P-74.2.2.2.2).
Page 664, P-61.8, box line 2.
For ...generated substituively using...
read ...generated substitutively using...
Page 666, P-61.10, line 7/8. [corrected 12 December 2018]
For ...formonitrile oxide (see P-66.5.1.2) and...
read ...formonitrile oxide (see P-66.5.4.1) and...
Page 666, P-61.10, box line1.
For ...potentially abiguous names...
read ...potentially ambiguous names...
Page 666, P-61.10, example 2. [corrected 21 November 2018]
For (oxo-λ5-azanylidyne)methyl (PIN)
read (oxo-λ5-azanylidyne)methyl (preferred prefix)
Page 666, P-61.10, example 4. [corrected 21 November 2018]
For (λ2-methylideneamino)oxy (PIN)
read (λ2-methylideneamino)oxy (preferred prefix)
Page 667, P-61.11.2, example 1. [corrected 12 December 2018]
For (pentasilane is a preselected name, see P-12)
read (pentasilane is a preselected name, see P-12.2)
Page 667, P-62, contents. [corrected 28 November 2018]
For P-62.4 Amines and imines substituted by compulsory prefixes
read P-62.4 N-Substitution of amines and imines by heteroatoms
Page 667, P-62, contents. [corrected 28 November 2018]
For P-62.5 Amine and imine oxides
read P-62.5 Amine oxides, imine oxides and chalcogen analogues
Page 668, P-62.1 (a) (2), lines 1/2. [corrected 26 January 2022]
For ...compounds having the structure R-N=CR2 (R = H or hydrocarbyl),...
read ...compounds having the structure R2C=N-R (R = H or hydrocarbyl),....
Page 669, P-62.2.1.2, Note line 5. [corrected 26 January 2022]
For ...functional class name were eliminated to form...
read ...functional class name is eliminated to form...
Page 672, P-62.2.2.1, example 2 on this page. [corrected 24 June 2020]
For (not N-(2-chloroethyl)propylamine)
read [not N-(2-chloroethyl)propylamine]
Page 672, P-62.2.2.2, example 1. (corrected 4 March 2020)
For (2) (4-methylpent-4-en-2-yn-1-yl)(dipropyl)azane
read (2) (4-methylpent-4-en-2-yn-1-yl)di(propyl)azane
For (3) (4-methylpent-4-en-2-yn-1-yl)(dipropyl)amine
read (3) (4-methylpent-4-en-2-yn-1-yl)di(dipropyl)amine
Page 673, P-62.2.2.2, example 6 on this page. (corrected 4 March 2020)
For 2-furyl(pyrrol-2-yl)azane
read 2-furyl(1H-pyrrol-2-yl)azane
For 2-furyl(pyrrol-2-yl)amine
read 2-furyl(1H-pyrrol-2-yl)amine
Page 675, P-62.2.3, example 2 on this page.
For (not disilazan-2-yl acetic acid)
read (not disilazan-2-ylacetic acid). [deleted space from name]
Page 675, P-62.2.3, example 3 on this page. [corrected 21 November 2018]
For (silylamino)silyl (preferred prefix)
read (silylamino)silyl (preselected prefix)
Page 675, P-62.2.4.1, line 1. [corrected 9 January 2019]
For ...polyamines, i.e., polyamines are compounds...
read ...polyamines are compounds...
Page 675, P-62.2.4.1.1, line 3.
For ...the 4,4′- isomer, with...
read ...the 4,4′-isomer, with... [delete space before isomer]
Page 676, P-62.2.4.1.2, example 5. (corrected 4 March 2020)
Replace the structures with:
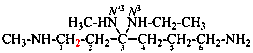
Page 676, P-62.2.4.1.2, example 6. [corrected 21 November 2018]
For N4,2-dimethylpentane-2,4-diamine
read N4,2-dimethylpentane-2,4-diamine (PIN)
Page 678, P-62.2.4.1.3, example 1 on this page. [corrected 12 December 2018]
For ...(see P-14.3; P-51.2; P-62.4)...
read ...(see P-15.3; P-51.3; P-62.2.5)...
delete N1-(2-aminoethyl)-N2-{2-[(aminomethyl)amino]ethyl}ethane-1,2-diamine
(substitutive name ; alphabetically inferior to the first substitutive name]
Page 678, P-62.2.4.1.3, example 2 on this page. [corrected 27 February 2019]
For ...alphanumerical order; P-45.1.3]
read ...alphanumerical order; P-14.5]
Page 678, P-62.2.4.1.3, example 4 on this page. [corrected 12 December 2018]
For ...(see P-14.3; P-51.2; P-62.4)...
read ...(see P-15.3; P-51.3; P-62.2.5)...
Page 680, P-62.2.5.2 (2) (ii), line 2. (corrected 4 March 2020)
For ...as needed (see (P-16.9.3). The...
read ...as needed (see P-16.9.3). The...
Page 680, P-62.2.5.2 (2) (ii), example 1. [corrected 21 November 2018]
For N,N1′-methylenedi(ethane-1,2-diamine)
read N,N1′-methylenedi(ethane-1,2-diamine) (PIN)
Page 682, P-62.3, line 4/5. [corrected 12 December 2018]
For ...three single bonds linked to carbon atoms (see P-62.0). Imines must have...
read ...three single bonds linked to at least one carbon atom (see P-62.1). Imines must have...
Page 682, P-62.3.1.1, line 3/4. [corrected 12 December 2018]
For ...methodology described in P-62.2.4.1 for amines...
read ...methodology described in P-62.2.4 for amines...
Page 685, P-62.4, pararaph 2, lines 1/2.
For ...atoms, -BrO and other acyl similar groups, -NO, -NO2, - OR, -SO2-R, -SO-R, and...
read ...atoms, –BrO and other acyl similar groups, –NO, –NO2, –OR, –SO2-R, –SO-R, and... [Deleted space before OR]
Page 685, P-62.5 (1), line 2. [corrected 24 June 2020]
For ...‘selenide’, and ‘teluride’ provided that...
read ...‘selenide’, and ‘telluride’ provided that...
Page 686, P-62.5, line 2/3 on this page. [corrected 14 November 2018]
For ... are present in the name of the amine’.
read ... are present in the name of the amine.
Page 687, P-62.6.1 (1), line 2. [corrected 26 January 2022]
For ...the terminal letter, ‘e’ if present...
read ...the terminal letter ‘e’, if present...
Page 689, P-63, title. [corrected 28 November 2018]
For P-63.5 Cyclic ethers and peroxides and chalcogen analogues
read P-63.5 Cyclic ethers, sulfides, selenides, and tellurides
For P-63.8 Salts of hydroxy compounds and their chalcogen analogues and hydroperoxy comopounds
read P-63.8 Salts of hydroxy compounds, hydroperoxy compounds and their chalcogen analogues
Page 689, P-63.0, line 7. [corrected 19 September 2018]
For ... name as an acid, orthosilicic acid.
read ... name as an acid, silicic acid.
Page 695, P-63.1.2, example 5 on this page. [corrected 12 December 2018]
For ...for numbering, see P-28.3.1)
read ...for numbering, see P-28.3)
for ...(see P-28.3.1)
read ...(see P-28.3)
Page 699, P-63.1.5, example 2 on this page. [corrected 12 December 2018]
For see P-52.2.9
read see P-52.2.8
Page 699, P-63.2, line 6. [corrected 22 April 2020]
For P-63.2.5 Chalcogen anaogues of ethers: sulfides, selenides, and tellurides
read P-63.2.5 Names of chalcogen anaogues of ethers, i.e., sulfides, selenides, and tellurides
Page 695, P-63.1.2, example 6 on this page. [corrected 12 December 2018]
For -...(PIN; see P-28.3.1)
read ..(PIN; see P-28.3)
for ...(see P-28.3.1)
read ...(see P-28.3)
Page 699, P-63.2, title. [corrected 28 November 2018]
For P-63.2.3 Retained names
read P-63.2.3 Retained names of ethers
Page 700, P-63.2.2.1.1, example 4. [corrected 23 December 2020]
For (not piperidinooxy)
read piperidinooxy
Page 701, P-63.2.2.2, example 6. [corrected 19 September 2018]
For tert-butoxy (referred prefix)
read tert-butoxy (preferred prefix)
Page 702, P-63.2.2.2, example 1 on this page. [corrected 27 February 2019]
For 1-methylpropoxy)
read 1-methylpropoxy
Page 703, P-63.2.4, (2) line 3. [corrected 27 February 2019]
For ...alphanumeerical order.
read ...alphanumerical order.
Page 703, P-63.2.4.1, line 2. [corrected 24 June 2020]
For ...Methods (1) or (4) leads to...
read ...Method (1) or (4) leads to...
Page 704, P-63.2.4.1, before last example. (corrected 4 March 2020)
For Examples:
read Example:
Page 705, P-63.2.5.1, title. [corrected 28 November 2018]
For P-63.2.5.1 General methodology
read General methodology
Page 706, P-63.2.5.1, example 5 on this page. [corrected 12 December 2018]
For (ring preferred to chain, see P-52.2.9)
read (ring preferred to chain, see P-52.2.8)
Page 707, P-63.3.1 (1). (corrected 4 March 2020)
For ...(not R′, ‘R′-disulfanyl’, R′-diselanyl’ or R′-ditellanyl’ attached...
read ...(not R′-dioxy), ‘R′-disulfanyl’, ‘R′-diselanyl’ or ‘R′-ditellanyl’ attached...
Page 709, P-63.3.2 (1), line 1. [corrected 27 February 2019]
For ... the substituent groups R′-O, R′-S–, ...
read ... the substituent groups R′-O–, R′-S–, ...
Page 709, P-63.3.2 (1), line 3. (corrected 4 March 2020)
For ... to ‘oxy’, ‘sulfanyl’, selanyl’, or ‘tellanyl’ and...
read ... to ‘oxy’, ‘sulfanyl’, ‘selanyl’, or ‘tellanyl’ and...
Page 716, P-63.7, second paragraph, line 3. [corrected 12 December 2018]
For ... choice (see P-52.2.9).
read ...choice (see P-52.2.8).
Page 717, P-63.7, example 1 on this page. [corrected 12 December 2018]
For ...name, see P-52.2.9)
read ...name, see P-52.2.8).
Page 719, P-63.8, title.
For ... HYDROPEROXY COMPOUNS AND THEIR...
read ... HYDROPEROXY COMPOUNDS AND THEIR...
Page 719, P-63.8.1, line 11. (corrected 4 March 2020)
For ...aminoxide, , for...
read ...aminoxide, for...
Page 719, P-63.8.1, examples 1-7. [corrected 9 January 2019]
Delete space before the minus signs in all these structures.
Page 719, P-63.8.1, example 3. [modified 9 January 2017]
For potassium propan -2-olate (PIN)
read potassium propan-2-olate (PIN) [Deleted space from name]
Page 719, P-63.8.1, example 7. (modified 4 March 2020)
For (C6H5-O –)4 Pb
read (C6H5-O–)4 Pb4+ [remove space in name]
Page 720, P-64, contents. [corrected 28 November 2018]
For P-64.5 Expressing carbonyl groups as prefixes
read P-64.5 Carbonyl groups as prefixes
Page 722, P-64.2.1.1, lines 2/3. [corrected 26 January 2022]
For ...lower than ‘ketone’. It is the stereospecific trans- or (E)- stereoisomer.
read ...lower than ‘ketone’. Chalcone refers only to the trans- or (E)- stereoisomer.
Page 722, P-64.1.2.2, line 2. [corrected 12 December 2018]
For ... heteroatom (see P-62.3.1.3 and P-63.1.3; see also P-68). ...
read ... heteroatom (see P-61.6 and P-64.4; see also P-68). ...
Page 723, P-64.2.1.2, lines 1/2. [modified 24 June 2020]
For ...names acetone, 1,4-benzoquinone, naphthoquinone and anthraquinone are retained...
read ...names acetone and 1,4-benzoquinone, together with naphthoquinone and anthraquinone with locants, are retained...
Page 723 , P-64.2.1.2, line 4. [corrected 27 February 2019]
For ...listed in P-15.1.8.2.1. The names...
read ...listed in P-15.1.8.2. The names...
Page 727, P-64.2.2.2, 2nd paragraph, line 4. [corrected 14 November 2018]
For ...‘added indicated hydrogen’. (see P-14.7and P-58.2.2).
read ... ‘added indicated hydrogen’ (see P-14.7 and P-58.2.2). [add space]
Page 728, P-64.2.2.2.3, lines1/2. [modified 24 June 2020]
For ...The names 1,4-benzoquinone, naphthoquinone, and anthraquinone are retained for use...
read...The name 1,4-benzoquinone, and those of naphthoquinone, and anthraquinone with locants, are retained for use...
Page 732, P-64.3.1, example 1. [corrected 12 December 2018]
For succinic anhydride (see P-65.7.3)
read succinic anhydride (see P-65.7.7)
Page 732, P-64.3.1, example 2. [corrected 12 December 2018]
For hexano-6-lactam (see P-66.1.4.1)
read hexano-6-lactam (see P-66.1.5.1)
Page 734, P-64.4, line 2. [modified 24 June 2020]
For ...to a heteroatom for heterols; for heteroimines...
read ...to a heteroatom, see P-64.1.2.2; for heterols, see P-63.1.3; for heteroimines...
Page 735, P-64.4.1, example 1. [corrected 21 November 2018]
For phosphanone (PIN; P-74.2.1.4)
read phosphanone (preselected name; P-74.2.1.4)
Page 738, P-64.5.2.1, example 1. [corrected 12 December 2018]
For (ring preferred to chain, see P-52.2.9)
read (ring preferred to chain, see P-52.2.8)
Page 739, P-64.5.2.2, example 2. [corrected 21 November 2018]
For 3-(silanecarbonyl)propanoic acid PIN)
read 3-(silanecarbonyl)propanoic acid
for 4-oxo-4-silylbutanoic acid
read 4-oxo-4-silylbutanoic acid (PIN)
Page 740, Title of section.
For 64.6.2 Seniority order of suffixes
read P-64.6.2 Seniority order of suffixes
Page 742, P-64.7.1, example 4 on this page. [corrected 11 November 2020]
For ...fluoro substituents are required, see P-14.3.3
read ...fluoro substituents are required, see P-14.3.4.5
Page 743, P-64.7.2, example 1. [corrected 24 June 2020]
For ...which has only one carbonyl groups (see P-44.1.1)]
read ...which has only one carbonyl group (see P-44.1.1)]
Page 744, P-65, line 6. [corrected 28 November 2018]
For P-65.5 Acid halides and pseudohalides
read P-65.5 Acyl halides and pseudohalides
Page 746, P-65.1.1.2.1, example 1.
For furoic acid (also 3- isomer)
read furoic acid (also 3-isomer) [delete space before isomer]
Page 745, P-65.1.1.1, line 1. [corrected 26 January 2022]
For Only the following five retained names are preferred IUPAC names....
read Only the following five carboxylic acids are retained names and are also preferred IUPAC names.....
Page 749, P-65.1.1.2.4, last paragraph. (corrected 4 March 2020)
Move to end of P-65.1.1.2.3
Page 752, P-65.1.2.3, example 3. (corrected 4 March 2020)
For [not 2-hexylbut-2-enoic acid; see P-44.3, criterion (b)
read [not 2-hexylbut-2-enoic acid; see P-44.3, criterion (b)]
Page 756, P-65.1.3.1.1, after two structures at top of page. [corrected 24 October 2018]
Add P-65.1.3.1.2, Substitutive nomenclature, prefix mode
Page 756, P-65.1.3.1.2 (formerly P-65.1.3.1.1), Note 2. [corrected 24 June 2020]
For The name carbonohydroximoyl, for –C(=NH)-OH, not used to generate preferred IUPAC names.
read The name carbonohydroximoyl, for –C(=NH)-OH, is not used to generate preferred IUPAC names.
Page 759, P-65.1.3.3.1, Note. [corrected 24 February 2021]
For The following former methodology is no longer recommended for preferred IUPAC names.
read The following former methodology is no longer used for preferred IUPAC names.
Page 759, P-65.1.3.3.1. [corrected 24 February 2021]
Replace (1) and (2) by
The name formed by modifying the ‘-oic acid’ or ‘-carboxylic acid’ suffix of a systematically named acid, or the ‘-ic acid’ ending of the retained name of an acid to ‘-hydroximic acid’ or ‘-carbohydroximic acid’. The letter ‘o’ is added for euphony between ‘h’ and a preceding consonant.
Page 759, P-65.1.3.3.1, example 3. [corrected 3 March 2021]
For butanehydroximic acid
read butanohydroximic acid
Page 760, P-65.1.3.1, lines 3/4. (modified 4 March 2020)
For ...for preferred IUPAC names buy may be continued in general nomenclature..
read ...for preferred IUPAC names.
Page 760, P-65.1.3.4, lines 3/4. [modified 24 March 2021]
For ...for preferred IUPAC names buy may be continued in general nomenclature.
read ...for preferred IUPAC names but may be used in general nomenclature.
Page 761, P-65.1.4.1, box, line 1/2. [corrected 9 January 2019]
For ... acid is a change change for formic acid ...
read ... acid is a change for formic acid ...
Page 762, P-65.1.4.2 (1), lines 2/3. [corrected 24 June 2020]
For ...formed by concatenation based, on the simple acyl group...
read ...formed by concatenation based on the simple acyl group...
Page 763, P-65.1.5.1, lines 2-4 of the second paragraph. [modified 6 March 2019]
For ...compound; compound prefixes such as ‘[hydroxy(carbonothioyl)]-’ and ‘(sulfanylcarbonyl)-’ are used in cyclic compounds, as appropriate (see P-64.2.1.6).
read ... compound. Compound prefixes such as ‘(hydroxycarbonothioyl)-’ and ‘(sulfanylcarbonyl)-’ are used when required as a substituent (see P-65.2.1.6).
Page 763, P-65.1.5.1, example 5. [corrected 9 January 2019]
For HSSC-CH2-CH2-CH2-CH2-CS-SH
read HS-CS-CH2-CH2-CH2-CH2-CS-SH
Page 764, P-65.1.5.1, example 1 from top of page.
Replace structure with HO-CS-CH2-CH2-COOH
Page 764, P-65.1.5.1, example 2 from top of page.
Replace structure with HS-CO-COOH
Page 765, P-65.1.5.2, example 3. [corrected 9 January 2019]
For methanethioic S-acid (PIN
read methanethioic S-acid (PIN)
Page 767, P-65.1.5.3, example 1 on this page. [corrected 24 June 2020]
For (not 3-carbono(thioperoxo)thioylpropanoic acid; ambiguous name)
read [not 3-carbono(thioperoxo)thioylpropanoic acid; ambiguous name]
Page 769, P-65.1.7 line 4. [corrected 22 April 2020]
For...(see P-65.1.1.1)
read ...(see P-65.1.1.1) i.e.carboacyl groups
Page 769, P-65.1.7.1, paragraph 2, line 1.
For ...carboacyl groups amd their functional trplacement analogues...
read ...carboacyl groups and their functional replacement analogues...
Page 770, P-65.1.7.2, 2nd paragraph, line 5/ 6. [corrected 19 September 2018]
For ...and ‘carbohydroximic acid’ to ‘carbohydroximidoyl’.
read ...and ‘carbohydroximic acid’ to ‘carbohydroximoyl’.
Page 770, P-65.1.7.2.1, example 5. [corrected 24 June 2020]
For (not carboxyformyl; not hydroxy(oxo)acetyl]
read [not carboxyformyl; not hydroxy(oxo)acetyl]
Page 775, P-65.1.7.4.2, example 5. [corrected 20 March 2019]
Add = hexane-2,3,5-triyltris(carbonyl)
Page 777, P-65.1.8.1, example 1. [corrected 7 November 2018]
For carbonohydrazidic acid; see P-65.2.1.4)
read carbonohydrazidic acid (see P-65.2.1.4)
Page 777, P-65.1.8.2, example 2. (modified 4 March 2020)
For H(S/O)C-COOH
read H{S/O}C-COOH
Page 777, P-65.1.8.2, examples. (corrected 4 March 2020)
For Example:
read Examples:
Page 777, P-65.1.8.3, line 1/2. [corrected 12 December 2018]
For ... are formed as described in P-65.1.7.1 and ...
read ... are formed as described in P-65.1.7.2 and ...
Page 777, P-65.2, example 1. [corrected 21 November 2018]
For carbonic acid HO-CO-OH (PIN)
read carbonic acid (PIN) HO-CO-OH
Page 777, P-65.2, example 2. [corrected 21 November 2018]
For cyanic acid HO-CN (PIN)
read cyanic acid (PIN) HO-CN
Page 779, P-65.2.1.2, example 5. [corrected 21 November 2018]
For HS-CS-SH (PIN) carbonotrithioic acid
read HS-CS-SH carbonotrithioic acid (PIN)
Page 779, P-65.2.1.2, example 6. [corrected 21 November 2018]
For H2N-CO-OOH (PIN) carbamoperoxoic acid
read H2N-CO-OOH carbamoperoxoic acid (PIN)
Page 780, P-65.2.1.4, line 5. [corrected 12 December 2018]
For ... isotellurocyanatido, –NCTe (see P-67).
read ... isotellurocyanatido, –NCTe (see P-67.1.2.3.2).
Page 780, P-65.2.1.4, last example. [corrected 6 March 2019]
For carbonohydrazidic acid (acids expressed by suffixes are preferred...
read carbonohydrazidic acid (carboxylic acids expressed by suffixes are preferred...
Page 782, P-65.2.1.5, example 13 on this page. [corrected 21 November 2018]
For carbonoperoxoic acid
read carbonoperoxoic acid (PIN)
Page 785, P-65.2.3.1, contents. [corrected 9 January 2019]
For P-65.2.3.1.2 Replacement by –OO–, –S–, =S, –Se–, =Se, –Te–, –NH–, =Te, =NH, and =NHNH2
read P-65.2.3.1.2 Replacement by –OO–, –S–, =S, –Se–, =Se, –Te–, =Te, –NH–, =NH, and =NHNH2
Page 785, P-65.2.3.1.1, line 2. [corrected 12 December 2018]
For ... inorganic oxo acids (see P-67)...
read ... inorganic oxoacids (see P-67.2.1.)...
Page 786, P-65.2.3.1.2.1, box, line 1. [corrected 3 October 2018]
For ...Primed letter locants, N′, N′′, N′′′, etc. ...
read ...Primed letter locants, N′, N′′, N′′′, etc. ...
Page 788, Table 6.2, column 2 and 3 headings. (corrected 4 December 2019)
For Preferred Suffix Preferred Prefix
read Preselected Suffix Preselected Prefix
Page 790, P-65.3.1.3, structure 1. [corrected 24 June 2020]
For –SO2-SH sulfonothioic S-acid (preferred suffix)
read –SO2-SH sulfonothioic S-acid (preselected suffix)
Page 790, P-65.3.1.3, structure 2. [corrected 24 June 2020]
For –Se(=S)-OH seleninothioic O-acid (preferred suffix)
read –Se(=S)-OH >seleninothioic O-acid (preselected suffix)
Page 790, P-65.3.1.3, structure 3. [corrected 24 June 2020]
For –SO2-OSH sulfono(thioperoxoic) OS-acid (preferred suffix)
read –SO2-OSH sulfono(thioperoxoic) OS-acid (preselected suffix)
Page 790, P-65.3.1.3, structure 4. [corrected 24 June 2020]
For –TeO-SeSH tellurino(selenothioperoxoic) SeS-acid (preferred suffix)
read –TeO-SeSH tellurino(selenothioperoxoic) SeS-acid (preselected suffix)
Page 790, P-65.3.1.3, example 1. [corrected 11 November 2020]
For CH3-CH2-CH2-S{O,Se}H
read CH3-CH2-CH2-S{O/Se}H
Page 791, P-65.3.1.5, line 2. [corrected 6 March 2019]
For ...and N-hydroxysulfonamide, etc. (see P-66.1.1.2),...
read ...and N-hydroxysulfonamide, etc. (see P-66.1.1.3.2),...
Page 792, P-65.3.2.2.2, box, line 5. [corrected 6 March 2019]
For ... are enclosed in parentheses even though they are simple prefixes.
read ... are enclosed in parentheses even though they are simple prefixes (P-16.5.1.5).
Page 793, P-65.3.2.3, all prefixes on this page except the example 1 at the bottom of the page. [corrected 6 March 2019]
For (preferred prefix)
read (preselected prefix)
Page 794, P-65.3.2.3, examples 1, 2, 5, 6, 7 and 8 on this page. [corrected 6 March 2019]
For (preferred prefix)
read (preselected prefix)
Page 794, P-65.3.2.3, example 3 on this page. [corrected 23 December 2020]
For (acetyloxy)sulfonyl (preferred prefix)
read (acetyloxy)sulfonyl (preferred prefix) acetoxysulfonyl
Page 796, P-65.5, line 4. [corrected 24 June 2020]
For ...cyanic, and the polycarbonic acids
read ...cyanic, and polycarbonic acids
Page 796, P-65.5.1.1, line 1. [corrected 6 March 2019]
For P-65.5.1.1 Acid halides in which...
read Acyl halides in which...
Page 798, P-65.5.3, title. [corrected 24 June 2020]
For ...cyanic, and the polycarbonic acids
read ...cyanic, and polycarbonic acids
Page 799, P-65.5.4, heading. [corrected 28 November 2018]
For P-65.5.4 Acyl halides and pseudo halides as substituent groups
read P-65.5.4 Acyl halides and pseudohalides as substituent groups [delete space in name]
Page 800, P-65.5.4, example 3. [modified 9 April 2025]
Delete correction in BB-minor
Page 800, P-65.5.4, line 1 on this page. (corrected 4 March 2020)
For ...for which see P-65.1.2.3 or P-65.3.4.
read ...for which see P-65.1.2.3.
Page 800, P-65.5.4, example 1. [corrected 24 June 2020]
For (1) (carbonochloridoyl)acetic acid
read (1) carbonochloridoylacetic acid
Page 800, P-65.5.4, example 3. [corrected 24 June 2020]
For (1) 2-(cyanosulfonyl)cyclohexane-1-carboxylic acid (PIN)
read (2) 2-(cyanosulfonyl)cyclohexane-1-carboxylic acid
for (2) 2-sulfurocyanidoylcyclohexane-1-carboxylic acid
read (1) 2-sulfurocyanidoylcyclohexane-1-carboxylic acid (PIN)
Page 800, P-65.5.4, example 3. [modified 9 April 2025]
Delete correction in BB-minor
Page 800, P-65.5.4, example 8. [corrected 28 October 2016]
For (1) 3-[(carbonobromidoyl)oxy]-3-oxopropanoic acid
read (1) 3-[(carbonobromidoyl)oxy]-3-oxopropanoic acid (PIN)
delete (PIN) below the structure
Page 801, P-65.6.2.1, line 6. [corrected 24 June 2020]
For ...oxalic and the polycarbonic acids.
read ...oxalic and polycarbonic acids.
Page 802, P-65.6.2.3.1, paragraph after (2), line 1. [corrected 6 July 2018]
For ...when the strcture of the acid...
read ...when the structure of the acid...
Page 802, P-65.6.2.3.1, line 10. [corrected 11 December 2019]
For ...Anionic substitutents, such as...
read ...Anionic substituents, such as...
Page 803, P-65.6.2.3.2, line 2. [corrected 19 September 2018]
For ... inorganic oxo acids (including ...
read ... inorganic oxoacids (including ... [delete space in name]
Page 803, P-65.6.3.1.1, line 1/2. [corrected 9 January 2019]
For ...(R can be H) or R-S(O)x-O-R (R ≠ H)...
read ...(R can be H) or R-S(O)x-O-R (R ≠ H)...
Page 803, P-65.6.3.1.1, line 3. [corrected 9 January 2019]
For ...R-C(O)-OH (R can be H) or R-S(O)x-OH (R ≠ H)...
read ...R-C(O)-OH (R can be H) or R-S(O)x-OH (R ≠ H)...
Page 804, P-65.6.3.1.2, lines 1/2. (corrected 4 March 2020)
For ...formula R-E(=O)x(OZ) and chalcogen analogues where x = 1 or 2 and...
read ...formula R-E(=O)x(OZ) and chalcogen analogues where x = 1 or 2 and...
Page 804, P-65.6.3.2.2, example 1. [corrected 21 November 2018]
For propane-1,2,3-triyl triacetate
read propane-1,2,3-triyl triacetate (PIN)
Page 805, P-65.6.3.2.3, third paragraph, line 1. [corrected 6 March 2019]
For Seniority of numbering follows that for acids, for which see P-65.1.2.3 or P-65.3.4.
read Seniority of numbering follows that for acids, for which see P-65.1.2.3.
Page 805, P-65.6.3.2.3, example 1. (corrected 4 March 2020)
Replace the structures with:
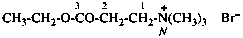
Page 807, P-65.6.3.3, line 6. [corrected 22 April 2020]
For...polybasic acids and salts
read ...polybasic acids and their salts
Page 807, P-65.6.3.3, contents. [corrected 28 November 2018]
For P-65.6.3.3.7 Esters of acids modified by functional replacement
read P-65.6.3.3.7 Esters of acids modified by functional replacement nomenclature
Page 809, P-65.6.3.3.2.2.2, line 1. [corrected 19 September 2018]
For ... for multiplicative names as describe above ...
read ... for multiplicative names as described above ...
Page 809, P-65.6.3.3.2.2.2, line 3/4. [corrected 12 December 2018]
For ... in general nomenclature [see P-15.3.0(2) and P-51.3.1].
read ... in general nomenclature [see P-15.3.2 and P-51.3.3].
Page 811, P-65.6.3.3.4, title. [modified 22 April 2020]
For...and multple alcoholic components
read ...and multiple 'alcoholic' components
Page 812, P-65.6.3.3.4.1. (corrected 4 March 2020)
For Examples
read Example:
Page 812, P-65.6.3.3.4.2, line 1. [corrected 24 June 2020]
For Polyesters that can not be name by functional class...
read Polyesters that cannot be named by functional class... [remove space in name]
Page 812, P-65.6.3.3.4.2, line 2. [corrected 24 June 2020]
For ...using substitutive nomenclature nomenclature to generate...
read ...using substitutive nomenclature to generate...
Page 815, P-65.6.3.3.4.3, example 1. (corrected 4 March 2020)
For ... skeletal replacement ('a') nomenclature.
read ... skeletal replacement ('a') nomenclature.]
Page 815, P-65.6.3.3.4.3, example 3. (corrected 4 March 2020)
For ... skeletal replacement ('a') nomenclature.
read ... skeletal replacement ('a') nomenclature.]
Page 818, P-65.6.3.3.7, title. [corrected 16 August 2016]
For Esters of acids modified by functional replacement nomrnclature
read Esters of acids modified by functional replacement nomenclature
Page 818, P-65.6.3.3.7.1, line 2. [corrected 12 December 2018]
For ...acid that are described in P-65.6.3.3.3, names of esters are...
read ...acid that are described in P-65.6.3.3.7.2, names of esters are...
Page 820, P-65.3.3.7.2, line 1. [corrected 24 June 2020]
For ...cycanic acid, and the polycarbonic acids...
read ...cycanic acid, and polycarbonic acids...
Page 821, P-65.6.3.4.1, example 7. [modified 24 June 2020]
For (hydroxylamine is a retained preferred IUPAC name; see P-68.3.1.1.1)
read (hydroxylamine is a preselected name; see P-68.3.1.1.1)
Page 822, P-65.6.3.5.1 (3), line 7. [corrected 6 March 2019]
For ... sultone or sultine rings.
read ... carbolactone rings.
Page 823, P-65.6.3.5.1, example 2 on this page. (corrected 4 March 2020)
For ...and at least two five-membered rings, see P-52.2.4.1)
read ...and at least two rings of five or more members, see P-52.2.4.1)
Page 827, P-65.7.1, example 4. [corrected 6 March 2019]
Delete anhydride below the name.
Page 828, P-65.7.3, after second text paragraph. (corrected 4 March 2020)
Add Examples:
Page 829, P-65.7.4, line 5 of second text paragraph. [corrected 24 June 2020]
For ...preceded by a the appropriate italicized...
read ...preceded by the appropriate italicized...
Page 830, P-65.7.6.1, example 1. [corrected 21 November 2018]
For acetic boric dianhydride (PIN)
read acetic boric dianhydride
Add bis(acetyloxy)borinic acid (PIN; acid is senior to anhydride).
Page 831, P-65.7.6.2, line 1.
For ...are names by one...
read ...are named by one...
Page 831, P-65.7.6.2, example 1. [corrected 6 March 2019]
For triacetic phosphoric trianhydride
read triacetic phosphoric trianhydride (PIN)
move this example to P-65.7.6.3
Page 832, P-65.7.6.3, examples. [corrected 6 March 2019]
Add example 1 from P-65.7.6.2.
Page 833, P-65.7.6.4.1, example 2. [corrected 21 November 2018]
For diacetic methanedisulfonic bis(thioanhydride)
read diacetic methanedisulfonic bis(thioanhydride) (PIN)
Page 835, P-65.7.7.1, example 7. [corrected 21 November 2018]
For 1H,3H-benzo[de]isochromene-1,3-dione (PIN)
read 1H,3H-benzo[de]isochromene-1,3-dione
Page 836, P-65.7.7.2, example 1. [corrected 3 October 2018]
For tetrahydrocyclobuta[1,2-c:3,4-c′]difuran-1,3,4,6-tetrone (PIN)
read tetrahydrocyclobuta[1,2-c:3,4-c′]difuran-1,3,4,6-tetrone (PIN)
Page 837, P-65.7.7.2, example 2 on this page. (corrected 4 March 2020)
For (not 4,9-dioxatricyclo[4.4.2.02,7]dodecane-3,5,8,10-tetrone [numbering shown in (II)
read {not 4,9-dioxatricyclo[4.4.2.02,7]dodecane-3,5,8,10-tetrone [numbering shown in (II)]}
Page 838, P-65.7.8.1, line 1. [corrected 9 January 2019]
For Anhydrides of substituted of monocarboxylic or monosulfonic...
read Anhydrides of substituted monocarboxylic or monosulfonic...
Page 839, P-65.7.8.1, example 2. [corrected 21 November 2018]
For bis(2-chloroacetic) anhydride
read bis(2-chloroacetic) anhydride (PIN)
Page 839, P-65.7.8.1, example 3. [corrected 21 November 2018]
For bis(6-aminohexanoic) anhydride
read bis(6-aminohexanoic) anhydride (PIN)
Page 839, P-65.7.8.2, example 1. [corrected 21 November 2018]
For 2-chloropropanoic 3-chloropropanoic anhydride
read 2-chloropropanoic 3-chloropropanoic anhydride (PIN)
Page 839, P-65.7.8.2, example 2. [corrected 21 November 2018]
For chloroacetic chloroethanethioic anhydride
read chloroacetic chloroethanethioic anhydride (PIN) .
Page 839, P-66 title. [corrected 26 January 2022]
For P-66 AMIDES, IMIDES, HYDRAZIDES, NITRILES, AND ALDEHYDES,
read P-66 AMIDES, IMIDES, HYDRAZIDES, NITRILES, AND ALDEHYDES
Page 840, P-66.1.1.1.1, example 2. [corrected 9 January 2019]
For H2N-OC-CH2-CH2-CH2-CO-NH2
read H2N-CO-CH2-CH2-CH2-CO-NH2
Page 840, P-66.1.1.1.1.1, heading.[corrected 14 November 2018]
For P-66-1.1.1.1.1
read P-66.1.1.1.1.1
Page 841, P-66.1.1.1.1.3.
For P-66-1.1.1.1.3
read P-66.1.1.1.1.3
Page 842, P-66.1.1.1.2.4, heading. [corrected 28 November 2018]
For P-66.1.1.1.2.4.
read P-66.1.1.1.2.4
Page 842, P-66.1.1.1.2.5, line 2. [corrected 12 December 2018]
For ..., and in P-103.2.6, respectively.
read ..., and in P-103.2.7, respectively.
Page 843, P-66.1.1.2, top six structures. [corrected 1 July 2020]
For (preferred suffix)
read (preselected suffix)
Page 844, P-66.1.1.3.1.1, example 7.
For N1,N5 -dimethylpentanediamide (PIN)
read N1,N5-dimethylpentanediamide (PIN). [remove space from name]
Page 845, P-66.1.1.3.1.2, example 1.
For N′1-ethyl-N1, N1, N3-trimethylpropane-1,1,3-tricarboxamide (PIN)
read N′1-ethyl-N1,N1,N3-trimethylpropane-1,1,3-tricarboxamide (PIN). [remove spaces from name]
Page 845, P-66.1.1.3.2, example 1. [corrected 24 February 2021]
For (not propanehydroxamic acid)
read propanohydroxamic acid
Page 845, P-66.1.1.3.1.2, example 2.
For N1-ethyl- N′1, N3-dimethylpropane-1,1,3-tricarboxamide (PIN)
read N1-ethyl-N′1,N3-dimethylpropane-1,1,3-tricarboxamide (PIN). [remove spaces from name]
Page 845, P-66.1.1.3.2, example 2. [corrected 24 February 2021]
For (not cyclohexanecarbohydroxamic acid)
read cyclohexanecarbohydroxamic acid
Page 846, P-66.1.1.3.5, line 3. [corrected 12 December 2018]
For ...described in P-65.1.1.2.
read ...described in P-65.1.2.4.
Page 847, P-66.1.1.4, line 2. [corrected 1 July 2020]
For ...in presence of a characteristic...
read ...in the presence of a characteristic...
Page 848, P-66.1.1.4.1.1, line 1. [corrected 1 July 2020]
For P-66.1.1.4.1.1 In presence of a characteristic...
read P-66.1.1.4.1.1 In the presence of a characteristic...
Page 849, P-66.1.1.4.2, line 1. [corrected 1 July 2020]
For In presence of a characteristic group
read In the presence of a characteristic group
Page 850, P-66.1.1.4.2, example 2 on this page. [corrected 13 March 2019]
For methyl 3-(anilinosulfonyl)propanoate’:
read methyl 3-(anilinosulfonyl)propanoate
Page 851, P-66.1.1.4.3, example 5. [corrected 13 March 2019]
For (1) N-(cyclohexylmethanesulfonyl)glycine
read N-(cyclohexylmethanesulfonyl)glycine
for (1-cyclohexyllmethanesulfonamido)acetic acid
read (1) (1-cyclohexyllmethanesulfonamido)acetic acid
Page 851, P-66.1.1.4.3, example 6. [corrected 13 March 2019]
For (1) N-cyclopropyl-N-(methanesufonyl)glycine
read N-cyclopropyl-N-(methanesufonyl)glycine
For (N-cyclopropylmethanesufonamido)acetic acid
read (1) (N-cyclopropylmethanesufonamido)acetic acid
Page 854, P-66.1.2.1. [corrected 6 December 2023]
For P-66.1.2.1 Amides having...
read Amides having...
Page 856, P-66.1.4, line 2. [corrected 13 March 2019]
For ...modifying retained names are no longer recommended.
read ...modifying retained names, are no longer recommended for preferred names.
Page 856, P-66.1.4.1.1, examples 3-5. (corrected 4 December 2019)
For (preferred suffix)
read (preselected suffix)
Page 857, P-66.1.4.2, line 2. [corrected 12 December 2018]
For ...of appropriate prefixes to names described in P-66.1.4.1.1
read ...of appropriate prefixes to names described in P-65.1.7.2.3.
Page 861, P-66.1.6.1.1.3, box lines 3/4. [corrected 13 March 2019]
For ...preferred IUPAC names and for general nomenclature.
read ...preferred IUPAC names.
Page 862, P-66.1.6.1.1.3, example 1 on this page. [corrected 13 March 2019]
For [(not 2-(3-methylureido)naphthalene-1-carboxylic acid]
read [not 2-(3-methylureido)naphthalene-1-carboxylic acid]
Page 862, P-66.1.6.1.1.4.
For P-66.1.6.1.1 4
read P-66.1.6.1.1.4
Page 863, P-66.1.6.1.1.5, example 2. [corrected 22 April 2020]
For H2N-CO-NH-CH2-CH2-CH2-HN-CHO
read H2N-CO-NH-CH2-CH2-CH2-NH-CHO
Page 863, P-66.1.6.1.2, title. [corrected 22 April 2020]
For P-66.1.6.1.2 Isourea
read P-66.1.6.1.2 Isourea and its derivatives
Page 863, P-66.1.6.1.2.1, example 1.
For ethyl N′ - methyl-N,N-diphenylcarbamimidate (PIN)
read ethyl N′-methyl-N,N-diphenylcarbamimidate (PIN) [delete spaces from name]
P-867, P-66.1.6.2, example 1. [corrected 22 April 2020]
For ( propan-2-yl)carbononitridic amide
read (propan-2-yl)carbononitridic amide [remove space before propan]
Page 867, P-66.1.6.3, line 1. [corrected 1 July 2020]
For ...amides of the polycarbonic acids...
read ...amides of polycarbonic acids...
Page 868, P-66.1.7, line 4. [corrected 12 December 2018]
For ...for acids, for which see P-65.1.2.3 and P-65.3.4.
read ...for acids, for which see P-65.1.2.3 and P-65.1.2.4.
Page 870, P-66.3.1.1, structure 3 and 4. [corrected 1 July 2020]
For (preferred suffix)
read (preselected suffix)
Page 872, P-66.3.1.2.1, example 1. [corrected 12 December 2018]
For hydrazinecarbonitirile (see P-66.5.1.1.2)
read hydrazinecarbonitirile (see P-66.5.1.1.3)
Page 872, P-66.3.1.2.1, last example. [corrected 21 November 2018]
For ethanimidohydrazide
read ethanimidohydrazide (PIN)
Page 872, P-66.3.1.2.1, example 2. [corrected 12 December 2018]
For (not hydrazinecarbaldehyde; see P-66.6.1.4)
read (not hydrazinecarbaldehyde; see P-66.6.1.3)
Page 873, P-66.3.1.2.4, line 2. [corrected 12 December 2018]
For ...discussed in P-102.5.6.6.2.1 and P-103.2.6, respectively.
read ...discussed in P-102.5.6.6.2.1 and P-103.2.7, respectively.
Page 874, P-66.3.2, line 1. [corrected 14 November 2018]
For ...are of two types; CO-NH-NH2, –SO2-NH-NH2, etc.; ...
read ...are of two types; –CO-NH-NH2, –SO2NH-NH2, etc.; ...
Page 874, P-66.3.2.1, line 2. [corrected 13 March 2019]
For ...except when the –CO-NH-NH2 group is not at the end of a carbon chain.
read ...except when the –CO-NH-NH2 group is at the end of a carbon chain.
Page 874, P-66.3.2.1, example 3. [corrected 22 April 2020]
For hydrazinesulfonic acid (PIN)
read hydrazinesulfonic acid (preselected name)
Page 874, P-66.3.2.1, example 4. [corrected 22 April 2020]
For (1) hydrazinesulfonic acid (preferred prefix,
read (1) hydrazinesulfonic acid (preselected prefix,
Page 874, P-66.3.2.1, example 5. [corrected 22 April 2020]
For hydrazinesulfinic acid (PIN)
read hydrazinesulfinic acid (preselected name)
Page 874, P-66.3.2.1, example 6. [corrected 22 April 2020]
For (1) hydrazinesulfinic acid (preferred prefix,
read (1) hydrazinesulfinic acid (preselected prefix,
Page 875, P-66.3.2.2, title. [corrected 14 November 2018]
For P 66.3.2.2 ...
read P-66.3.2.2 ...
Page 875, P-66.3.2.2. [corrected 22 April 2020]
For Examples:
read Example:
Page 876, P-66.3.2.3, example at top of this page. [corrected 1 July 2020]
For (2) (2-acetyl-2-ethylhydrazin-1-yl)benzene-1-sulfonic acid
read (2) 4-(2-acetyl-2-ethylhydrazin-1-yl)benzene-1-sulfonic acid
Page 875, P-66.3.2.2, example 2. [corrected 22 April 2020]
Move to end of P-66.3.2.1.
Page 876, P-66.3.2.3, line 1 on this page. [corrected 9 January 2019]
For The groups R-CO-N(NH2)–, -SO2N(NH2)–, etc. are named ...
read The groups R-CO-N(NH2)–, R-SO2N(NH2)–, etc. are named ...
Page 876, P-66.3.3.1, line 3. [corrected 14 November 2018]
For ... The locants ‘1′‘and ‘2′’ have been ...
read ... The locants ‘1′’ and ‘2′’ have been ...
Page 876, P-66.3.3.2, lines 4/5. [corrected 12 December 2018]
For ...(see also P-62.2.1.2.2).
read ...(see also P-62.2.4.1.2).
Page 877, P-66.3.3.2, example 1, last line of the sentences in the parentheses. [corrected 13 March 2019]
For ... is lower than N′, N4)
read ... is lower than N′1, N4)
Page 878, P-66.3.4, line 3. [corrected 10 February 2021]
For ...as described in P-33.2.2 and Table 4.4)
read ...as described in P-33.2.2 and Table 4.4.
Page 878, P-66.3.5, title. [corrected 1 July 2020]
For ...cyanic, and di- and the polycarbonic acids...
read ...cyanic, and di- and polycarbonic acids...
Page 878, P-66.3.5.1, line 1. [corrected 13 March 2019]
For ...hydrazides derived from carbonic and cyanic are chosen...
read ...hydrazides derived from carbonic and cyanic acids are chosen...
Page 878, P-66.3.5.2, line 3. [corrected 13 March 2019]
For ...by the numerical locant ‘di’ to...
read ...by the numerical prefix ‘di’ to...
Page 880, P-66.4.1, line 6. [corrected 1 July 2020]
For ...carbonic, and di- and the polycarbonic acids...
read ...carbonic, and di- and polycarbonic acids...
Page 881, P-66.4.1.1, structure 4 on this page. [corrected 13 March 2019]
For -selenonimidamide (preselected suffix)
read -seleninimidamide (preselected suffix)
Page 883, P-66.4.1.2, title. [corrected 11 November 2020]
For P-66.4.1.2 Amidines of carbonic, and the di- and polycarbonic acids
read P-66.4.1.2 Amidines of carbonic, and di- and polycarbonic acids
Page 883, P-66.4.1.2.1.2, example 1.
For N,N,N′,N′ -tetramethyl-N′′-phenylguanidine (PIN)
read N,N,N′,N′-tetramethyl-N′′-phenylguanidine (PIN) [delete space from name]
Page 883, P-66.4.1.2.1.2, example 2.
For N,N,N′ -trimethylcarbonimidic diamide
read N,N,N′-trimethylcarbonimidic diamide [delete space from name]
Page 883, P-66.4.1.2.1.2, example 3.
For N, N′-dimethylguanidine (PIN)
read N,N′-dimethylguanidine (PIN) [delete space from name]
for (not N, N′′-dimethylguanidine)
read (not N,N′′-dimethylguanidine) [delete space from name]
for N, N′-dimethylcarbonimidic diamide
read N,N′-dimethylcarbonimidic diamide [delete space from name]
Page 884, P-66.4.1.2.1.3, line 1. [corrected 1 July 2020]
For ...P-66.4.1.2.1.3 In presence of a characteristic
read ...P-66.4.1.2.1.3 In the presence of a characteristic
Page 884, P-66.4.1.2.1.3, lines 1/2. [corrected 12 December 2018]
For ...seniority over guanidine (see P-41.2), ...
read ...seniority over guanidine (see item 11 in P-41), ...
Page 884, P-66.4.1.2.1.3, line 2. [corrected 23 December 2020]
For The prefix guanidino is no longer recommended.
read The prefix guanidino may be used in general nomenclature.
Page 884, P-66.4.1.2.1.3, box. [corrected 23 December 2020]
Delete the box and its contents.
Page 884, P-66.4.1.2.1.3, structure 1. [corrected 23 December 2020]
For (not guanidino)
read guanidino
Page 884, P-66.4.1.2.1.3, example 2. [corrected 6 July 2018]
For 4-[(diaminomethylidene)amino]butanoic acid( PIN)
read 4-[(diaminomethylidene)amino]butanoic acid (PIN)
Page 884, P-66.4.1.2.1.3, example 3. [corrected 6 July 2018]
For 4-[methyl(N-methyl-N-phenylcarbamimidoyl)amino]benzoic acid(PIN)
read 4-[methyl(N-methyl-N-phenylcarbamimidoyl)amino]benzoic acid (PIN) [add space after acid]
for 4-(N,N′ -dimethyl-N′-phenylcarbamimidamido)benzoic acid
read 4-(N,N′-dimethyl-N′-phenylcarbamimidamido)benzoic acid [remove space from name]
Page 885, P-66.4.1.3.1, box, lines 2/3. [corrected 13 March 2019]
For ...preferred IUPAC names and in general nomenclature.
read ...preferred IUPAC names.
Page 886, P-66.4.1.3.1, example on this page. [corrected 22 April 2020]
For 4-[(dimethylamino)(ethylimino) methyl]benzoic acid
read 4-[(dimethylamino)(ethylimino)methyl]benzoic acid [delete space in name]
Page 886, P-66.4.1.3.4, three prefixes. [corrected 1 July 2020]
For (preferred prefix)
read (preselected prefix)
Page 887, P-66.4.1.4.1, box, line 3. [corrected 9 January 2019]
For ...were used in the in the 1979 recommendations (ref. 1).
read ...were used in the 1979 recommendations (ref. 1).
Page 890, P-66.4.1.6, line 3. [corrected 13 March 2019]
For ...formula R-C(=NR′)-N(R)-C′′(=NR′′′)-R′′′ ′. Preferred...
read ...formula R-C(=NR′)-N(R′′)-C(=NR′′′)-R′′′ ′. Preferred...
Page 891, P-66.4.2.1, example 3 on this page.
For N,N-dimethyl- N′-isopropylideneformohydrazonamide
read N,N-dimethyl-N′-isopropylideneformohydrazonamide [delete space from name]
Page 891, P-66.4.2.1, last example on this page.
Page 892, P-66.4.2.2, line 2. [corrected 1 July 2020]
Page 893, P-66.4.2.3.1, example 1. [corrected 25 November 2020]
Page 893, P-66.4.2.3.1, example 2. [corrected 25 November 2020]
Page 897, P-66.4.3.1, example 3 on this page. [modified 22 April 2020]
Page 897, P-66.4.3.2, line 1. [corrected 12 December 2018]
Page 898, P-66.4.3.3, Example. [corrected 22 April 2020]
Page 898, P-66.4.3.3, example 1. [modified 3 March 2021]
Page 898, P-66.4.3.3, example 2. [corrected 13 March 2019]
Page 899, P-66.4.4, Example. [corrected 22 April 2020]
Page 899, P-66.5, lines 5/6. [corrected 1 July 2020]
Page 900, P-66.5.1.1.1, example 1.
Page 901, P-66.5.1.1.3, example 2.
Page 903, P-66.5.1.2.4, line 2. [corrected 12 December 2018]
Page 903, P-66.5.1.2.4, example 2. [corrected 12 December 2018]
Page 903, P-66.5.1.3.1, example 3. [corrected 19 September 2018]
Page 904, P-66.5.2, line 5. [corrected 12 December 2018]
Page 905, P-66.5.3, title. [modified 1 July 2020]
Page 905, P-66.5.3.1, line 1. [corrected 1 July 2020]
Page 905, P-66.5.4.1 (3). [corrected 12 December 2018]
Page 905, P-66.5.4.1, example 1.
Page 906, P-66.6. [corrected 28 November 2018] for P-66.6.2 Aldehydes from oxalic acid and the polycarbonic acids for P-66.6.5Acetals and ketals, hemiacetals and hemiketals, and their chalcogen analogues
Page 907, P-66.6.1.1.2, line 2.
Page 908, P-66.6.1.2.3, example 1.
Page 908, P-66.6.1.3, example 1. [corrected 13 March 2019]
Page 909, P-66.6.2, title. [corrected 16 August 2016]
Page 910, P-66.6.4, line 1. [corrected 1 July 2020]
Page 910, P-66.6.4, line 3/4. [corrected 12 December 2018]
Page 911, P-66.6.4, example 1. [corrected 13 March 2019]
Page 913, P-66.6.5.1.2, example 1 on this page. [corrected 13 March 2019]
Page 914, P-66.6.5.3, example 1 on this page. [corrected 13 March 2019]
Page 915, P-67, line 4. [corrected 16 August 2016]
Page 916, P-67.1, line 8 on this page. [corrected 22 April 2020]
Page 916, P-67.1, lines 9/10 on this page. [corrected 22 April 2020]
Page 916, P-67.1.1.1, example 6. [corrected 21 November 2018]
Page 918, P-67.1.1.2 example 2. [corrected 22 April 2020]
Page 919, P-67.1.2, lines 5/6. [corrected 22 April 2020]
Page 919, P-67.1.2, lines 7/8. [corrected 22 April 2020]
Page 919, P-67.1.2.1, line 1. [corrected 1 July 2020]
Page 921, P-67.1.2.3, example. [corrected 1 July 2020]
Page 922, P-67.1.2.3.2 (2). [corrected 20 March 2019]
Page 922, P-67.1.2.3.2, (2). [corrected 25 November 2020]
Page 922, P-67.1.2.3.3, example (3). [corrected 22 April 2020]
Page 922, P-67.1.2.3.4 (2). [corrected 20 March 2019]
Page 922, P-67.1.2.3.4, (2). [corrected 25 November 2020]
Page 923, P-67.1.2.4, title. [corrected 22 April 2020]
Page 923, P-67.1.2.4.1.1, example 3. [corrected 21 November 2018] .
Page 924, P-67.1.2.4.1.1, example 1 on this page.
Page 924, P-67.1.2.4.1.1, example 2 on this page. [corrected 1 July 2020]
Page 927, P-67.1.2.6, line 3. [corrected 16 August 2016]
Page 928, P-67.1.2.6.1, example 1. [corrected 1 July 2020]
Page 928, P-67.1.2.6.1, example 3. [corrected 1 July 2020]
Page 928, P-67.1.2.6.1, example 7.
Page 928, P-67.1.2.6.1, example 9. [corrected 1 July 2020]
Page 929, P-67.1.2.6.2, line 1. [corrected 16 August 2016]
Page 931, P-67.1.3.1, last example. [corrected 1 July 2020]
Page 931, P-67.1.3.2, line 4. [corrected 22 April 2020]
Page 931, P-67.1.3.2, line 7. [corrected 16 August 2016]
Page 931, P-67.1.3.2 example 7. [corrected 22 April 2020]
Page 932, P-67.1.3.2, last example on this page.
Page 933, P-67.1.3.3, line 9. [corrected 1 July 2020]
Page 934, P-67.1.4, title. [corrected 11 December 2019]
Page 934, P-67.1.4, line 3. [corrected 22 April 2020]
Page 934, P-676.1.4, lines 5/6. [corrected 22 April 2020]
Page 935, P-67.1.4.1.1.2, title, lines 1/2. [corrected 16 August 2016]
Page 935, P-67.1.4.1.1.2, line 1. [corrected 16 August 2016]
Page 935, P-67.1.4.1.1.2, lines 7/8. [corrected 16 August 2016]
Page 936, P-67.1.4.1.1.3, title, line 2. [corrected 16 August 2016]
Page 936, P-67.1.4.1.1.3, lines 2/3. [corrected 16 August 2016]
Page 936, P-67.1.4.1.1.3, Examples, line 1. [corrected 16 August 2016]
Page 937, P-67.1.4.1.1.4, line 3/4. [corrected 12 December 2018]
Page 937, P-67.1.4.1.1.4, Examples, line 1. [corrected 16 August 2016]
Page 938, P-67.1.4.1.1.4, example 12 on this page. [corrected 20 March 2019]
Page 938, P-67.1.4.1.1.5, line 1/2. [corrected 9 January 2019]
Page 939, P-67.1.4.1.1.5, example 2. [corrected 16 August 2016]
Page 939, P-67.1.4.1.1.5, example 9. [corrected 16 August 2016]
Page 940, P-67.1.4.1.1.6, example 11. [corrected 1 July 2020]
Page 940, P-67.1.4.1.1.6, example 12. [corrected 1 July 2020]
Page 941, P-67.1.4.1.2. [corrected 22 April 2020]
Page 943, P-67.1.4.3.2, line 3. [corrected 21 November 2018]
Page 943, P-67.1.4.3.3, example 1. [corrected 21 November 2018]
Page 943, P-67.1.4.3.3, example 2. [corrected 21 November 2018]
Page 943, P-67.1.4.3.3, example 3. [corrected 21 November 2018]
Page 945, P-67.1.4.4.2, line 5. [corrected 20 March 2019]
Page 946, P-67.1.5, title. [corrected 22 April 2020]
Page 948, P-67.1.6, line 2 on this page. [corrected 16 August 2016]
Page 948, P-67.2, title. [corrected 22 April 2020]
Page 948, P-67.2, line 17. [corrected 22 April 2020]
Page 948, P-67.2, line 18. [corrected 22 April 2020]
Page 948, P-67.2, line 19. [corrected 22 April 2020]
Page 949, P-67.2, line 1 on this page. [corrected 22 April 2020]
Page 949, P-67.2, line 2 on this page. [corrected 22 April 2020]
Page 949, P-67.2.1, line 4. [corrected 6 December 2023]
Page 950, P-67.2.1, example 16 on this page. [corrected 22 April 2020]
Page 950, P-67.2.1, example 17 on this page. [corrected 22 April 2020]
Page 951, P-67.2.2.1, line 7/8. [corrected 12 December 2018]
Page 952, P-67.2.2.2, second box, line 1. [corrected 6 July 2018]
Page 952, P-67.2.2.2, second box, lines 2/3. [corrected 6 July 2018]
Page 952, P-67.2.2.2, example 2. [corrected 6 July 2018]
Page 953, P-67.2.2.2, example 1 on this page. [corrected 9 January 2019]
Page 954, P-67.2.2.2, example 1 on this page. [modified 1 July 2020]
Page 955, P-67.2.3, example 1. [corrected 22 April 2020]
Page 955, P-67.2.4, line 7. [corrected 6 July 2018]
Page 956, P-67.2.4, example 4 on this page. [corrected 24 October 2018]
Page 958, P-67.2.5, contents. [corrected 28 November 2018] for P-67.2.2.5.2 Esters for P-67.2.2.5.3 Anhydrides
Page 958, P-67.2.5.1.1, line 3. [corrected 9 January 2019]
Page 960, P-67.2.5.3, title. [corrected 28 November 2018]
Page 960, P-67.2.6, line 1. [corrected 1 July 2020]
Page 960, P-67.2.6, line 7. [corrected 12 December 2018]
Page 962, P-67.3.1, example 2 on this page. [corrected 22 April 2020]
Page 963, P-67.3.2, line 3.
Page 963, P-67.3.2, box, lines 3/4. [corrected 16 August 2016]
Page 964, P-68.0, 3rd paragraph, line 2.
Page 965, P-68.1.1.1, line 1. [corrected 16 August 2016]
Page 967, P-68.1.1.3.1, title. [corrected 1 July 2020]
Page 968, P-68.1.1.3.2, example 7 on this page. [corrected 11 November 2020]
Page 969, P-68.1.1.3.2, example 1 on this page. [corrected 11 November 2020]
Page 969, P-68.1.1.3.2.2 (to be P-68.1.1.3.3), heading. [corrected 16 August 2016]
Page 969, P-68.1.1.3.3 (to be P-68.1.1.3.4), heading. [corrected 16 August 2016]
Page 970, P-68.1.2, example 9. [corrected 1 July 2020]
Page 970, P-68.1.2, example 10. [modified 1 July 2020]
Page 970, P-68.1.2, example 11. [corrected 1 July 2020]
Page 970, P-68.1.2, example 12. [corrected 1 July 2020]
Page 971, P-68.1.3, line. (corrected 4 December 2019)
Page 973, P-68.1.5.1, example 2. [corrected 1 July 2020]
Page 975, P-68.1.5.2.2, lines 1/2. [corrected 1 July 2020]
Page 979, P-68.1.6.1, line 3. [corrected 1 July 2020]
Page 980, P-68.1.6.1, line 1 on this page. [corrected 1 July 2020]
Page 980, P-68.1.6.2 (formerly P-68.1.6.1.1), paragraph 1, line 3. [corrected 16 August 2016]
Page 980, P-68.1.6.2 (formerly P-68.1.6.1.1), title. [corrected 22 April 2020]
Page 980, P-68.1.6.2 (formerly P-68.1.6.1.1), paragraph 2, line 3. [corrected 16 August 2016]
Page 982, P-68.1.6.1.2, title. [corrected 22 April 2020]
Page 982, P-68.1.6.3 (formerly P-68.1.6.1.2), line 3. [corrected 22 April 2020]
Page 984, P-68.2, heading. [corrected 16 August 2016]
Page 990, P-68.2.6, line 3. [corrected 22 April 2020]
Page 990, P-68.2.6.1, example 1. [corrected 16 August 2016]
Page 992, P-68.2.6.2, example 3 on this page. [corrected 21 November 2018]
Page 992, P-68.3, line 15.
Page 993, P-68.3.1, line 4. [corrected 22 April 2020]
Page 993, P-68.3.1.0, line 3/4. [corrected 20 March 2019]
Page 993, P-68.3.1.1, lines 1/3.
Page 994, P-68.3.1.1.1.1, example 1 on this page. [corrected 16 August 2016]
Page 994, P-68.3.1.1.1.1, example 2 on this page. [corrected 16 August 2016]
Page 994, P-68.3.1.1.1.1, example 5 on this page. [corrected 24 February 2021]
Page 1001, P-68.3.1.2.3.3, line 1. [corrected 1 July 2020]
Page 1001, P-68.3.1.2.4, line 5. [corrected 14 November 2018]
Page 1003, P-68.3.1.2.5, line 1 on this page. [corrected 22 April 2020]
Page 1005, P-68.3.1.3.1, lines 2/3. [corrected 16 August 2016]
Page 1007, P-68.3.1.3.2.2, last example on this page. [corrected 14 November 2018]
Page 1008, P-68.3.1.3.2.3, (1). [corrected 22 April 2020]
Page 1008, P-68.3.1.3.2.3, (2). [corrected 22 April 2020]
Page 1012, P-68.3.1.3.5.1, line 4. [corrected 16 August 2016]
Page 1014, P-68.3.1.3.5.2, example on this page. [modified 1 July 2020]
Page 1015, P-68.3.1.4.1, line 2. [corrected 20 March 2019]
Page 1016, P-68.3.1.4.2, line 3. [corrected 20 March 2019]
Page 1020, P-68.3.2.3.2.2, example 2. [corrected 1 July 2020]
For (arsinomethyl)diphenylphosphane
Page 1021, P-68.3.2.3.2.2, example 2 on this page. [corrected 16 August 2016]
Page 1024, P-68.4, heading. [corrected 16 August 2016]
Page 1026, P-68.4.1.3, line 2. [corrected 1 July 2020]
Page 1026, P-68.4.2, title. [corrected 22 April 2020]
Page 1026, P-68.4.2.1, line 1. [corrected 20 March 2019]
Page 1027, P-68.4.2.2, line 1. [corrected 20 March 2019]
Page 1027, P-68.4.2.2, example 10. [corrected 1 July 2020]
Page 1028, P-68.4.2.4, example 2. [corrected 20 March 2019]
Page 1028, P-68.4.2.4, example 3. [corrected 20 March 2019]
Page 1029, P-68.4.2.4, example 5 on this page. [corrected 1 July 2020]
Page 1029, P-68.4.3, line 16. [corrected 1 July 2020]
Page 1032, P-68.4.3.6, title. [corrected 22 April 2020]
Page 1033, P-68.5, heading. [corrected 16 August 2016]
Page 1033, P-68.5, contents. [corrected 19 September 2018]
Page 1035, P-68.5.3, example 1. [corrected 9 January 2019]
Page 1035, P-69.0, line 10. [corrected 22 April 2020]
Page 1035, P-69.0, line 11. [corrected 22 April 2020]
Page 1035, P-69.0, 5th paragraph, line 4 . [corrected 20 March 2019]
Page 1036, P-69.1, line 3. [corrected 20 March 2019]
Page 1036, P-69.2.2, last line on this page. [corrected 19 September 2018]
Page 1037, P-69.2.2, 3rd paragraph, line 2. [corrected 9 January 2019]
Page 1039, P-69.2.4, example 2. [corrected 9 October 2024]
Page 1040, P-69.2.5, line 1. (corrected 4 December 2019)
Page 1040, P-69.2.5, line 5. [corrected 1 July 2020]
Page 1040, P-69.2.6, line 6. [corrected 13 January 2021]
Page 1041, P-69.2.7, line 6. [corrected 1 July 2020]
Page 1046, P-69.5, line 2. [corrected 1 July 2020]
Page 1047, P-69.5.3, line 4. [corrected 22 April 2020]
Page 1049, Table 7.1. [corrected 14 November 2018]
Page 1050, P-70.3.3.2.2, line 1. [corrected 8 July 2020]
Page 1050, P-70.4 (3), line 3. [corrected 8 July 2020]
Page 1051, P-71, line 3. [corrected 8 July 2020]
Page 1051, P-71.1, line 7. [corrected 8 July 2020]
Page 1051, P-71, contents. [corrected 28 November 2018]
Page 1052, P-71.2.1.2, line 1 on this page. [corrected 8 July 2020]
Page 1052, P=71.2.1.2, line 5 on this page. [modified 11 November 2020]
Page 1052, P-71.2.1.2, example 9. [corrected 11 November 2020]
Page 1052, P-71.2.1.2, example 10. [corrected 17 June 2020]
Page 1053, P-71.2.2.1, lines 1/2. [corrected 11 November 2020]
Page 1055, P-71.2.3, example 5.
Page 1056, P-71.2.6, title.
Page 1057, P-71.2.6, example 3.
Page 1057, P-71.2.6, last example.
Page 1058, P-71.3.1, box, line 2.
Page 1058, P-71.3.1 example 3. [corrected 17 June 2020]
Page 1059, Table 7.2. [corrected 14 November 2018]
Page 1059, P-71.3.2, example 2. [corrected 17 June 2020]
Page 1060, P-71.3.3, line 1. [corrected 8 July 2020]
Page 1061, P-71.3.4, 2nd paragraph, line 1. [corrected 27 March 2019]
Page 1061, P-71.3.4, 2nd paragraph, line 3.
Page 1062, P-71.4, lines 2-3. [corrected 19 December 2018]
Page 1062, P-71.4, line 5. [corrected 11 December 2019]
Page 1063, P-71.5, 2nd paragraph, line 2/3. [corrected 9 January 2019]
Page 1064, P-71.7 (a), line 1. [corrected 21 April 2021]
Page 1064, P-71.7 (b), line 1. [corrected 21 April 2021]
Page 1064, P-71.7 (b) example. [corrected 21 April 2021]
Page 1064, P-71.7 (c), line 1. [corrected 21 April 2021]
Page 1064, P-71.7 (c), line 2. [corrected 27 March 2019]
Page 1064, P-71.7 (c) example. [corrected 21 April 2021]
Page 1065, P-71.7 (d), lines 1/2. [corrected 21 April 2021]
Page 1065, P-71.7 (d) (2) example. [corrected 21 April 2021]
Page 1065, P-72, line 4. [corrected 8 July 2020]
Page 1066, P-72.2.1, line 4.
Page 1067, P-72.2.1, example 2 on this page. [corrected 17 June 2020]
Page 1067, P-72.2.2.1, example 6. [corrected 17 June 2020]
Page 1067, P-72.2.2.1.1, title.
Page 1068, P-72.2.2.1.1, example 4.
Page 1069, P-72. 2.2.2 (1) (c), line 2. [corrected 14 November 2018]
Page 1071, P-72.2.2.2.2, line 3. [corrected 11 November 2020]
Page 1071, P-72.2.2.2.2, line 13. [corrected 8 July 2020]
Page 1072, P-72. 2.2.2.3, line 4. [corrected 14 November 2018]
Page 1074, P-72.3, line 2. [corrected 14 November 2018]
Page 1074, P-72.3 (1), line 2. [corrected 27 March 2019]
Page 1074, P-72.3, (2) line 4. [corrected 9 January 2019]
Page 1074, P-72.3, box lines 1/2. [corrected 9 January 2019]
Page 1074, P-72.3, example 1.
Page 1074, P-72.3, line 1. [corrected 8 July 2020]
Page 1075, P-72.3, example 2 on this page. replace structure with:
Page 1075, P-72.3, example 6 on this page.
Page 1075, P-72.3, example 7 on this page.
Page 1076, P-72.4, 2nd paragraph, line 1. [corrected 19 September 2018]
Page 1080, P-72.7 (c), example.
Page 1080, P-72.7 (a), lines 1-2.. [corrected 21 April 2021]
Page 1080, P-72.7 (a), example. [corrected 7 November 2018]
Page 1080, P-72.7 (a) example. [corrected 21 April 2021]
Page 1080, P-72.7 (b), line 1. [corrected 21 April 2021]
Page 1080, P-72.7 (b), example. [modified 17 June 2020]
Page 1080, P-72.7 (c), line 1. [corrected 21 April 2021]
Page 1080, P-72.7 (c) example. [corrected 21 April 2021]
Page 1081, P-72.7 (d), line 2. [corrected 27 March 2019]
Page 1081, P-72.7 (d), box line 1. [corrected 27 March 2019]
Page 1081, P-72.7 (d), box line 3. [corrected 3 March 2021]
Page 1081, P-72.7 (d) example. [corrected 21 April 2021]
Page 1081, P-72.7 (e) example 2. [corrected 21 April 2021]
Page 1082, P-73.0, contents. [corrected 28 November 2018] for P-73.3 Cationic compounds with cationic centers having nonstandard valence states
Page 1082, P-73.1, title. [modified 17 June 2020]
Page 1083, P-73.1.1.1, Table 7.3, title. [corrected 7 August 2019]
Page 1086, P-73.1.2.1 (2), line 2. [corrected 9 April 2025]
Page 1090, P-73.2.2.1.2, line 7.
Page 1091, P-73.2.2.1.2, example 5 on this page. [corrected 17 June 2020]
Page 1091, P-73.2.2.2, title.
Page 1097, Table 7.5, example 2.
Page 1097, Table 7.5, structure 3.
Page 1098, P-73.4, line 8.
Page 1098, P-73.4, line 13.
Page 1100, P-73.4, example 1 on this page. [corrected 19 December 2018]
Page 1105, P-73.6, example 2. [corrected 9 October 2024]
Page 1106, P-73.7, line 1. [corrected 17 June 2020]
Page 1106, P-73.7 (formerly (P-73.7.1), (a) lines 1/2. [corrected 21 April 2021]
Page 1106, P73.7 (a), example. [corrected 21 April 2021]
Page 1106, P-73.7 (b), line 1. [corrected 21 April 2021]
Page 1106, P-73.7.1 (b), line 2. [corrected 19 September 2018]
Page 1106, P-73.7 (b), example. [corrected 21 April 2021]
Page 1106, P-73.7.1 (c), line 2. [corrected 27 March 2019]
Page 1106, P-73.7.1 (c), box line 1. [corrected 27 March 2019]
Page 1106, P-73.7 (c), example 1. [corrected 21 April 2021]
Page 1106, P-73.7 (c), example 2. [corrected 21 April 2021]
Page 1106, P-73.7 (c) (formerly P-73.7.1), box line 3. [corrected 3 March 2021]
Page 1107, P-73.7 (d), lines 2/3. [corrected 21 April 2021]
Page 1107, P-73.7 (d) example 1. [corrected 21 April 2021]
Page 1107, P-73.7 (d) example 2. [corrected 21 April 2021]
Page 1107, P-73.8.1, line 1.
Page 1110, P-74.1.1, Note on this page. [corrected 10 February 2021]
Page 1112, P-74.2.1.1, line 1/2 on this page. [corrected 27 March 2019] for ..if ‘X’ is second, third, etc. row element...
Page 1112, P-74.2.1.1, line 3 on this page. [corrected 8 July 2020]
Page 1113, P-74.2.1.2, line 1. [corrected 8 July 2020]
Page 1113, P-74.2.1.1.4, line 1. [corrected 27 March 2019]
Page 1114, P-74.2.1.5, example. [corrected 27 March 2019] for (1) triphenylphosphane-N-ethylimide
Page 1116, P-74.2.2.1.4, line 1. [corrected 11 November 2020]
Page 1117, P-74.2.2.1.8, line 1. [corrected 8 July 2020]
Page 1118, P-74. 2.2.1.9, line 3. [corrected 9 January 2019]
Page 1119, P-74.2.2.2.1.2, line 2. [corrected 19 December 2018]
Page 1119, P-74.2.2.2.1.3, heading.
Page 1119, P-74.2.2.2.2 (1). [corrected 19 December 2018]
Page 1119, P-74.2.2.2.3 (1). [corrected 27 March 2019]
Page 1120, P-74.2.2.3.1. line 4. [corrected 19 December 2018]
Page 1122, P-75, line 2. [corrected 17 June 2020]
Page 1122, P-75.1 (1) note, line 4. [corrected 8 July 2020]
Page 1123, P-75.2.1, example 1. [corrected 21 November 2018] for azanidyl
Page 1124, P-75.2.2, example 1 on this page. [corrected 21 November 2018]
Page 1124, P-75.2.4, line 3. [corrected 19 December 2018]
Page 1125, P-75.3.1 line 2. [corrected 21 November 2018]
Page 1127, P-76.1. [corrected 17 June 2020]
Page 1127, P-77.1.2, example. [corrected 17 June 2020]
Page 1128, P-77.1.3, example. [corrected 16 August 2016]
for (b) bis(N,N-dimethyl-1,3-thiazolidin-2-amine) sulfate
Page 1128, P-77.2.1, line 8. [corrected 13 January 2021]
Page 1129, P-77.3.1, line 2. [corrected 19 December 2018]
Page 1130, P-81.2, line 2.
Page 1131, P-81.2, line 2 on this page. [corrected 17 June 2020]
Page 1134, P-82.2.2, line 1/2 in the box. [corrected 3 April 2019]
Page 1134, P-82.2.2.2, line 4. [corrected 20 November 2024]
Page 1137, P-82.2.4, example 2 on this page. [corrected 3 April 2019]
Page 1137, P-82.2.5. line 4. [corrected 13 January 2021]
Page 1138, P-82.4, (2) line 2.
Page 1139, P-82.4.2, example 1. (corrected 4 December 2019)
Page 1139, P-82.4.2, last example on this page. [corrected 3 April 2019]
Page 1141, P-82.6.1.1, example 3. [corrected 17 June 2020]
Page 1142, P-82.6.1.3 (formerly P-82.6.1.4), example. [corrected 17 June 2020]
Page 1142, P-82.6.1.4, example. [corrected 17 June 2020]
Page 1143, P-82.6.3.1, example 2. [modified 23 December 2020]
for L-(guanidino-14C,N′-15N)arginine (see Rule H-4.2.1, ref. 1)
Page 1143, P-82.6.3.1, example 3. [corrected 8 July 2020]
Page 1144, P-82.6.3.2, example 1 on this page. [corrected 19 December 2018]
Page 1144, P-82.6.4, example 5. [corrected 21 November 2018]
Page 1144, P-82.6.4, example 6. [corrected 9 January 2019]
Page 1145, P-83.1.1, example 3, right version. [corrected 3 April 2019]
Page 1147, P-83.1.2.2, example 3. [corrected 8 July 2020]
Page 1148, P-83.1.2.2, example 4 on this page. [corrected 9 January 2019]
Page 1149, P-83.2.1.1, examples, column 1 heading. [corrected 3 April 2019]
Page 1150, P-83.2.1.2, line 8. [corrected 8 July 2020]
Page 1152, P-83.2.2, example 2 on this page. [corrected 3 April 2019]
Page 1152, P-83.2.2, example 3 on this page. [corrected 3 April 2019]
Page 1153, P-83.5.1, example 1. [corrected 21 November 2018]
Page 1154, P-83.5.2, line 2. [corrected 19 September 2018]
Page 1154, P-83.5.2, example 1. [corrected 21 November 2018]
Page 1155, P-84, example 1. [corrected 21 November 2018]
Page 1155, P-84, example 4. [corrected 21 November 2018]
Page 1155, P-84, example 6.
Page 1155, P-84, example 7. [corrected 21 November 2018]
Page 1156, P-9, contents. [corrected 28 November 2018]
Page 1158, P-91.2.1.2, title. [corrected 9 January 2019]
Page 1158, P-91.2.1.2, line 4. [corrected 2 September 2020]
Page 1158, P-91.2.1.2.1, title. [corrected 2 September 2020]
Page 1158, P-91.2.1.2.1, (a) (i), lines 3/4. [corrected 2 September 2020]
Page 1159, P-91.2.1.2.1 (a) (ii), line 1. [corrected 2 January 2019]
Page 1159. P-91.2.1.2.1, (c), line 1. [corrected 2 September 2020]
Page 1159, P-91.2.1.2.1 (c) (v), line 3. [corrected 10 April 2019]
Pages 1159-60, P-91.2.1.2.1, last paragraph. [corrected 2 September 2020]
Page 1160, P-91.2.1.2.1, lines 4/5 . [corrected 2 January 2019]
Page 1160, P-91.2.2, line 9. [corrected 2 September 2020]
Page 1160, P-91.2.2, line 13. (corrected 4 December 2019)
Page 1160, P-91.3, line 7. [corrected 2 September 2020]
Page 1160, P-91.3, 1st paragraph, last line. [corrected 10 April 2019]
Page 1161, P-91.3, example 1 on this page. (corrected 4 December 2019)
Page 1162, P-91.3, example on this page note.
Page 1163, P-92.1.1. (b), line 3. [corrected 10 October 2018]
Page 1164, P-92.1.1 (d), example 1 on this page. (corrected 4 December 2019)
Page 1164, P-92.1.1 (d), example 1. [corrected 2 September 2020]
Page 1168, P-92.1.3, line 1. [corrected 2 January 2019]
Page 1169, P-92.1.3.4 (b) (i). [modified 2 September 2020]
Page 1169, P-92.1.3.4 (b) (ii). [corrected 2 September 2020]
Page 1170, P-92.1.4.1, example 1. [corrected 7 November 2018]
Page 1174, P-92.1.4.4, structure at top of page. [corrected 10 October 2018]
Page 1175, P-92.1.5 (a), line 3. [corrected 2 September 2020]
Page 1175, P-92.1.5, Figure [corrected 2 September 2020]
Page 1179, P-92.2.1.1.3, example 1. [corrected 2 January 2019]
Page 1180, P-92.2.1.1.3, Example 1, Explanation, line 9. [corrected 14 November 2018]
Page 1180, P-92.2.1.1.3, Explanation, paragraph, 2 lines 2/3. [corrected 30 September 2020]
Page 1180, P-92.2.1.1.3, Explanation, paragraph 2, line 5 on this page. [corrected 21 October 2020]
Page 1183, P-92.2.1.2, Example 3, explanation, line 2. [corrected 2 September 2020]
Page 1183, P-92.2.1.2, example 3, Explanation, line 3. [corrected 7 November 2018]
Page 1183, P-92.2.1.2, example 4, Explanation, line 3. [corrected 7 November 2018]
Page 1184, P-92.2.1.3, example 1, explanation, line 5. [corrected 30 September 2020]
Page 1185, P-92.2.1.3, example 4, Explanation, line 5. [corrected 2 January 2019]
Page 1186, P-92.2.2, line 6. [corrected 14 November 2018]
Page 1186, P-92.2.2, line 6. [corrected 30 September 2020]
Page 1188, P-92.3, example 1. [modified 2 September 2020]
Page 1189, P-92.4.1, heading. [corrected 7 November 2018]
Page 1190, P-92.4.1, line 1 on this page. [corrected 2 January 2019]
Page 1191, P-92.4.2.2, line 4. [corrected 2 January 2019]
Page 1192, P-92.4.2.2, Example 1 Explanation line 9. [corrected 6 July 2018]
Page 1195, P-92.5.1, example, under image 1 on this page. [corrected 2 September 2020]
Page 1195, P-92.5.1, example, under image 2 on this page. [corrected 2 September 2020]
Page 1195, P-92.5.1, example, under image 3 on this page. [corrected 2 September 2020]
Page 1195, P-92.5.1, example, final paragraph. [corrected 2 September 2020]
Page 1195, P-92.5.2 (ii). [corrected 2 September 2020]
Page 1195, P-92.5.2.1, lines 3/4. [corrected 21 October 2020]
Page 1195, P-92.5.2.1, line 4. [corrected 2 September 2020]
Page 1196, P-92.5.2.1 (ii), paragraph under simplified digraph, lines 4/5. [corrected 21 October 2020]
Page 1196, P-92.5.2.1 (ii), paragraph under simplified digraph, line 21. [corrected 21 October 2020]
Page 1196, P-92.5.2.1 (ii), line 4. [corrected 30 September 2020]
Page 1196, P-92.5.2.1 (ii), lines 9-12. [corrected 10 April 2019]
Page 1196, P-92.5.2.1, line 18, under digraph. [corrected 30 September 2020]
Page 1196, P-92.5.2.2, line 2.
Page 1197, P-92.5.2.2, Explanation lines 1/2.
Page 1200, P-92.5.2.2, Example 4, last line. [corrected 2 September 2020]
Page 1201, P-92.5.2.2, Example 4, Explanation, lines 4/5. [corrected 21 October 2020]
Page 1201, P-92.5.2.2, Example 4, Explanation, lines 6/7. [corrected 21 October 2020]
Page 1203, P-92.5.2.2, example 5, Explanation, 1st paragraph, last line. [corrected 3 October 2018]
Page 1203, P-92.5.2.2, example 5, Explanation, 3rd paragraph, line 4. [corrected 19 September 2018]
Page 1204, P-92.5.2.2, Example 6, explanation, line 1. [corrected 30 September 2020]
Page 1204, P-92.5.3. [corrected 30 September 2020]
Page 1205, P-92.5.3, line 1 on this page. [corrected 30 September 2020]
Page 1205, P-92.6, line 6. [corrected 10 April 2019]
Page 1206, P-92.6, Example 2. Line 4 of explanation.
Page 1207, P-92.6. example 5, Explanation, line 1. [corrected 10 April 2019]
Page 1212, P-93.1.2.2, line 2. [corrected 10 April 2019]
Page 1213, P-93.1.3, example 1 on this page. [corrected 16 August 2016]
Page 1213, P-93.1.4, example. [corrected 2 September 2020]
Page 1213, P-93.1.4, example. (corrected 4 December 2019) for 2-ambo-(2R)-2,5,7,8-tetramethyl-2[(4R,8R)-4,8,12-trimentltridecyl]-3,4-dihydro-2H-1-benzopyran-6-ol (PIN)
Page 1213, P-93.2, contents line 2. [corrected 30 September 2020]
Page 1213, P-93.2, contents.
Page 1213, P-93.2, contents, line 5. [corrected 2 September 2020]
Page 1214, P-93.2.1, line 1. [corrected 21 October 2020]
Page 1214, P-93.2.2, example 1. [corrected 3 March 2021]
Page 1214, P-93.2.2, example 2. [corrected 3 March 2021]
Page 1215, P-93.2.3, example 1. [corrected 10 June 2021]
Page 1216, P-93.2.5, examples. [corrected 2 September 2020]
Page 1218, P-93.3.2, line 2. [corrected 19 September 2018]
Page 1221, P-93.3.3.2, example 1. [corrected 7 November 2018]
Page 1222, P-93.3.3.4, line1. [corrected 30 September 2020]
Page 1222, P-93.3.3.5.1, line 1. [corrected 2 September 2020]
Page 1223, P-93.3.3.5.2, line 3. [corrected 19 December 2018]
Page 1225, P-93.3.3.7, line 1.
Page 1226, P-93.3.3.7, example. [corrected 2 September 2020]
Page 1230, P-93.3.4.2.2, line 1. [corrected 21 October 2020]
Page 1230, P-93.3.4.2.2, line 2. [corrected 21 October 2020]
Page 1230, P-93.3.4.2.2, line 3. [corrected 10 April 2019]
Page 1231, P-93.4.1.1, line 5. [corrected 10 April 2019]
Page 1231, P-93.4.1.1, line 5. [modified 7 August 2019]
Page 1232, P-93.4.1.2, line 6. [corrected 19 December 2018]
Page 1233, P-93.4.1.2, example 2 on this page. [corrected 2 September 2020]
Page 1233, P-93.4.1.2, example 3 on this page. [corrected 2 September 2020]
Page 1234, P-93.4.1.3, step 3. [corrected 2 September 2020]
Page 1235, P-93.4.2, line 4. [corrected 30 September 2020]
Page 1236, P-93.4.2.1.2, line 4. [corrected 2 January 2019]
Page 1237, P-93.4.2.1.3, lines 5/6. [corrected 10 April 2019]
Page 1238, P-93.4.2.2, line 7. [corrected 2 January 2019]
Page 1238, P-93.4.2.2, example 1. [corrected 30 September 2020]
Page 1239, P-93.4.2.3, line 6. [corrected 2 January 2019]
Page 1241, P-93.5.1.1.1, example 2. [corrected 30 September 2020]
Page 1243, P-93.5.1.1.2 (b) lines 3/4. [corrected 30 September 2020]
Page 1245, P-93.5.1.2, line 3 on this page. [corrected 2 September 2020]
Page 1246, P-93.5.1.3.1, last line. [corrected 19 September 2018]
Page 1247, P-93.5.1.3.2, lines 3/4. [corrected 30 September 2020]
Page 1247, P-93.5.1.3.2, example 3, Explanation, line 4. [corrected 19 December 2018]
Page 1248, P-93.5.1.4, contents. [corrected 28 November 2018] for P-93.5.4.2 Specification of exo-cyclic double bonds
Page 1248, P-93.5.1.4.1, lines 2-4. [corrected 30 September 2020]
Page 1248, P-93.5.1.4.1, example 2. [corrected 2 September 2020]
Page 1248, P-93.5.1.4.1, example 5. [corrected 30 September 2020]
Page 1249, P-93.5.1.4.1, line 1 on this page. [corrected 2 January 2019]
Page 1249, P-93.5.1.4.2.1 (1) (b), lines 4/5. [modified 30 September 2020]
Page 1249, P-93.5.1.4.2.1 (1), example 2. [corrected 10 April 2019]
Page 1250, P-93.5.1.4.2.1 (2), lines 6-8. [corrected 2 September 2020]
Page 1250, P-93.5.1.4.2.1 (2), Example 1. [modified 2 September 2020]
Page 1251, P-93.5.1.4.2.1 (2), Example 3. [corrected 2 September 2020]
Page 1252, P-93.5.1.4.2.2, Example 4. Retain printed PIN. [corrected 30 September 2020]
Page 1252, P-93.5.2, line 3.
Page 1253, P-93.5.1.4.2.2, Example 4, second explanation. [corrected 11 November 2020]
Page 1253, P-93.5.1.4.2.2, example 4, explanation, lines 8/9. [corrected 2 September 2020]
Page 1253, P-93.5.1.4.2.2, example 4. [modified 11 November 2020]
Page 1255, P-93.5.2.2, line 2. [corrected 19 December 2018]
Page 1256, P-93.5.2.2.1, example 4.
Page 1258, P-93.5.2.3, line 1 on this page. [corrected 10 April 2019]
Page 1258, P-93.5.2.3, line 4 on this page. [corrected 30 September 2020]
Page 1259, P-93.5.3, line 2. [corrected 2 September 2020]
Page 1259, P-93.5.3, line 7. [corrected 26 June 2019]
Page 1261, P-93.5.3.2, Example 1.
Page 1263, P-93.5.3.2, Example 5, explanation. [corrected 2 September 2020]
Page 1263, P-93.5.3.3, example 1,
Page 1265, P-93.5.3.5, example 1, third digraph. [corrected 2 September 2020]
Page 1269, P-93.5.5, line 2. [corrected 21 October 2020]
Page 1269, P-93.5.5.1, line 2. [corrected 11 November 2020]
Page 1270, P-93.5.5.1, example 1. [corrected 2 September 2020]
Page 1270, P-93.5.5.1, example 3 on this page.
Page 1271, P-93.5.5.2, title. [corrected 21 October 2020]
Page 1272, P-93.5.6.1, Fig. 9.2, first ellipse. [corrected 2 September 2020]
Page 1273, P-93.5.6.1, Fig. 9.2, oblong on this page. [corrected 2 September 2020]
Page 1273, P-93.5.6.2, line 1.
Page 1273, P-93.5.6.2, line 14. [corrected 10 April 2019]
Page 1273, P-93.5.6.2, lines 15/16. [corrected 10 April 2019]
Page 1273, P-93.5.6.2, line17. [corrected 19 December 2018]
Page 1274, P-93.5.6.2, example I. [corrected 2 September 2020]
Page 1275, P-93.5.6.4, line 2. [corrected 27 November 2019]
Page 1275, P-93.5.6.4, line 2. [corrected 19 September 2018]
Page 1275, P-93.5.6.4, line 8. [corrected 2 September 2020]
Page 1275, P-93.5.6.4, lines 4/5. [corrected 19 December 2018]
Page 1277, P-93.5.6.5, explanation (b), line 2. [corrected 30 September 2020]
Page 1278, P-93.5.6.6, example. [corrected 21 November 2018]
Page 1278, P-93.5.6.6, example, Explanation line 5. [corrected 21 November 2018]
Page 1278, P-93.5.7, contents. [corrected 28 November 2018]
Page 1280, P-93.5.7.2, line 3. [corrected 19 December 2018]
Page 1282, P-93.5.7.3, line 2.
Page 1286, P-94, title. [corrected 28 November 2018]
Page 1287, P-94.2.1, criteria. [corrected 2 January 2019] for (b) if one of a set... for (c) if all of a set...
Page 1289, P-94.3.1.1, line 1.
Page 1289, P-94.3.1.1, line 5. [corrected 9 January 2019]
Page 1294, P-100 (b), line 2/3. [corrected 19 December 2018]
Page 1294, P-100 (b), line 4. [corrected 19 December 2018]
Page 1295, P-101.2.0, line 5. [corrected 23 September 2020]
Page 1296, P-101.2.2.6, line 1. [modified 26 June 2019]
Page 1298, P-101.2.6, line 2. [corrected 21 October 2020]
Page 1299, P-101.2.6.1.1, line 1. [corrected 21 October 2020]
Page 1299, P-101.2.6.1.1, line 1. [corrected 17 April 2019]
Page 1299, P-101.2.6.1.1, line 7. [corrected 21 October 2020]
Page 1299, P-101.2.6.1.1, second paragraph, line 1. [corrected 21 October 2020]
Page 1300, P-101.2.6.1.3, line 4. [corrected 21 October 2020]
Page 1301, Table 10.1 (a) alkaloids. [corrected 19 September 2018]
Page 1301, Table 10.1 (a) alkaloids. [corrected 9 January 2019] for 18-oxayohimban read oxyacanthan
Page 1302, Table 10.1 (d) Miscellanous. [corrected 9 January 2019] for porphyrin read prostane
Page 1302, P-101.3. [corrected 28 November 2018]
Page 1302, P-101.3, line 2. [corrected 23 September 2020]
Page 1302, P-101.3, line 3. [corrected 23 September 2020]
Page 1302, P-101.3, line 7. [corrected 23 September 2020]
Page 1304, P-101.3.1.1, example 1 on this page.
Page 1306, P-101.3.2.2.1, structure 3. [corrected 23 September 2020]
Page 1307, P-101.3.2.2.3, line 5. [corrected 19 December 2018]
Page 1308, P-101.3.3, line 2 on this page. [corrected 23 September 2020]
Page 1311, P-101.3.4.2, line 9. [corrected 23 September 2020]
Page 1311, P-101.3.4.1, examples. [corrected 23 September 2020]
Page 1312, P-101.3.5.1, line 7. [corrected 19 December 2018]
Page 1315, P-101.3.7.1, structure (II). [corrected 23 September 2020]
Page 1315, P-101.3.7.1, structure 4 on this page. [modified 11 November 2020]
Page 1316, P-101.3.7.2, line 4. [corrected 17 April 2019]
Page 1316, P-101.3.7.2, line 5. [corrected 23 September 2020]
Page 1316, P-101.3.7.2, structure 2. [corrected 21 October 2020]
Page 1316, P-101.3.7.2, structure 3. [corrected 7 November 2018]
Page 1317, P-101.4.1, lines 1/2. [corrected 19 December 2018]
Page 1317, P-101.4.1, lines 6-7.
Page 1325, P-101.5.2, example 2 on this page. [corrected 17 April 2019]
Page 1325, P-101.5.2, last line on this page. [corrected 19 December 2018]
Page 1327, P-101.6, lines 3/4. [corrected 19 December 2018]
Page 1327, P-101.6.1, line 3. [corrected 17 April 2019]
Page 1328, P-101.6.2, line 5. [corrected 13 January 2021]
Page 1330, P-101.6.4, line 6. [corrected 13 January 2021]
Page 1333, P-101.7.1.1.2, lines 3/4. [corrected 23 September 2020]
Page 1338, P-101.7.3, line 5. [corrected 13 January 2021]
Page 1338, P-101.7.4, line 3. (corrected 4 December 2019)
Page 1341, P-101.8.1, line 6. [corrected 19 December 2018]
Page 1342, P-101.8.4, line 5. [corrected 13 January 2021]
Page 1344, P-102.0, line 5. [corrected 19 December 2018]
Page 1348, P-102.2.1, Table 10.3, title. [modified 21 October 2020]
Page 1369, P-102.5.6.2.1, line 3. [corrected 19 December 2018]
Page 1377, P-102.5.6.6.2.2, lines 1/2. [corrected 19 December 2018]
Page 1379, P-102.5.6.6.3.2, example. [corrected 21 November 2018]
Page 1342, P-101.8.2, lines 3/4. [corrected 21 October 2020]
Page 1342, P-101.8.3, line 5. [corrected 14 November 2018]
Page 1342, P-101.8.4, line 2. [corrected 21 October 2020]
Page 1344, P-102.1.2, line 2.
Page 1345, P102.1.2.1, line 4. [corrected 11 November 2020]
Page 1348, P-102.2.1, Table 10.3, Title.
Page 1349, P-102.3.1, line 7.
Page 1350, P-102.3.4, line 3.
Page 1352, P-102.3.4.2.1, lines 2/3. [corrected 19 September 2018]
Page 1352, P-102.3.4.1.2, lines 4/5. [corrected 23 September 2020]
Page 1355, P-102.3.7.2, example. [corrected 23 September 2020]
Page 1356, P-102.4 (f), example. [corrected 17 April 2019]
Page 1357, P-102.5.1.1.2, line 1. [corrected 21 October 2020]
Page 1357, P-102.5.1.1.2, line 3. [corrected 23 September 2020]
Page 1357, P-102.5.1.1.2, lines 5/6. [corrected 21 October 2020]
Page 1357, P-102.5.1.1.2, example. [corrected 23 September 2020]
Page 1357, P-102.5.1.1.2, example. for D-gluco- D-glycero-heptose
Page 1357, P-102.5.1.1.3, lines 1/2. [corrected 21 October 2020]
.Page 1357, P-102.5.1.1.4, line 2. [corrected 21 October 2020]
Page 1359, P-102.5.2.3, line 2 on this page. [corrected 21 October 2020]
Page 1362, P-102.5.3.3, line 8-9.
Page 1362, P-102.5.3.4, example 3.
Page 1363, P-102.5.4, title. [corrected 17 April 2019]
Page 1364, P-102.5.4.1.1, example 5.
Page 1365, P-102.5.5, paragraph 2, line 4. [corrected 23 September 2020]
Page 1366, P-102.5.5, example 2 on this page. [corrected 24 October 2018]
Page 1366, P-102.5.6, line 1. [corrected 21 October 2020]
Page 1366, P-102.5.6, line 4. [corrected 21 October 2020]
Page 1366, P-102.5.6, line 6. [corrected 23 September 2020]
Page 1368, P-102.5.6.1.2, example 5.
Page 1369, P-102.5.6.2.1, line 3. [modified 23 September 2020]
Page 1370, P-102.5.6.3, title. [corrected 21 October 2020]
Page 1370, P-102.5.6.3, line 2. [corrected 23 September 2020]
Page 1370, P-102.5.6.3.1, example 2. [corrected 7 November 2018]
Page 1371, P-102.5.6.3.3, line 3. [corrected 17 April 2019]
Page 1372, P-102.5.6.4 (1), line 2. [corrected 21 October 2020]
Page 1373, P-102.5.6.5.1, example 4.
Page 1374, P-102.5.6.5.2, example. [corrected 23 September 2020]
Page 1374, P-102.5.6.5.2, example 2.
Page 1378, P-102.5.6.6.2.2, example 1.
Page 1378, P-102.5.6.6.2.2, example 3.
Page 1380, P-102.5.6.6.4.2, line 1. [corrected 19 September 2018]
Page 1381, P-102.5.6.6.5.1, example 1. [corrected 17 October 2018]
Page 1381, P-102.5.6.6.5.1, example 2. [corrected 17 October 2018]
Page 1381, P-102.5.6.6.5.2, example 1. [corrected 17 October 2018]
Page 1381, P-102.5.6.6.5.2, example 2. [modified 14 November 2018]
Page 1382, P-102.5.6.6.5.3, line 3. [corrected 17 April 2019]
Page 1382, P-102.5.6.6.5.3, example 3.
Page 1382, P-102.5.6.6.5.3, example 4.
Page 1384, P-102.6.1.1.1, example 2. [4 December 2019]
Page 1385, P-102.6.1.2, example 1. [corrected 26 June 2019]
Page 1386, P-102.6.1.2, example 1 on this page, explanation line 2. [corrected 23 September 2020]
Page 1386, P-102.6.1.4, example. [corrected 23 September 2020]
Page 1386, P-102.6.1.4, example.
Page 1387, P-102.6.1.5, examples. [corrected 23 September 2020]
Page 1388, P-102.6.1.6 (to be P-102.6.2), example 3 on this page. [corrected 17 April 2019]
Page 1390, P-102.7.2.2, line 1. [corrected 19 September 2018]
Page 1391, P-103.0, line 8. [corrected 19 December 2018]
Page 1393, P-103.1.1.1, Table 10.4, entry 1 on this page. [corrected 2 January 2019]
Page 1393, P-103.1.1.1, Table 10.4, entry 8 on this page. [corrected 2 January 2019]
Page 1394, P-103.1.1.2, lines 2/3. [corrected 19 December 2018]
Page 1394, P-103.1.1.2, Table 10.5, entry 2. [corrected 2 January 2019]
Page 1394, P-103.1.1.2, Table 10.5, entry 3. [corrected 2 January 2019]
Page 1394, P-103.1.1.2, table 10.5, last entry on this page.
Page 1396, P-103.1.1.3, line 8. [corrected 19 December 2018]
Page 1396, P-103.1.1.3, second paragraph, line 6. [corrected 19 December 2018]
Page 1396, P-103.1.2, lines 9/10
Page 1398, P-103.1.3.1, line 3 on this page. [corrected 17 April 2019]
Page 1398, P-103.1.3.2.1 example 2. for cis-3-hydroxy- L-proline
Page 1398, P-103.1.3.2.1 example 3. for trans-3-hydroxy- L-proline
Page 1399, P-103.2.1, line 4. [corrected 23 September 2020]
Page 1399, P-103.2, line 15. [corrected 28 November 2018]
Page 1399, P-103.2, line 16. [corrected 28 November 2018]
Page 1400, P-103.2.1, example 4. [corrected 17 October 2018]
Page 1401, P-103.2.2.1, lines 1/2. [corrected 21 October 2020]
Substituent groups with the free valence on a carbon atom of an...
Page 1401, P-103.2.2.2, example. [corrected 23 September 2020]
Page 1402, P-103.2.3, example 2. [corrected 19 December 2018]
Page 1403, P-103.2.3, example 1 on this page. [corrected 23 September 2020]
Page 1403, P-103.2.3, example 3 on this page. [corrected 23 September 2020]
Page 1404, P-103.2.4.1, lines 4/5. [corrected 21 October 2020]
Page 1404, P-103.2.4.1, line 5. [corrected 14 November 2018]
Page 1404, P-102.2.4.3.1, example 2. [corrected 23 September 2020]
Page 1404, P-103.2.4.2, line 3. [corrected 17 April 2019]
Page 1405, P-103.2.3.3.2, title. [corrected 28 November 2018]
Page 1405, P-103.2.3.3.2 (changed to P-103.2.4.3.2), line 2.
Page 1405, P-103.2.3.3.2 (changed to P-103.2.4.3.2), line 3. [corrected 17 April 2019]
Page 1405, P-103.2.3.3.2 (changed to P-103.2.4.3.2), line 4. [corrected 14 November 2018]
Page 1405, P-103.2.3.4, title. [corrected 28 November 2018]
Page 1405, P-103.2.3.4 (changed to P-103.2.4.4), example 2. [corrected 19 September 2018]
Page 1405, P-103.2.5, lines 3/4. [corrected 9 January 2019]
Page 1405, P-103.2.5, example 1. [corrected 9 January 2019]
Page 1406, P-103.2.6, examples. [corrected 23 September 2020]
Page 1406, P-103.2.7, title. [corrected 28 November 2018]
Page 1407, P-103.2.7, after example 3.
Page 1407, P-103.2.7 (changed to P-103.2.8), line 1. [corrected 17 April 2019]
Page 1407, P-103.2.7 (changed to P-103.2.8), line 3. [corrected 17 April 2019]
Page 1408, P-103.3, lines 2/3. [corrected 23 September 2020]
Page 1408, P-103.3.1, line 6. [corrected 23 September 2020]
Page 1408, P-103.3.1, line 9-10.
Page 1410, P-103.3.5.1, example 1. [corrected 17 April 2019]
Page 1412, P-103.3.5.2.2, after title. [corrected 23 September 2020]
Page 1414, P-104.1, 2nd paragraph, line 3. [corrected 14 November 2018]
Page 1417, P-104.2.3, example 3. [corrected 21 October 2020]
Page 1418, P-104.3.1, line 7. [corrected 12 August 2020]
Page 1425, P-106, contents. [corrected 19 September 2018]
Page 1425, P-106.0, line 2.
Page 1426, P-106.2, heading. [corrected 19 September 2018]
Page 1427, P-106.3.1, line 4. [corrected 23 September 2020]
Page 1427, P-106.3.1, example 1. [corrected 23 September 2020]
Page 1429, P-106.3.3, lines 3/4. [corrected 19 September 2018]
Page 1433, P-107.3.1, line 1. [corrected 19 September 2018]
Page 1434, P-107.3.4, example 1. [corrected 3 March 2021]
Page 1436, P-107.4.2, line 2. [corrected 19 December 2018]
Page 1437, P-107.4.3.1, example 1 on this page. [corrected 23 September 2020]
Page 1438, P-107.4.3.2, example.
Page 1439, Reference 12, line 2. [corrected 14 November 2018]
Page 1440, reference 16. [corrected 23 September 2020]
Page 1440, reference 17. [corrected 23 September 2020]
Page 1440, reference 18. [corrected 23 September 2020]
Page 1440, reference 23, line 3. [corrected 7 August 2019]
Page 1440, Reference 26, line 2. [corrected 9 January 2019]
Page 1440, Reference 27, line 4. [corrected 6 July 2018]
Page 1440, Reference 28, line 2. (corrected 4 December 2019)
Page 1441, Reference 38. [corrected 24 March 2021]
Page 1441, reference 39. [corrected 23 September 2020]
Page 1441, reference 40. [corrected 23 September 2020]
Page 1441, reference 44. [corrected 23 September 2020]
Page 1441, reference 45. [corrected 23 September 2020]
Page 1441, Reference 46, line 1. [corrected 6 July 2018]
Page 1441, Reference 46, line 4. [corrected 6 July 2018]
Page 1441, reference 47. [corrected 23 September 2020]
Page 1442, reference 48. [corrected 23 September 2020]
Page 1445, appendix 2, lines 5/6. [corrected 10 February 2021]
Page 1446, appendix 2, below line 2. [added 8.12.2023]
Page 1446, appendix 2, below line 3 of printed book. [modified 8.11.2023]
Page 1446, appendix 2, line 11. [corrected 6 July 2018]
Page 1446, appendix 2, line 12. [corrected 6 July 2018]
Page 1446, appendix 2, after line 14. [corrected 6 July 2018]
Page 1446, appendix 2, column 3, line 8. [corrected 6 July 2018]
Page 1446, appendix 2, below line 21. [corrected 6 July 2018]
Page 1446, appendix 2, after line 23. [corrected 25 November 2020]
Page 1446, appendix 2, line 27. [corrected 25 November 2020]
Page 1446, appendix 2, column 3, line 7. [corrected 25 November 2020]
Page 1446, appendix 2, column 3, line 8. [modified 24 March 2021]
Page 1446, appendix 2, column 3, line 9. [corrected 25 November 2020]
Page 1447, appendix 2, lines 1/2. [corrected 25 November 2020]
Page 1447, appendix 2, below line 12. [corrected 6 July 2018]
Page 1447, appendix 2, lines 15/16. [corrected 25 November 2020]
Page 1447, appendix 2, line 19. [corrected 23 December 2020]
Page 1447, appendix 2, lines 22/23. [corrected 25 November 2020]
Page 1447, appendix 2, line 24. [corrected 6 July 2018]
Page 1447, appendix 2, lines 25/26. [corrected 25 November 2020]
Page 1447, appendix 2, column 3, line 2. [corrected 10 February 2021]
Page 1448, appendix 2, columns 1 and 2, line 2. [corrected 7 November 2018]
for H2N-S-CH=N–
Page 1448, appendix 2, line 8. [corrected 6 July 2018]
Page 1448, appendix 2, column 3, line 13. [corrected 24 March 2021]
Page 1448, appendix 2, after line 21, share structure and reference with the previous entry. [corrected 25 November 2020]
Page 1449, appendix 2, line 3. [corrected 6 July 2018]
Page 1449, appendix 2, below line 7. [corrected 6 July 2018]
Page 1449, appendix 2, line 25. [modified 25 November 2020]
Page 1449, appendix 2, column 3, line 10. [corrected 6 July 2018]
Page 1450, appendix 2, line 1. [modified 10 February 2021]
add in column 3 P-35.2.1; P-62.3.1.2
Page 1450, appendix 2, lines 18/19. [modified 3 March 2021]
Page 1450, appendix 2, column 3, line 4. [corrected 25 November 2020]
Page 1450, appendix 2, column 3, line 5. [corrected 25 November 2020]
Page 1450, appendix 2, column 3, line 7. [corrected 26 December 2018]
Page 1450, appendix 2, column 3, line 9. [corrected 2 December 2020]
Page 1450. appendix 2, column 3, line 13. [modified 30 December 2020]
Page 1451, appendix 2, line 19. [corrected 25 November 2020]
Page 1451, appendix 2, after line 22. [corrected 25 November 2020]
Page 1451, appendix 2, column 3, line 6. [corrected 24 April 2019]
Page 1451, appendix 2, column 3, line 7. [modified 30 December 2020]
Page 1452, appendix 2, line 3. [modified 24 March 2021]
Page 1452, appendix 2, line 5.
Page 1452, appendix 2, line 9. [corrected 10 February 2021]
Page 1452, appendix 2, line 11. [corrected 10 February 2021]
Page 1452, appendix 2, line 14. [corrected 10 February 2021]
Page 1452, appendix 2, column 3, line 14. [modified 30 December 2020]
Page 1453, appendix 2, line 7. [corrected 6 July 2018]
Page 1453, appendix 2, below line 15. [corrected 6 July 2018]
Page 1453, appendix 2, line 19. [modified 25 November 2020]
Page 1453, appendix 2, line 23. [corrected 6 July 2018]
Page 1453, appendix 2, line 24. [corrected 6 July 2018]
Page 1454, appendix 2, line 18. [corrected 24 April 2019]
Page 1454, appendix 2, lines 25/26. [corrected 24 April 2019]
Page 1454, appendix 2, column 3, line 4. [corrected 2 December 2020]
Page 1454, appendix 2, column 3, line 13. [corrected 10 March 2021]
Page 1454, appendix 2, column 3, line 17. [modified 25 November 2020]
Page 1454, appendix 2, column 3, line 18. [corrected 24 April 2019]
Page 1455, appendix 2, line 6. [corrected 2 December 2020]
Page 1455, appendix 2, lines 11/12. [corrected 25 November 2020]
Page 1455, appendix 2, column 3, line 10. [corrected 10 March 2021]
Page 1455, appendix 2, column 3, line 11. [corrected 10 March 2021]
Page 1456, appendix 2, line 1. [corrected 24 April 2019]
Page 1456, appendix 2, line 9. [modified 20 January 2021]
Page 1456, appendix 2, after line 13. [corrected 2 December 2020]
Page 1456, appendix 2, line 15. [corrected 27 January 2021]
Page 1456, appendix 2, line 22. [corrected 25 November 2020]
Page 1456, appendix 2, lines 23/24. [corrected 27 January 2021]
delete see 2-methylpropan-2-yloxy*
Page 1457, appendix 2, line 10. [corrected 23 December 2020]
Page 1457, appendix 2, line 16. [corrected 23 December 2020]
Page 1457, appendix 2, line 27. [corrected 24 April 2019]
Page 1457, appendix 2, column 3, line 1. [corrected 24 April 2019]
Page 1457, appendix 2, column 3, line 2. [corrected 25 November 2020]
Page 1458, appendix 2, line 9. [corrected 24 April 2019]
Page 1458, appendix 2, line 14. [corrected 24 April 2019]
Page 1458, appendix 2, line 18. [corrected 24 April 2019]
Page 1458, appendix 2, after line 23. [modified 2 December 2020]
Page 1458, appendix 2, line 23. [corrected 24 April 2019]
Page 1458, appendix 2, below line 23. [corrected 24 April 2019]
Page 1458, appendix 2, line 25.
Page 1458, appendix 2, line 28. [corrected 24 April 2019]
Page 1458, appendix 2, lines 29/30. [corrected 24 April 2019]
Page 1458, appendix 2, column 3, line 12. [corrected 25 November 2020]
Page 1459, appendix 2, line 1. [corrected 24 April 2019]
Page 1459, appendix 2, line 10. [corrected 24 April 2019]
Page 1459, appendix 2, line 14. [corrected 25 November 2020]
Page 1459, appendix 2, line 15. [corrected 25 November 2020]
Page 1459, appendix 2, line 16. [corrected 25 November 2020]
Page 1459, appendix 2, column 3, line 2. [corrected 24 April 2019]
Page 1459, appendix 2, column 3, line 8. [corrected 2 December 2020]
Page 1459, appendix 2, column 3, line 9. [corrected 2 December 2020]
Page 1459, appendix 2, column 3, line 10. [corrected 10 February 2021]
Page 1459, appendix 2, column 3, line 16. [corrected 2 December 2020]
Page 1459, appendix 2, column 3, line 17. [corrected 2 December 2020]
Page 1459, appendix 2, column 3, line 18. [corrected 24 April 2019]
Page 1460, appendix 2, line 6. [corrected 25 November 2020]
Page 1460, appendix 2, line 22. [corrected 2 December 2020]
Page 1460, appendix 2, lines 24-26. [corrected 25 November 2020]
Page 1460, appendix 2, lines 27-29. [corrected 25 November 2020]
Page 1460, appendix 2, column 3, line 10. [corrected 25 November 2020]
Page 1460, appendix 2, column 3, line 13. [corrected 10 March 2021]
Page 1460, appendix 2, column 3, line 15. [corrected 1 May 2019]
Page 1461, appendix 2, line 4. [corrected 1 May 2019]
Page 1461, appendix 2, line 10. [corrected 1 May 2019]
Page 1461, appendix 2, after line 11. [modified 2 December 2020]
Page 1461, appendix 2, below line 11. [corrected 1 May 2019]
Page 1461, appendix 2, line 13. [modified 2 December 2020]
Page 1461, appendix 2, line 16. [modified 2 December 2020]
Page 1461, appendix 2, after line 16. [modified 20 January 2021]
Page 1461, appendix 2, after line 16. [corrected 20 January 2021]
Page 1461, appendix 2, line 17. [corrected 1 May 2019]
Page 1461, appendix 2, below line 18. [modified 2 December 2020]
Page 1461, appendix 2, line 20. [corrected 1 May 2019]
Page 1461, appendix 2, line 21. [modified 2 December 2020]
Page 1461, appendix 2, line 22. [corrected 1 May 2019]
Page 1461, appendix 2, line 25. [corrected 1 May 2019]
Page 1461, column 3, line 6. [corrected 2 December 2020]
Page 1462, appendix 2, line 3. [modified 1 May 2019]
Page 1462, appendix 2, line 11. [corrected 2 December 2020]
Page 1462, appendix 2, line 25. [modified 10 February 2021]
Page 1462, appendix 2, column 3, line 5. [corrected 26 December 2018]
Page 1463, appendix 2, line 19. [corrected 2 December 2020]
Page 1463, appendix 2, line 20. [corrected 2 December 2020]
Page 1463, appendix 2, line 21. [corrected 2 December 2020]
Page 1463, appendix 2, line 22. [corrected 2 December 2020]
Page 1463, appendix 2, line 23. [corrected 2 December 2020]
Page 1463, appendix 2, line 24. [corrected 2 December 2020]
Page 1463, appendix 2, below line 26. [corrected 1 May 2019]
Page 1463, appendix 2, column 3, line 1. [modified 2 December 2020]
Page 1463, appendix 2, column 3, line 3. [corrected 10 March 2021]
Page 1463, appendix 2, column 3, line 4. [corrected 10 March 2021]
Page 1463, appendix 2, column 3, line 13. [corrected 1 May 2019]
Page 1463, appendix 2, column 3, line 15. [corrected 1 May 2019]
Page 1463, appendix 2, column 3, line 16. [corrected 1 May 2019]
Page 1463, appendix 2, column 3, line 17. [corrected 1 May 2019]
Page 1463, appendix 2, column 3, line 18. [corrected 1 May 2019]
Page 1463, appendix 2, column 3, line 19. [corrected 1 May 2019]
Page 1463, appendix 2, column 3, line 20. [modified 20 January 2021]
Page 1463, appendix 2, column 3, line 21. [corrected 1 May 2019]
Page 1463, appendix 2, column 3, line 22. [corrected 1 May 2019]
Page 1464, Appendix 2, line 11. [corrected 8 May 2019]
Page 1464, appendix 2, lines 28/29. [corrected 10 February 2021]
Page 1464, appendix 2, lines 30/31. [corrected 10 February 2021]
Page 1464, appendix 2, column 3, line 2. [corrected 2 December 2020]
Page 1464, appendix 2, column 3, line 8. [corrected 26 December 2018]
Page 1465, appendix 2, under line 19. [corrected 2 December 2020]
Page 1465, appendix 2, column 3, line 4. [corrected 2 December 2020]
Page 1465, appendix 2, column 3, line 8. [corrected 10 March 2021]
Page 1465, appendix 2, column 3, line 9. [corrected 10 March 2021]
Page 1465, appendix 2, column 3, line 10. [corrected 10 March 2021]
Page 1465, appendix 2, column 3, line 12. [corrected 26 December 2018]
Page 1465, appendix 2, column 3, line 13. [corrected 2 December 2020]
Page 1466, appendix 2, after line 5. [corrected 2 December 2020]
Page 1466, appendix 2, line 16. [corrected 10 March 2021]
Page 1466, appendix 2, under line 19. [corrected 10 March 2021]
Page 1466, appendix 2, line 23. [corrected 8 May 2019]
Page 1466, appendix 2, column 3, line 2. [corrected 10 March 2021]
Page 1466, appendix 2, column 3, line 5. [corrected 2 December 2020]
Page 1466, appendix 2, column 3, line 13. [corrected 2 December 2020]
Page 1468, appendix 2, line 15.
Page 1465, appendix 2, line 20. [corrected 8 May 2019]
Page 1467, appendix 2, line 2. [corrected 8 May 2019]
Page 1467, appendix 2, line 10. [corrected 2 December 2020]
Page 1467, appendix 2, line 13. [corrected 8 May 2019]
Page 1467, appendix 2, line 19. [modified 2 December 2020]
Page 1467, appendix 2, column 2, entry 9. [corrected 10 February 2021]
Page 1468, appendix 2, line 1. [corrected 8 May 2019]
Page 1468, appendix 2, line 2. [corrected 8 May 2019]
Page 1468, appendix 2, line 3. [corrected 8 May 2019]
Page 1468, appendix 2, line 4. [corrected 8 May 2019]
Page 1468, appendix 2, after line 4. [corrected 2 December 2020]
Page 1468, appendix 2, line 5. [modified 2 December 2020]
Page 1468, appendix 2, line 19. [deleted 10 March 2021]
Page 1468, appendix 2, line 29. [corrected 8 May 2019]
Page 1468, appendix 2, column 3, line 1. [corrected 8 May 2019]
Page 1468, appendix 2, column 3, line 2. [corrected 8 May 2019]
Page 1468, appendix 2, column 3, line 3. [corrected 8 May 2019]
Page 1468, appendix 2, column 3, line 4. [corrected 8 May 2019]
Page 1468, appendix 2, column 3, line 11. [corrected 20 January 2021]
Page 1469, appendix 2, line 27. [corrected 27 January 2021]
Page 1469, appendix 2, line 30. [corrected 15 May 2019]
Page 1469, appendix 2, column 3, line 11. [corrected 15 May 2019]
Page 1469, appendix 2, column 3, line 22. [corrected 26 December 2018]
Page 1470, appendix 2, lines 5/6. [corrected 15 May 2019]
Page 1470, appendix 2, line 7. [modified 20 January 2021]
Page 1470, appendix 2, line 11. [correction deleted 27 January 2021]
Page 1470, appendix 2, line 20. [corrected 15 May 2019]
Page 1470, appendix 2, below line 24. [modified 20 January 2021]
Page 1470, appendix 2, column 2, structure 8. [corrected 15 May 2019]
Page 1470, appendix 2, column 3, line 1. [corrected 26 December 2018]
Page 1470, appendix 2, column 3, line 19. [corrected 20 January 2021]
Page 1470, appendix 2, column 3, line 20. [corrected 20 January 2021]
Page 1471, appendix 2, line 12. [corrected 10 March 2021]
Page 1471, appendix 2, line 14. [corrected 10 March 2021]
Page 1471, appendix 2, column 3, line 5. [corrected 26 December 2018]
Page 1471, appendix 2, column 3, line 7. [corrected 15 May 2019]
Page 1471, appendix 2, column 3, line 8. [corrected 15 May 2019]
Page 1471, appendix 2, column 3, line 12. [corrected 10 March 2021]
Page 1471, appendix 2, column 3, line 13. [corrected 15 May 2019]
Page 1471, appendix 2, column 3, line 14. [corrected 24 March 2021]
Page 1472, appendix 2, column 3, line 1. [corrected 26 December 2018]
Page 1472, appendix 2, column 3, line 2. [corrected 15 May 2019]
Page 1472, appendix 2, column 3, line 3. [corrected 24 March 2021]
Page 1472, appendix 2, column 3, line 4. [corrected 15 May 2019]
Page 1473, appendix 2, line 6. [corrected 23 December 2020]
Page 1473, appendix 2, structure 16.
Page 1473, appendix 2, structure 17.
Page 1473, appendix 2, column 3, line 3. [corrected 15 May 2019]
Page 1473, appendix 2, column 2, line 12, heptanylidene*. [corrected 9 October 2024]
Page 1473, appendix 2, column 3, line 14. [corrected 2 December 2020]
Page 1474, appendix 2, below line 16. [modified 3 March 2021]
Page 1474, Appendix 2, addition after line 16. (modified 27 November 2019)
Page 1474, appendix 2, column 3 line 10. [corrected 20 January 2021]
Page 1475, appendix 2, after line 11. [corrected 9 December 2020]
Page 1475, appendix 2, line 16. [corrected 9 December 2020]
Page 1475, appendix 2, lines 18/19. (corrected 27 November 2019)
Page 1475, appendix 2, below line 19. [corrected 15 May 2019]
Page 1475, appendix 2, line 27. [corrected 9 December 2020]
Page 1475, appendix 2, column 3, line 7. [modified 20 January 2021]
Page 1476, appendix 2, below line 11. [corrected 22 May 2019]
Page 1476, appendix 2, below line 13. [corrected 22 May 2019]
Page 1476, appendix 2, below line 14. [corrected 22 May 2019]
Page 1476, appendix 2, line 15. [corrected 10 February 2021]
Page 1476, appendix 2, line 21. [modified 9 December 2020]
Page 1476, appendix 2, column 3, line 1. [corrected 10 March 2021]
Page 1476, appendix 2, column 3, lines 9, 10, 14, and 16. [corrected 26 December 2018]
Page 1476, appendix 2, column 3, line 9.. [modified 9 December 2020]
Page 1476, appendix 2, column 3, line 10. [modify 9 December 2020]
Page 1476, appendix 2, column 3, line 14. [modify 9 December 2020]
Page 1476, appendix 2, column 3, line 16. [modified 16 December 2020]
Page 1477, appendix 2, below line 1. [corrected 22 May 2019]
Page 1477, appendix 2, below line 1. [corrected 10 March 2021]
Page 1477, appendix 2, line 4.
Page 1477, appendix 2, lines 10/11. [modified 24 February 2021]
Page 1477, appendix 2, lines 12/13. [modified 24 February 2021]
Page 1477, appendix 2, lines 23/24. [corrected 22 May 2019]
Page 1477, Appendix 2, addition after line 27. (modified 27 November 2019)
Page 1477, Appendix 2, column 3, line 13. (modified 27 November 2019)
Page 1478, appendix 2, line 13. [corrected 10 March 2021]
Page 1478, appendix 2, line 23. [corrected 22 May 2019]
Page 1478, appendix 2, line 24. [corrected 22 May 2019]
Page 1478, appendix 2, lines 30/31. [corrected 22 May 2019]
Page 1478, appendix 2, column 3, line 5. [corrected 26 December 2018]
Page 1478, appendix 2, column 3, line 7. [corrected 9 December 2020]
Page 1479, appendix 2, line 2. [modify 9 December 2020]
Page 1479, appendix 2, line 3. [corrected 22 May 2019]
Page 1479, appendix 2, line 5. [corrected 9 December 2020]
Page 1479, appendix 2, below line 5. [modify 9 December 2020]
Page 1479, appendix 2, line 29.
Page 1479, appendix 2, column 3, line 3. [corrected 9 December 2020]
Page 1479, appendix 2, column 3, line 4. [corrected 10 February 2021]
Page 1479, appendix 2, column 3, line 5. (corrected 4 December 2019)
Page 1480, appendix 2, lines 3/4. [corrected 22 May 2019]
Page 1480, appendix 2, line 11. [corrected 22 May 2019]
Page 1480, appendix 2, column 3, line 7. [corrected 9 December 2020]
Page 1480, column 3, line 8. [modified 24 March 2021]
Page 1480, appendix 2, column 3, line 11.[corrected 26 December 2018]
Page 1480, appendix 2, column 1, line 19 [corrected 9 October 2024]
Page 1481, appendix 2, line 6. [corrected 9 December 2020]
Page 1481, appendix 2, lines 19-21. [corrected 22 May 2019]
Page 1481, appendix 2, column 2, structure 6. [corrected 22 May 2019]
Page 1481, appendix 2, column 3, line 1. [corrected 26 December 2018]
Page 1481, appendix 2, column 3, line 2. [corrected 10 March 2021]
Page 1481, appendix 2, column 3, line 4. [corrected 10 March 2021]
Page 1481, appendix 2, column 3, line 5. [corrected 10 March 2021]
Page 1482, appendix 2, lines 3-5. [corrected 22 May 2019]
Page 1482, appendix 2, line 10. [corrected 22 May 2019]
Page 1482, appendix 2, line 13. [corrected 22 May 2019]
Page 1482, appendix 2, line 14.
Page 1482, appendix 2, line 17. [corrected 22 May 2019]
Page 1482, appendix 2, line 18. [modified 10 March 2021]
Page 1482, appendix 2, lines 19/20. [modified 10 March 2021]
Page 1482, appendix 2, after line 23. [corrected 22 May 2019]
Page 1482, appendix 2, line 26. [corrected 22 May 2019]
Page 1482, appendix 2, column 3, line 11. [corrected 26 December 2018]
Page 1482, appendix 2, column 3, line 17. [corrected 22 May 2019]
Page 1483, appendix 2, line 11. [corrected 22 May 2019]
Page 1483, appendix 2, lines 12-14. [modify 9 December 2020]
Page 1483, appendix 2, line 18. [corrected 9 December 2020]
Page 1483, appendix 2, after line 21. [modify 9 December 2020]
Page 1483, appendix 2, after line 28. [corrected 9 December 2020]
Page 1483, appendix 2, column 2, line 19.
Page 1483, appendix 2, column 2, line 21.
Page 1483, appendix 2, column 3, line 3. [corrected 9 December 2020]
Page 1484, appendix 2, line 2. [corrected 20 January 2021]
Page 1484, appendix 2, line 11. [corrected 29 May 2019]
Page 1484, appendix 2, after line 11. [corrected 29 May 2019]
Page 1484, appendix 2, line 13. [corrected 29 May 2019]
Page 1484, appendix 2, after line 13. [corrected 29 May 2019]
Page 1484, appendix 2, lines 22-23. [corrected 29 May 2019]
Page 1484, appendix 2, column 3, line 3. [corrected 10 February 2021]
Page 1484, appendix 2, column 3, line 6. [corrected 29 May 2019]
Page 1484, appendix 2, column 3, line 18. [corrected 9 December 2020]
Page 1485, appendix 2, after line 2. [corrected 9 December 2020]
Page 1485, appendix 2, line 8. [corrected 9 December 2020]
Page 1485, appendix 2, line 10. [corrected 20 January 2021]
Page 1485, appendix 2, line 14. [corrected 10 February 2021]
Page 1485, appendix 2, line 17. [corrected 10 February 2021]
Page 1485, appendix 2, line 22. [corrected 27 January 2021]
Page 1485, appendix 2, line 23. [modify 9 December 2020]
Page 1485, appendix 2, line 26. [corrected 9 December 2020]
Page 1485, appendix 2, column 3, line 3. [corrected 10 March 2021]
Page 1485, appendix 2, column 3, line 5.
Page 1485, appendix 2, column 3, line 7. [corrected 26 December 2018]
Page 1485, appendix 2, column 3, line 12. [corrected 10 March 2021]
Page 1485, appendix 2, column 3, line 17. [corrected 10 February 2021]
Page 1486, appendix 2, line 8. [corrected 29 May 2019]
Page 1486, appendix 2, line 9. [modified 29 May 2019]
Page 1486, appendix 2, line 14. [modified 10 March 2021]
Page 1486, appendix 2, line 15 move to after line 8. [corrected 29 May 2019]
Page 1486, appendix 2, line 16. [corrected 29 May 2019]
Page 1486, appendix 2, line 17. [corrected 29 May 2019]
Page 1486, appendix 2, line 19.
Page 1486, appendix 2, column 2, structure 5. [corrected 29 May 2019]
Page 1486, appendix 2, column 3, line 2. [modified 10 March 2021]
Page 1486, appendix 2, column 3, line 4. [modified 10 March 2021]
Page 1486, appendix 2, column 3, line 7. [corrected 9 December 2020]
Page 1486, appendix 2, column 3, line 15 (to be moved below line 8). [corrected 9 December 2020]
Page 1486, appendix 2, column 3, line 18. [corrected 9 December 2020]
Page 1486, appendix 2, column 3, line 19. [modify 9 December 2020]
Page 1486, appendix 2, column 3, line 22. [corrected 9 December 2020]
Page 1487, appendix 2, line 9 move to under line 4. [corrected 29 May 2019]
Page 1487, appendix 2, below line 9. [modify 9 December 2020]
Page 1487, appendix 2, lines 14/15 snd move to page 1488, under line 2. [modify 9 December 2020]
Page 1487, appendix 2, column 3, line 2.
Page 1488, appendix 2, line 7. [corrected 16 December 2020]
Page 1488, appendix 2, after line 8. [corrected 20 January 2021]
Page 1488, appendix 2, line 12. [corrected 29 May 2019]
Page 1488, appendix 2, column 3, line 1.
Page 1488, appendix 2, column 3, line 2. [corrected 9 December 2020]
Page 1489, appendix 2, column 3, line 8. [modified 22 January 2020]
Page 1489, appendix 2, column 3, line 9. [corrected 26 December 2018]
Page 1489, appendix 2, column 3, line 10. [corrected 10 March 2021]
Page 1489, appendix 2, column 3, line 19. [corrected 10 March 2021]
Page 1490, appendix 2, lines 1-2. [corrected 29 May 2019]
Page 1490, appendix 2, line 8. [corrected 29 May 2019]
Page 1490, appendix 2, line 9. [corrected 29 May 2019]
Page 1490, appendix 2, lines 15-17. [corrected 29 May 2019]
Page 1490, appendix 2, lines 18-20. [corrected 29 May 2019]
Page 1490, appendix 2, column 2, last line. [corrected 17 October 2018]
Page 1490, appendix 2, column 3, line 2. [corrected 24 March 2021]
Page 1490, appendix 2, column 3, line 17. [corrected 9 December 2020]
Page 1491, appendix 2, lines 19-20. [corrected 29 May 2019]
Page 1491, appendix 2, line 23. [modified 9 December 2020]
Page 1491, appendix 2, column 3, line 2. [corrected 9 December 2020]
Page 1491, appendix 2, column 3, line 7. [corrected 10 March 2021]
Page 1491, appendix 2, column 3, line 10. [corrected 26 December 2018]
Page 1491, appendix 2, column 3, line 13. [corrected 10 March 2021]
Page 1491, appendix 2, column 3, line 14. [corrected 9 December 2020]
Page 1491, appendix 2, column 3, line 17. [modified 30 December 2020]
Page 1492, appendix 2, after line 7. [corrected 29 May 2019]
Page 1492, appendix 2, line 8. [corrected 29 May 2019]
Page 1492, appendix 2, after line 9. [corrected 29 May 2019] add oxo(pyridin-3-yl)methyl = nicotinoyl = pyridine-3-carbonyl* = 3-pyridylcarbonyl 3-C5H4N-CO– P-65.1.7.3.1; P-65.1.7.4.2
add oxo(pyridin-4-yl)methyl = isonicotinyl = pyridine-4-carbonyl* = 4-pyridylcarbonyl 4-C5H4N-CO– P-65.1.7.3.1; P-65.1.7.4.2
Page 1492, appendix 2, line 14. [corrected 29 May 2019]
Page 1492, appendix 2, line 28. [corrected 29 May 2019]
Page 1492, appendix 2, column 2, line 6.
Page 1492, appendix 2, column 3, line 4. [corrected 16 December 2020]
Page 1492, appendix 2, column 3, line 5. [corrected 10 March 2021]
Page 1492, appendix 2, column 3, line 10. [corrected 29 May 2019]
Page 1492, appendix 2, column 3, line 13. [corrected 10 March 2021]
Page 1492, appendix 2, column 3, line 14. [corrected 10 March 2021]
Page 1493, appendix 2, line 2. [corrected 29 May 2019]
Page 1493, appendix 2, lines 14/15. [modified 24 March 2021]
Page 1493, appendix 2, after line 15. [corrected 29 May 2019]
Page 1493, appendix 2, column 3, line 10. [corrected 24 March 2021]
Page 1493, appendix 2, line 18. [modified 27 January 2021]
Page 1494, appendix 2, lines 6-8. [corrected 16 December 2020]
Page 1494, appendix 2, line 9. [modified 16 December 2020]
Page 1494, appendix 2, line 10. [modified 16 December 2020]
Page 1494, appendix 2, line 11. [modified 16 December 2020]
Page 1494, appendix 2, after line 11. [corrected 5 June 2019]
Page 1494, appendix 2, line 12. [modified 30 December 2020]
Page 1494, appendix 2, after line 12. [corrected 16 December 2020]
Page 1495, appendix 2, line 6. [corrected 5 June 2019]
Page 1495, appendix 2, line 7. [corrected 5 June 2019]
Page 1495, appendix 2, line 9. [corrected 16 December 2020]
Page 1495, appendix 2, line 11. [modified 27 January 2021]
Page 1495, appendix 2, after line 11. [corrected 5 June 2019]
Page 1495, appendix 2, line 21. [modified 16 December 2020]
Page 1495, appendix 2, line 25. [modified 10 February 2021]
Page 1495, appendix 2, line 27. [modified 10 February 2021]
Page 1495, appendix 2, column 3, line 9.[corrected 26 December 2018]
Page 1496, appendix 2, line 4. [corrected 5 June 2019]
Page 1496, appendix 2, line 5. [modified 16 December 2020]
Page 1496, appendix 2, line 19. [corrected 5 June 2019]
Page 1496, appendix 2, line 21. [corrected 5 June 2019]
Page 1496, appendix 2, column 3, line 9. [corrected 16 December 2020]
Page 1496, appendix 2, column 3, line 17. [modified 16 December 2020]
Page 1496, appendix 2, column 3, line 18. [modified 16 December 2020]
Page 1497, appendix 2, line 10. [modified 16 December 2020]
Page 1497, appendix 2, lines 12-14. [corrected 16 December 2020]
Page 1497, appendix 2, line 27. [modified 24 March 2021]
Page 1497, appendix 2, lines 18/19. [corrected 5 June 2019]
Page 1497, appendix 2, line 21. [corrected 5 June 2019]
Page 1497, appendix 2, after line 23. [corrected 16 December 2020]
Page 1497, appendix 2, line 27. [corrected 5 June 2019]
Page 1497, appendix 2, column 3, line 2. [corrected 16 December 2020]
Page 1497, appendix 2, column 3, line 3. [corrected 16 December 2020]
Page 1497, appendix 2, column 3, line 8. [corrected 16 December 2020]
Page 1498, appendix 2, after line 4. [corrected 16 December 2020]
Page 1498, appendix 2, line 5. [modified 24 March 2021]
Page 1498, appendix 2, line 16.
Page 1498, appendix 2, line 17.
Page 1498, appendix 2, lines 21/22. [corrected 5 June 2019]
Page 1498, appendix 2, column 3, line 1. [corrected 24 March 2021]
Page 1498, appendix 2, column 3, line 2. [corrected 24 March 2021]
Page 1498, appendix 2, column 3, line 16. [corrected 10 March 2021]
Page 1499, appendix 2, lines 4/5. [corrected 5 June 2019]
Page 1499, appendix 2, line 21. [corrected 5 June 2019]
Page 1499, Appendix 2, lines 22/23. [corrected 5 June 2019]
Page 1499, appendix 2, column 3, line 5. [corrected 5 June 2019]
Page 1499, appendix 2, column 3, line 12. [corrected 26 December 2018]
Page 1500, appendix 2, line 20. [correction deleted 27 January 2021]
Page 1500, appendix 2, below line 21 [corrected 12 June 2019]
Page 1500, appendix 2, line 24. [corrected 27 January 2021]
Page 1500, appendix 2, column 2, structure 14. [corrected 17 October 2018]
Page 1500, appendix 2, column 3, line 1. [modified 20 January 2021]
Page 1500, appendix 2, column 3, line 8. [corrected 12 June 2019]
Page 1500, appendix 2, column 3, line 9. [corrected 12 June 2019]
Page 1500, appendix 2, column 3, line 17. [corrected 16 December 2020]
Page 1501, appendix 2, after line 3. [corrected 16 December 2020]
Page 1501, appendix 2, line 15. [corrected 12 June 2019]
Page 1501, appendix 2, column 3, line 3. [corrected 24 March 2021]
Page 1501, appendix 2, column 3, line 7. [corrected 24 March 2021]
Page 1502, appendix 2, lines 2/3. [corrected 12 June 2019]
Page 1502, appendix 2, below line 3. [corrected 12 June 2019]
Page 1502, appendix 2, below line 16. [corrected 10 March 2021]
Page 1502, appendix 2, below line 23. [corrected 12 June 2019]
Page 1502, appendix 2, line 28.
Page 1502, appendix 2, column 3, line 1. [corrected 16 December 2020]
Page 1502, appendix 2, column 3, line 9. [corrected 12 June 2019]
Page 1502, appendix 2, column 3, line 18. [corrected 12 June 2019]
Page 1503, appendix 3, before line 1. [corrected 10 February 2021]
Page 1503, appendix 2, below line 1. [corrected 12 June 2019]
Page 1503, appendix 2, below line 25. [corrected 12 June 2019]
Page 1503, appendix 2, column 3, line 1. [corrected 16 December 2020]
Page 1504, appendix 2, line 10. [corrected 16 December 2020]
Page 1504, appendix 2, line 14. [corrected 12 June 2019]
Page 1504, appendix 2, under line 17. [corrected 16 December 2020]
Page 1504, appendix 2, line 28. [corrected 10 February 2021]
Page 1504, appendix 2, column 2, structure 13. [corrected 17 October 2018]
Page 1504, appendix 2, column 3, line 2. [corrected 16 December 2020]
Page 1504, appendix 2, column 3, line 3. [corrected 16 December 2020]
Page 1504, appendix 2, column 3, line 8. [corrected 16 December 2020]
Page 1504, appendix 2, column 3, line 10. [corrected 16 December 2020]
Page 1504, appendix 2, column 3, line 13. [corrected 16 December 2020]
Page 1504, appendix 2, column 3, line 18. [corrected 16 December 2020]
Page 1505, appendix 2, after line 2. [corrected 16 December 2020]
Page 1505, appendix 2, column 3, line 3. [corrected 10 March 2021]
Page 1505, appendix 2, line 10. [corrected 12 June 2019]
Page 1505, appendix 2, line 11. [corrected 12 June 2019]
Page 1505, appendix 2, line 12. [corrected 12 June 2019]
Page 1505, appendix 2, below line 14. [corrected 12 June 2019]
Page 1505, appendix 2, column 3, line 4.
Page 1505, appendix 2, column 3, line 6. [corrected 16 December 2020]
Page 1505, appendix 2, column 3, line 7.
Page 1506, appendix 2, lines 1/2. [corrected 12 June 2019]
Page 1506, appendix 2, below line 2. [corrected 12 June 2019]
Page 1506, appendix 2, lines 3/4. [corrected 12 June 2019]
Page 1506, appendix 2, lines 10/11. [corrected 12 June 2019]
Page 1506, appendix 2, below line 27. [corrected 12 June 2019]
Page 1506, appendix 2, column 2, structure 5. [corrected 17 October 2018]
Page 1507, appendix 2, line 6. [corrected 12 June 2019]
Page 1507, appendix 2, lines 27/28. [corrected 12 June 2019]
Page 1507, appendix 2, column 3, line 2. [corrected 12 June 2019]
Page 1507, appendix 2, column 3, line 7. [corrected 12 June 2019]
Page 1507, appendix 2, column 3, line 12. [corrected 10 March 2021]
Page 1507, appendix 2, column 3, line 13. [corrected 10 March 2021]
Page 1507, appendix 2, column 3, line 14. [corrected 20 January 2021]
Page 1507, appendix 2, column 3, line 20. [modified 20 January 2021]
Page 1508, appendix 2, line 8. [modified 20 January 2021]
Page 1508, appendix 2, line 10. [corrected 19 June 2019]
Page 1508, appendix 2, below line 13. [corrected 19 June 2019]
Page 1508, appendix 2, line 18. [corrected 19 June 2019]
Page 1508, appendix 2, below line 24. [corrected 19 June 2019]
Page 1508, appendix 2, below line 27. [corrected 19 June 2019]
Page 1508, appendix 2, column 2, structure 7. [corrected 17 October 2018]
Page 1508, appendix 2, column 3, line 3. [corrected 19 June 2019]
Page 1508, appendix 2, column 3, line 7. [corrected 10 March 2021]
Page 1508, appendix 2, column 3, line 12. [corrected 16 December 2020]
Page 1508, appendix 2, column 3, line 16. [corrected 19 June 2019]
Page 1508, appendix 2, column 3, line 20. [corrected 19 June 2019]
Page 1508, appendix 2, column 3, line 22. [corrected 16 December 2020]
Page 1509, appendix 2, below line 1. [corrected 19 June 2019]
Page 1509, appendix 2, line 4. [corrected 19 June 2019]
Page 1509, appendix 2, lines 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, and 7. [corrected 19 June 2019]
Page 1509, appendix 2, line 9. [corrected 19 June 2019]
Page 1509, appendix 2, line 12. [corrected 10 March 2021]
Page 1509, appendix 2, line 20. [corrected 19 June 2019]
Page 1509, appendix 2, column 2, structure 9. [corrected 17 October 2018]
Page 1509, appendix 2, column 3, line 3. [corrected 16 December 2020]
Page 1509, appendix 2, column 3, line 6. [corrected 24 March 2021]
Page 1510, appendix 2, lines 2/3. [corrected 19 June 2019]
Page 1510, appendix 2, line 13. [modified 16 December 2020]
Page 1510, appendix 2, column 2, line 5. [corrected 10 February 2021]
Page 1510, appendix 2, column 3, line 15. [corrected 16 December 2020]
Page 1510, appendix 2, line 17. [modified 30 December 2020]
Page 1510, appendix 2, line 18. [corrected 16 December 2020]
Page 1510, appendix 2, line 27. [corrected 16 December 2020]
Page 1510, appendix 2, line 27. [corrected 19 June 2019]
Page 1511, appendix 2, lines 1/2. [corrected 19 June 2019]
Page 1511, appendix 2, line 3. [corrected 19 June 2019]
Page 1511, appendix 2, line 5. [modified 20 January 2021]
Page 1511, appendix 2, line 11. [corrected 23 December 2020]
Page 1511, appendix 2, lines 14/15. [corrected 19 June 2019]
Page 1511, appendix 2, line 17. [corrected 23 December 2020]
Page 1511, appendix 2, line18. [modified 23 December 2020]
Page 1511, appendix 2, lines 20/21. [corrected 19 June 2019]
Page 1511, appendix 2, below line 21, [corrected 19 June 2019]
Page 1511, appendix 2, line 23. [corrected 19 June 2019]
Page 1511, appendix 2, columns 2 and 3, line 2. [corrected 17 October 2018] for P-67.1.4.3
Page 1511, appendix 2, column 3, line 6. [corrected 24 March 2021]
Page 1511, appendix 2, column 2, line 9. [corrected 23 December 2020]
Page 1511, appendix 2, column 2, line 12. [modified 10 February 2021]
Page 1511, appendix 2, column 3, line 8. [corrected 23 December 2020]
Page 1511, appendix 2, column 3, line 14. [corrected 19 June 2019]
Page 1512, appendix 2, line 2. [corrected 10 February 2021]
Page 1512, appendix 2, line 4. [corrected 23 December 2020]
Page 1512, appendix 2, line 8. [corrected 19 June 2019]
Page 1512, appendix 2, line 10. [corrected 19 June 2019]
Page 1512, appendix 2, line 11. [corrected 19 June 2019]
Page 1512, appendix 2, line 19. [corrected 19 June 2019]
Page 1512, appendix 2, below line 20. [corrected 19 June 2019]
Page 1512, appendix 2, line 21. [corrected 23 December 2020]
Page 1512, appendix 2, line 22. [corrected 19 June 2019]
Page 1512, appendix 2, line 23. [corrected 19 June 2019]
Page 1512, appendix 2, column 2, structure 1. [modified 23 December 2020]
Page 1512, appendix 2, column 2, structure 3. [corrected 19 June 2019]
Page 1512, appendix 2, column 3, line 2. [corrected 24 March 2021]
Page 1513, appendix 2, above line 1. [corrected 26 June 2019]
Page 1513, appendix 2, line 4.
Page 1513, appendix 2, below line 4. [corrected 10 March 2021]
Page 1513, appendix 2, line 5. [corrected 26 June 2019]
Page 1513, appendix 2, line 6. [corrected 26 June 2019]
Page 1513, appendix 2, below line 6. [corrected 26 June 2019]
Page 1513, appendix 2, line 7. [corrected 26 June 2019]
Page 1513, appendix 2, line 12. [corrected 23 December 2020]
Page 1513, appendix 2, line 17. [corrected 26 June 2019]
Page 1513, appendix 2, line 19. [corrected 26 June 2019]
Page 1513, appendix 2, column 3, line 7. [corrected 26 June 2019]
Page 1514, appendix 2, after line 4. [corrected 21 April 2021]
Page 1515, Appendix 3, line 1.
Page 1515, Appendix 3, aporphine. [corrected 14 October 2020]
Page 1516, Appendix 3, structure 1 on this page. [corrected 24 October 2018]
Page 1516, Appendix 3, structure 3 on this page. [corrected 24 October 2018]
Page 1517, Appendix 3, cinchonan. [corrected 14 October 2020]
Page 1518, Appendix 3, structure 4 on this page. [corrected 17 October 2018]
Page 1519, Appendix 3, example 2 on this page. [corrected 17 June 2020]
Page 1521, Appendix 3, kopsan. [corrected 14 October 2020]
Page 1522, Appendix 3, nupharidine. [corrected 14 October 2020]
Page 1523, Appendix 3, rodiasine. [corrected 14 October 2020]
Page 1526, Appendix 3, veratraman. [corrected 14 October 2020]
Page 1526, Appendix 3, structure 2 on this page. [corrected 24 October 2018]
Page 1526, Appendix 3, vincane. [corrected 14 October 2020]
add footnote †† The CAS name for this structure is based on eburnamenine.
Page 1527, Appendix 3, vobtusine. [modified 14 October 2020]
replace the structure with:
Page 1530, Appendix 3, pregnane. [corrected 14 October 2020]
replace the structure with:
Page 1531, Appendix 3, spirostan. [corrected 14 October 2020]
Add footnote †† The CAS name for this structure requires the chirality at C-22 to be specified.
Page 1531, Appendix 3, footnote.
Page 1532, Appendix 3, aristolane. [corrected 14 October 2020]
Page 1532, Appendix 3, beyerane. [corrected 14 October 2020]
Add footnote †† The CAS name for this structure is based on kaurane
Page 1532, Appendix 3, footnote.
Page 1534, Appendix 3, structure 9 on this page. [corrected 24 October 2018]
Page 1535, Appendix 3, dammarane. [corrected 14 October 2020]
replace the structure with:
Page 1536, Appendix 3, gibbane. [corrected 14 October 2020]
replace the structure with:
Page 1565, index, steroids. [corrected 9 January 2019]
Page 1541, Appendix 3, lignane. [corrected 14 October 2020]
Page 1542, Appendix 3, 3,3′-neolignane. [corrected 14 October 2020]
Page 1541, Appendix 3, porphyrin. [corrected 14 October 2020]
For N 3, N
read N3,N
For ...carbonic, di-, and the polycarbonic acids...
read ...carbonic, di-, and polycarbonic acids...
Add (C-hydrazinylcarbonimidoyl)acetic acid
Add 3-(C-hydrazinylcarbonimidoyl)benzoic acid
For ...P-62.2.4.1.2, P-66.4.4, P- 66.3.1.2 and P-66.3.3, P-66.4.1.1, and P-66.4.2.1)
read ...P-62.2.4.1.2, P-66.4.1.4, P-66.3.1.2, P-66.3.3, P-66.4.1.1, and P-66.4.2.1) [delete space in reference]
For Hydrazidine derived from sulfonic acid, and similar selenium...
read Hydrazidine derived from sulfonic, sulfinic acids, and similar selenium...
For Example:
read Examples:
For carbonohydrazonic dihydrazide (P-65.2.1.5)
read carbonohydrazonic dihydrazide (P-65.2.1.3)
For dicarbonohydrazonic dihydrazide (PIN, P-65.2.1.5)
read dicarbonohydrazonic dihydrazide (PIN, P-65.2.3.1.3)
For Example:
read Examples:
For ...carbonic and di- and the polycarbonic acids...
read ...carbonic and di- and polycarbonic acids...
For hexanenitrile (PIN))
read hexanenitrile (PIN)
For hydrazinyl cyanide (se P-66.5.1.3)
read hydrazinyl cyanide (see P-66.5.1.3)
For ... discussed in P-102.5.6.2.1 and P-103.2.7, respectively.
read ... discussed in P-102.5.6.6.2.1 and P-103.2.8, respectively.
For aminoacetonitrile (see P-103.2.7)
read aminoacetonitrile (see P-103.2.8)
For 2-oxooxtanenitrile
read 2-oxooctanenitrile
For ...see P-65.1.2.3 and P-65.3.4.
read ...see P-65.1.2.3 and P-65.1.2.4.
For P-66.5.3 Nitriles/cyanides corresponding to carbonic and the polycarbonic acids...
read P-66.5.3 Nitriles/cyanides corresponding tocarbonic and di- and polycarbonic acids...>
For ...carbonic acid and di- and the polycarbonic acids...
read ...carbonic acid and di- and polycarbonic acids...
For (3) as zwitterions (see P-74.2.2.2.1.1).
read (3) as zwitterions (see P-74.2.2.2.1.2).
For (3)_(benzylidyneazaniumyl)oxidanide
read (3) (benzylidyneazaniumyl)oxidanide
For P-66.6.0 Definition
read P-66.6.0 Introduction
read P-66.6.2 Aldehydes from di- and polycarbonic acids
read P-66.6.5 Acetals and ketals, hemiacetals and hemiketals, and their chalcogen analogues [add space]
For ...attached to an alkane.
read ...attached to an unbranched alkane chain.
For propanal (PIN))
read propanal (PIN)
Replace the structure with:
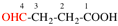
For Aldehydes from di- and the polycarbonic acids
read Aldehydes from di- and polycarbonic acids
For In presence of an aldehyde group
read In the presence of an aldehyde group
For ...for which see P-65.1.2.3 and P-65.3.4.
read ...for which see P-65.1.2.3. and P-65.1.2.4
For 3-oxobutyraldehyde
read (not 3-oxobutyraldehyde)
For 3-(trimethylsilyl)propanal ethylene ketal
read 3-(trimethylsilyl)propanal ethylene acetal
For acetaldehyde ethylene monothioketal
read acetaldehyde ethylene monothioacetal
For P-67.3 Substuitive names
read P-67.3 Substuitive names and functional class names of polyacids
For P-67.1.3 Esters and anhydrides of noncarbon oxoacids
read P-67.1.3 Salts, esters, and anhydrides of noncarbon oxoacids
For P-67.1.4 Substitutent groups derived from noncarbon oxoacids expressed as prefixes
read P-67.1.4 Substituent prefix groups derived from mononuclear noncarbon oxoacids
For arsorous acid (formerly arsen(i)ous acid)
read arsorous acid (formerly arsen(i)ous acid) (preselected name)
For (not P-ethylethanephosphinic acid
read (not P-ethylethanephosphinic acid)
For P-67.1.2.3 General methodology for functional replacement nomenclature
read P-67.1.2.3 General methodology for functional replacement nomenclature using infixes
For P-67.1.2.4 Acids modified by functional replacement nomenclature
read P-67.1.2.4 Mononuclear noncarbon oxoacids modified by functional replacement nomenclature
For ...oxoacids modified by infixes, The following acid...
read ...oxoacids modified by infixes. The following acid...
For (not diphenyl(sulfanyl)phosphane)
read [not diphenyl(sulfanyl)phosphane]
For azido, cyanido, isocyanido, isocyanatido, isothiocyanatido, isoselenocyanatido, isotellurocyanatido
read azido, cyanido, isocyanatido, isocyanido, isoselenocyanatido, isotellurocyanatido, isothiocyanatido
Add –OCN cyanatido, –SeCN selenocyanatido, –TeCN tellurocyanatido, –SCN thiocyanatido
For ...telluroperoxy)
read ...ditelluroperoxy)
For azido, cyano, isocyano, isocyanato, isothiocyanato, isoselenocyanato, isotellurocyanato
read azido, cyano, isocyanato, isocyano, isoselenocyanato, isotellurocyanato, isothiocyanato
Add –OCN cyanato, –SeCN selenocyanato, –TeCN tellurocyanato, –SCN thiocyanato
For P-67.1.2.4 Mononuclear noncarbon oxoacids modified by functional replacement
read P-67.1.2.4 Mononuclear noncarbon oxoacids modified by functional replacement nomenclature
For methylazonothious acid
read methylazonothious acid (PIN)
For N,N-dimethyl-N′ -phenylphosphoramidimido(thiocyanatidic) acid (PIN)
read N,N-dimethyl-N′-phenylphosphoramidimido(thiocyanatidic) acid (PIN) [delete space from name]
For (C6H5)P(OH)(SH)
read C6H5-P(OH)(SH)
For ...nitrous acid are discussed in P-67.1.2.6.2.
read ...nitrous acid are discussed in P-67.1.2.6.3.
For (not phosphoric tris(dimethylamide)
read [not phosphoric tris(dimethylamide)]
For (not phenylphosphonic bis(methylamide)
read [not phenylphosphonic bis(methylamide)]
For N,N-diethyl-N′, N′-dimethyl-As-phenylarsonothioic diamide
read N,N-diethyl-N′,N′-dimethyl-As-phenylarsonothioic diamide. [Deleted space from name]
For (not phosphorothioic tris(2,2-dimethylhydrazide)
read [not phosphorothioic tris(2,2-dimethylhydrazide)]
For Preferred IUPAC names of amides...
read Preselected names of amides...
For Na+ [B(OH)(OCN)(O–]
read Na+ B(OH)(OCN)(O–)
For ...Partial (acid) esters of polybasic...
read ...Partial acid esters of polybasic...
For Salts of partial (acid esters) are named by citing...
read Salts of partial acid esters are named by citing...
For P(Cl)[ N(CH3)2](O-CH3)
read P(Cl)[N(CH3)2](O-CH3) [delete space in structure]
For methyl bis(1-hydroxybutan-2-yl)borinate PIN)
read methyl bis(1-hydroxybutan-2-yl)borinate (PIN)
For ...and the sulfur acids acids expressed by suffixes.
read ...and the sulfur acids expressed by suffixes.
For P-67.1.4 Substitutent prefix groups derived from mononuclear noncarbon oxoacids
read P-67.1.4 Substituent prefix groups derived from mononuclear noncarbon oxoacids
For P-67.1.4.2 Substituent groups derived from boric acid and silicic acid
read P-67.1.4.2 Substituent groups derived from boron acid and silicic acid
For P-67.1.4.4 Substituent groups derived from sulfur, selenium and tellurium acids
read P-67.1.4.4 Substituent groups derived from chalcogen acids
For ...for substituent derived from mononuclear noncarbon oxoacids;
read ...for substituents derived from mononuclear noncarbon oxoacids
For ...groups from an mononuclear...
read ...groups from a mononuclear...
For Prefixes formed in this manner are preferred IUPAC prefixes.
read Prefixes formed in this manner are preselected prefixes.
For ...mononuclear noncarbon oxoacids;
read ...mononuclear noncarbon oxoacids
For ...acids generated by the method described in P-67.1.4.1.1(b) Preferred IUPAC names of acyl groups are those derived from the preferred names of acids.
read ...acids generated by the method described in P-67.1.4.1.1.2. Preferred prefix names of acyl groups are those derived from the preferred IUPAC names of acids.
For Derived preselected prefix
read Derived preferred prefix
For ...Table 1.6 and cited in P-65.2.1.5 are allowed.
read ...Table 1.6 and cited in P-67.1.2.3 are allowed.
For Derived preselected prefix
read Derived preselected or preferred prefix
Add peroxyphosphoryl
For ...groups and theirchalcogen analogues in substituent groups the or to groups that are not...
read ...groups and their chalcogen analogues in substituent groups or groups that are not... [add space]
For dimethoxyphosphoroselenoyl (PIN)
read dimethoxyphosphoroselenoyl (preferred prefix)
For hydroxy(methylphosphonoyl) (PIN)
read hydroxy(methylphosphonoyl) (preferred prefix)
Add (see P-67.1.6)
Add (see aci-nitro compounds, P-67.1.6)
Move text to a sepearate paragraph and add title:
Substituent groups for general nomenclature
For ...for naming amides (see P-66.1.1.4.2); ...
read ...for naming amides (see P-66.1.1.4.3); ...
For 2-nitrohydrazin-1-yl (preselected name)
read 2-nitrohydrazin-1-yl (preselected prefix)
For nitrosohydrazinylidene (preselected name)
read nitrosohydrazinylidene (preselected prefix)
For 1-nitrohydrazin-1-yl (preselected name)
read 1-nitrohydrazin-1-yl (preselected prefix)
For ...in P-65.3.2.2.2 and P-67.1.4.4.1.
read ...in P-65.3.2.3 and P-67.1.4.4.1.
For 67.1.5 Seniority order of inorganic acids and derivatives
read 67.1.5 Seniority order among noncarbon oxoacids and derivatives
For ... is preferred to ‘nitroryl’ [see P-67.1.4.1.1(b)].
read ... is preferred to ‘nitroryl’ (see P-67.1.4.1.1.2).
For P-67.2 DI- AND POLYNUCLEAR NONCARBON ACIDS
read P-67.2 DI- AND POLYNUCLEAR NONCARBON OXOACIDS
For P-67.2.2 Functional replacement nomenclature
read P-67.2.2 Functional replacement derivatives of di- and polynuclear noncarbon oxoacids
For P-67.2.3 Acid halides and pseudohalides
read P-67.2.3 Acid halides and pseudohalides of di- and polynuclear noncarbon oxoacids
For P-67.2.4 Amides and hydrazides
read P-67.2.4 Amides and hydrazides of di- and polynuclear noncarbon oxoacids
For P-67.2.5 Esters and anhydrides
read P-67.2.5 Esters and anhydrides of di- and polynuclear noncarbon oxoacids
For P-67.2.6 Substituent groups cited as prefixes
read P-67.2.6 Substituent groups derived from polyacids
For ...they are preferred IUPAC names if the...
read ...they are preselected names if the...
For metaarsoric acid (only for general (nomenclature)
read metaarsoric acid (only for general nomenclature)
For metaarsorous acid only for general (nomenclature)
read metaarsorous acid (only for general nomenclature)
For ...and pseudohalides (see P-67.2.2.3), amides and hydrazides (see P-67.2.2.4).
read ...and pseudohalides (see P-67.2.3), amides and hydrazides (see P-67.2.4).
For This is a change prom previous...
read This is a change from previous...
For ...location of chalcogen atoms in acids groups was described by an on line arabic numbers prefixed...
read ...location of a chalcogen atom in acid groups was described by an on line arabic number prefixed...
For 1-thiophosphoric S1-acid ( name derived...
read 1-thiophosphoric S1-acid (name derived... [delete space before ‘name’]
For ...the ‘imido’ replacememt prefix determines...
read ...the ‘imido’ replacement prefix determines...
For (not 1-(methylimido)-2-thiodithionous 2-S-acid)
read [not 1-(methylimido)-2-thiodithionous 2-S-acid]
For ...the 'Br', bromide), is preferred to 'Cl', chloride (alaphabetically) and determines...
read ...the 'Br', bromide, is preferred to 'Cl', chloride (alphabetically) and determines...
For ...locants N1, N′1, etc. are used...
read ...locants N1, N′1, etc. are used...
Replace the structure with:
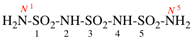
For P-67.2.2.5.1 Salts
read P-67.2.5.1 Salts of di- and polynuclear noncarbon oxoacids
read P-67.2.5.2 Esters of polynuclear noncarbon oxoacids
read P-67.2.5.3 Anhydrides of polynuclear non-carbon oxoacids
For ...by changing the ‘ic acid’ending to ‘ate’and the ‘ous acid’...
read ...by changing the ‘ic acid’ ending to ‘ate’ and the ‘ous acid’... [add spaces]
For P-67.2.5.3 Anhydrides
read P-67.2.5.3 Anhydrides of polynuclear non-carbon oxoacids
For In presence of a characteristic group
read In the presence of a characteristic group
For (3) skeletal replacement nomenclature (see P-15.3 and P-51.3), ...
read (3) skeletal replacement nomenclature (see P-15.4 and P-51.4), ...
For (a substitutive name only is possible in this case)
read (only a substitutive name is possible in this case)
For ...structure,,HO-SO-SO2-OH, is...
read ...structure, HO-SO-SO2-OH, is...
For Accordingly, the preferred IUPAC name for the latter is...
read Accordingly, the preselected name for the latter is...
For ...when compound contains...
read ...when a compound contains...
For ... hydrides are listed in Table 2.
read ... hydrides are listed in Table 2.1.
For P-68.1.1.3.1 Poyhedral polyboranes
read P-68.1.1.3.1 Polyhedral polyboranes
For borazine
read borazine (see D-7.54, ref. 1)
For borthiin
read borthiin (see D-7.54, ref. 1)
For P-68.1.1.3.2.2 von Baeyer and spiro compounds
read P-68.1.1.3.3 von Baeyer and spiro compounds
For P-68.1.1.3.3 Fused ring systems
read P-68.1.1.3.4 Fused ring systems
For alumanyl
read alumanyl (preselected name)
For gallanyl
read gallanyl (preselected name)
For indiganyl
read indiganyl (preselected name)
For thallanyl
read thallanyl (preselected name)
For ...ending or by the use of ‘hydro’ prefixes with names of mancude ring systems, as described...
read ...ending or by saturation of double bonds of mancude ring systems by the use of ‘hydro’ prefixes, as described...
For (not tetrahydroxydiborane(4)
read [not tetrahydroxydiborane(4)]
For ...as diborane, the polyboranes, and related ...
read ...as diborane, polyboranes, and related ...
For ...formula using a centre dot. When...
read ...formula using a center dot. When...
For ...is the formal respresentation of structure...
read ...is the formal representation of structure...
For ...component by an ‘em’ dash (see P-16.2.5) or by the set ...
read ...component by an ‘em’ dash (see P-16.2.4.5) or by the set ...
For P-68.1.6.1.1 General organic method for naming Lewis adducts
read P-68.1.6.2 General organic method for naming Lewis adducts
For ... joined by an ‘em’ dash (see P-16.2.5), enclosed in ...
read ...joined by an ‘em’ dash (see P-16.2.4.5), enclosed in ...
For P-68.1.6.1.2 Intramolecular adducts
read P-68.1.6.3 Intramolecular adducts
For ...as described in Rule P-68.1.6.1, but enclosed...
read ...as described in Rule P-68.1.6.2, but enclosed...
For P-68.2 NOMENCLATURE COMPOUNDS OF THE GROUP 14 ELEMENTS
read P-68.2 NOMENCLATURE FOR COMPOUNDS OF THE GROUP 14 ELEMENTS
For P-68.2.8.1 Substituted parent hydrides
read P-68.2.6.1 Substituted parent hydrides
For di(dodecyl)silane
read di(dodecyl)silane (PIN)
For (thiophene-2,5-diyl)bis(trimethylstannane)
read (thiophene-2,5-diyl)bis(trimethylstannane) (PIN)
For ...bismuthane, BiH3 (see P-68.3.3.
read ...bismuthane, BiH3 (see P-68.3.3).
For P-68.3.1.2 Hydrazine and related compounds
read P-68.3.1.2 Hydrazine and related compounds: hydrazones, azines, semicarbazides, semicarbazones, and carbonohydrazides
For ...Hydroxylamine, urea, guanidine, and...
read ...Hydroxylamine is a preselected name and urea, guanidine, and...
For Several nitrogen compounds having one nitrogen atom belong to classes identified as: hydroxylamines, oximes, and nitrolic and nitrosolc acids. The methodology for naming them is illustrated here.
read Compounds containing a nitrogen atom which belong to classes identified as hydroxylamines, oximes, and nitrolic and nitrosolic acids are illustrated here.
For N-hydroxysilanamine (PIN)
read N-hydroxysilanamine (preselected name)
For N-hydroxyboranamine (PIN)
read N-hydroxyboranamine (preselected name)
For (no longer propanohydroxamic acid or propionohydroxamic acid)
read propanohydroxamic acid propionohydroxamic acid
Page 998, P-68.3.1.2.1, line 2. [corrected 16 August 2016]
For ...is preferred to the systematic hetrane name ‘diazane’.
read ...is preferred to the systematic heterane name ‘diazane’.
For P-68.3.1.2.3.3 In presence of functions
read P-68.3.1.2.3.3 In the presence of functions
For ...systematically named ‘hydrazinecarboxamide’ The systematic name...
read ...systematically named ‘hydrazinecarboxamide’. The systematic name...
For Examples:
read Example:
For ...68.3.1.2.1) and as such can be substituted by suffixes and prefixes as described in P-59.1.10. The prefix ‘diazenyl’ is a preselected prefix.(see P-32.1.10).
read
...68.3.1.2.1). The prefix ‘diazenyl’ is a preselected prefix (see P-32.1.1).
For [not 2-aminonaphthalene-1-azo-(4′-chloro-2′-methylbenzene)...]
read [not 2-aminonaphthalene-1-azo(4′-chloro-2′-methylbenzene)...]
For 68.3.1.3.2.1 above...
read ...in P-68.3.1.3.2.1 above...
For ...in 68.3.1.3.2.1
read ...in P-68.3.1.3.2.1
For ... according to the seniority rules applied in constructing names (see P-59.1.10).
read ... according to the seniority rules applied in constructing names (see P-4).
For (‘cyanohydroxysulfophenyldiazenyl] is lower alphanumerically than ‘cyanohydroxysulfophenylhydrazinylidene...’)
read (‘cyanohydroxysulfophenyldiazenyl...’ is lower alphabetically than ‘cyanohydroxysulfophenylhydrazinylidene...’)}
For ... the retained name and the preferred IUPAC name for diazane...
read ... the retained name and the preselected name for diazane...
For ...of parent hydride name ‘triazene’. The prefix...
read ...of the parent hydride name ‘triazene’ if there is present no characteristic group to be cited as a suffix. The prefix...
For (arsanylmethyl)diphenylphosphane (PIN)
read (arsanylmethyl)di(phenyl)phosphane (PIN)
read (arsinomethyl)di(phenyl)phosphane
For 4-[ethyl(methyl)phosphino]-1H-imidazole (PIN)
read 4-[ethyl(methyl)phosphino]-1H-imidazole
For P-68.4 NOMENCLATURE OF COMPOUNDS OF THE GROUP 16 ELEMENTS
read P-68.4 NOMENCLATURE FOR COMPOUNDS OF THE GROUP 16 ELEMENTS
For ...pseudoketone (see P-64.1.2.1 and P-65.7.5.1) on the...
read ...pseudoketone (see P-64.1.2.1, P-64.3 and P-65.7.5.1) on the...
For P-68.4.2 Three heterogeneous contiguous chalcogen atoms
read P-68.4.2 Three or more heterogeneous contiguous chalcogen atoms
For Compounds of the type a(ab)n are parent...
read Compounds of the type a[ab]n are parent...
For Compounds of the type R-(chalcogen)x-H where x = 3,4,...
read Compounds of the type R-(chalcogen)x-H where x = 3,4,...
For (not (methylsulfanyl)oxidane-SO-thioperoxol)
read [not (methylsulfanyl)oxidane-SO-thioperoxol]
For methyl(methylsulfanyl)dioxidane
read [not methyl(methylsulfanyl)dioxidane]
For ethoxy(methyl)disulfane
read [not ethoxy(methyl)disulfane]
For 1- [(methylsulfanyl)peroxy]propan-1-one (PIN)
read 1-[(methylsulfanyl)peroxy]propan-1-one (PIN) [delete space in name]
For P-68.4.3.7 Sulfur dimides, HN=E=NH and chalcogen analogues...
read P-68.4.3.7 Sulfur diimides, HN=E=NH and chalcogen analogues...
For ...where (E = Se, Te).
read ...where E = Se, Te.
For P-68.5 NOMENCLATURE OF COMPOUNDS OF THE GROUP 17 ELEMENTS
read P-68.5 NOMENCLATURE FOR COMPOUNDS OF THE GROUP 17 ELEMENTS
For P-68.5.3 Amides if halogen acids
read P-68.5.3 Amides of halogen acids
For N-methylbromic amide(PIN)
read N-methylbromic amide (PIN) [add space]
For ...involving the elemens of Groups 1 and 2;
read ...involving the elements of Groups 1 and 2;
For ...involving the elements of Goups 1 and 2;
read ...involving the elements of Groups 1 and 2;
For ...that of a central atom (ref. 12, Chapters I-7, I-9). However...
read ...that of a central atom (ref. 12, Chapters IR-7, IR-9). However...
For ...hydride; they are the preferred IUPAC names. Principles,...
read ...hydride. Principles,...
For ...terms ‘monodentate’, ‘didentate’, etc.
read ...terms ‘monodentate’, ‘bidentate’, etc.
For ...of the ligand(s). which are are listed...
read ...of the ligand(s), which are listed...
For [(2,3,5,6-η) -bicyclo[2.2.1]hepta-2,5-diene]tricarbonyliron
read [(2,3,5,6-η)-bicyclo[2.2.1]hepta-2,5-diene]tricarbonyliron
For The prefix ‘μ’ (see IR-10.2.3.1, ref 12)...
read The prefix ‘μ’ (see IR-9.2.5.2, ref 12)...
For Examples:
read Example:
For Example:
read Examples:
For ...extension of the the list of seniority...
read ...extension of the list of seniority...
For ...name. Metals are classifed into:
read ...name. Metals are classified into:
For Example:
read Examples:
For Table 7.1.
read Table 7.1
For P-70.3.3.2.2 In a zwitterionic compounds, cumulative...
read P-70.3.3.2.2 In zwitterionic compounds, cumulative...
For ...NH2–; CH3-C(O)–, acetyl.
read ...NH2–; CH3-C(O)–, acetyl anion.
For P-71.3 Radical centres on characteristic groups
read P-71.3 Radical centers on characteristic groups
For The suffix ‘hydryl’ denotes to the additive
read The suffix ‘hydryl’ denotes the additive
For P-71.7 Choice of parent structure
read P-71.7 Choice of parent radical
For ...the IUPAC prefered name for HO• is...
read ...the IUPAC preferred name for HO• is...
For ...is named ‘methoxyl’ or methyloxidanyl, and not ‘methylhydroxyl’ (see P-71.3.4).
read ...is named ‘methoxyl’ or ‘methyloxidanyl’, and not ‘methylhydroxyl’ (see P-71.3.4).
For tert-butyl [see P-70.4 (2)]
read tert-butyl [see P-70.4 (1)]
For cyclopentadienyl (see P-76.1)
read cyclopentadienyl (see P-76)
For ...from one sketetal atom of a mononuclear parent...
read ...from one skeletal atom of a mononuclear parent...
For 1,4-phenylene [see p-70.4.(1)]}
read 1,4-phenylene [see P-70.4 (1)]}
For ‘Added indicated hydrogen’
read ‘Added indicated hydrogen’ for radicals of mancude ring systems
For naphthalene-4a,8a-diyl (P IN)
read naphthalene-4a,8a-diyl (PIN) [delete space in PIN]
Replace structure with:
For ...‘sulfanylidene’ amd ‘imino’...
read ...‘sulfanylidene’ and ‘imino’...
For 1- sulfanylideneethyl
read 1-sulfanylideneethyl [remove space in name]
For Table 7.2.
read Table 7.2
For propan-1- iminyl (PIN)
read propan-1-minyl (PIN)l [remove space in name]
For Polyradicals with radical centres identically
read Polyradicals with radical centers identically
For The names methoxyl, ethoxyl, propoxyl, butoxyl, phenoxyl, and ...
read The names methoxyl, ethoxyl, propoxyl, butoxyl, tert-butoxyl, phenoxyl, and ...
For ...IUPAC names (see p-63.2.2.2 for names...
read ...IUPAC names (see P-63.2.2.2 for names...
For ... or polyimide radicals described in P-71.3.1 and P-71.3.4, respectively) ...
read ... or polyamide radicals described in P-71.3.1 and P-71.3.3, respectively) ...
For ...by multivalent substitutents (see P-15.3).
read ...by multivalent substituents (see P-15.3).
For ...in a substituent to cited as a prefix or the...
read ...in a substituent cited as a prefix or the...
For (a) Maximum number...
read (a) Parent with the maximum number...
For (b) Maximum number...
read (b) Parent with the maximum number...
Add {not 1-[3-(2-yloethyl)phenyl]ethylidene; ethyl is senior to ethylidene}
For (c) Maximum number...
read (c) Parent with the maximum number...
For ... N > P > As > Pb > Al > Ga > In >...
read ... N > P > As > Sb > Bi > Si > Ge > Sn > Pb > B > Al > Ga > In >...
Add (not 2-methyl-2-ylooxidanylpropyl; oxyl is senior to propyl)
For ...is made by applying the general criteria for chains and rings given in Chapters 1 to 6 for neutral compounds.
read ..is made by giving priority to the corresponding suffixes (see Table 4.4) and by using the general seniority order of classes (see P-41) and parent structures (see P-44).
Add [not 1-(3-ylocyclopentyl)ethyl; cyclopentyl is senior to ethyl]
For P-72.4 Skeketal replacement nomenclature
read P-72.4 Skeletal replacement nomenclature
For ...The names are formed by using the NAMES of...
read ...The names are formed by using the names of...
For cyclopentadienide (see P-76.1)
read cyclopentadienide (see P-76)
For cyclopentadienide (see P-76.1)
read cyclopentadienide (see P-76)
For ‘Added indicated hydrogen’
read ‘Added indicated hydrogen’ for anions of mancude ring systems
Replace structure with:
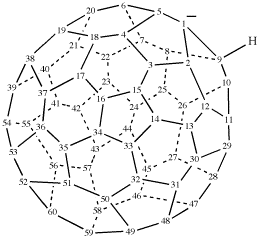
For ...the final ‘e’ of ‘amine, i.e.,...
read ...the final ‘e’ of ‘amine’, i.e.,...
For ...‘ol’, ‘thiol’, ‘-peroxol’, etc., is preferably...
read ...‘ol’, ‘thiol’, ‘peroxol’, etc., is preferably...
For ...are retained as preferred IUPAC names.
read ...are retained as preferred IUPAC names or preselected name.
For ...aminide suffixes,. The resulting...
read ...aminide suffixes. The resulting
For ...hydride ion, H–.:
read ...hydride ion, H–:
For ...ion, H–, to a parent hydride named; the by multiplying prefixes...
read ...ion, H–, to a parent hydride name; the multiplying prefixes...
For ...a hydride ion, H–, to the parent...
read ...a hydride ion, H–, to the parent...
For ...its standard 'borata’ was used...
read ...its standard ‘borata’ was used...
Replace structure with:
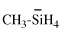
For There are two methods are used
read Two methods are used
For difluoro(phenyl)- λ4-sulfanide
read difluoro(phenyl)-λ4-sulfanide [delete space in name]
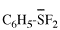
Replace structure with:
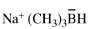
Replace structure with:
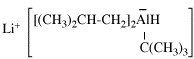
For ...preferred IUPAC names. in other words, ...
read ...preferred IUPAC names. In other words, ...
Replace structure with:
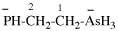
For (a) maximum number of anionic centres on characteristic groups of any kind, including anionic suffixes;
read (a) parent with the maximum number of anionic centers, including anionic suffixes;
For 2-(borinan-1-uid-4-yl)ethane-1,2-bis(olate) (PIN
read 1-(borinan-1-uid-4-yl)ethane-1,2-bis(olate) (PIN)
Add [not 4-(1,2-dioxidoethyl)borinan-1-uide; two anionic centre is senior to one]
For (b) maximum number of anionic centers ‘uide’ and ‘ide’;
read (b) parent with the maximum number of ‘uide’ and ‘ide’ anionic centers;
For 1-(1,1-dimethylborinan-1-uid-4-yl)ethane-1,2-bis(dithioperoxolate) PIN)
read 1-(1,1-dimethylborinan-1-uid-4-yl)ethane-1,2-bis(dithioperoxolate) (PIN)
For (b) maximum number of ‘uide’ centers;
read (b) parent with the maximum number of ‘uide’ centers;
Add [not (2-arsanuidylethyl)phosphanide]
For ... N > P > As > Pb > Al > Ga > In >...
read ... N > P > As > Sb > Bi > Si > Ge > Sn > Pb > B > Al > Ga > In >...
For The seniority order for radicals is now ...
read The seniority order for anions is now ...
For ...used in RC-81.3.3.2, ref 3.
read ...used in RC-83.4.7.4, ref 3.
Add [not (2-phosphanidylethyl)silanide; P > Si]
Add (carboxylate senior to olate)
For P-73.2 Cations formed by the removal of hydride ions
read P-73.2 Cationic compounds with cationic centers derived formally by the removal of hydride ions
read P-73.3 The λ-convention with the suffix ‘ylium’
For 73.1 CATIONIC COMPOUNDS WITH CATIONIC CENTERS DERIVED FORMALLY BY ADDITION OF HYDRON
read P-73.1 CATIONIC COMPOUNDS WITH CATIONIC CENTERS DERIVED FORMALLY BY THE ADDITION OF HYDRON
For Table 7.3 Retained preselected names for the mononuclear...
read Table 7.3 Retained names for the mononuclear...
For ...atom is present.
read ...atom is present or when they are nitrogen containing compounds other than those described in (1).
For ...Chapters P- and P-5...
read ...Chapters P-2 and P-5...
For cyclopentadienylium (see P-76.1)
read cyclopentadienylium (see P-76)
For ‘Added indicated hydrogen’
read ‘Added indicated hydrogen’ for cations of mancude ring systems
For 1λ4- benzopyran-1-ylium
read 1λ4-benzopyran-1-ylium [delete space in name]
For 2λ4- benzopyran-1-ylium
read 2λ4-benzopyran-1-ylium [delete space in name]
For ...a bonding order one higher...
read ...a bonding number one higher...
For ...a bonding order one lower...
read ...a bonding number one lower...
For ... compound, see P-24.8.4)
read ... compound, see P-24.8.2)
For triaz-2-en-1-ium-1- yl (preselected prefix)
read triaz-2-en-1-ium-1-yl (preselected prefix)
For P-73.7.1 A parent structure...
read A parent structure...
For (a) maximum number of cationic centres of any kind, including cationic suffix groups, including those derived from characteristic groups.
read (a) parent with the maximum number of cationic centers, including cationic suffixes.
Add [not 3-(1,2-diaminiumylpropan-2-yl)piperidin-1-ium; bis(aminium) is senior to piperidinium]
For (b) maximum number of ‘ylium’ ....
read (b) parent with the maximum number of ‘ylium’ ....
For ...names names based on the...
read ...names based on the...
Add [not (1,5-dimethylcyclohex-4-en-1-ylium-3-ylidene)(methyl)oxidanium; ylium is senior to ium]
For ... N > P > As > Pb > Al > Ga > In >...
read ... N > P > As > Sb > Bi > Si > Ge > Sn > Pb > B > Al > Ga > In >...
For The seniority order for radicals is now...
read The seniority order for cations is now...
Add [not dimethyl[6-(trimethylphosphaniumyl)hexyl]sulfanium; P > S]
Add {not dimethyl[6-(trimethylazaniumyl)hexyl]sulfanium; N> S}
For ...used in RC-81.3.3.2, ref 3.
read ...used in RC-82.5.8.4, ref 3.
For ...criteria, in accordance with the principles, rules and conventions described in Chapters P-1 through P-6.
read ...criteria, giving priority to the corresponding suffixes (see Table 4.4) and by using the general seniority order of classes (see P-41) and parent structures (see P-44).
Add (longest chain)
Add (amidium is senior to aminium)
For P-73.8.1 The the suffix ‘-ylium’ ...
read P-73.8.1 The suffix ‘-ylium’ ...
For ...adduct, see P.68.1.6.1.1)
read ...adduct, see P.68.1.6.2.
For ...the first row of the periodic system, the ‘ylide’ is...
read ...the second row of the periodic system, the ‘ylide’ is...
read ...if ‘X’ is a third, fourth, etc. row element...
For ... usually shown, RmX=YR.
read ... usually shown, RmX=YRn.
For ...formulae R3N+–O– and R2=N+–O– respectively;...
read ...formulae R3N+–O– and R2C=N+(R)–O– respectively;...
For Sulfur and selenium ylides have the ...
read Sulfur ylides have the ...
For (2) ethyl(triphenylphosphaniumyl)azanide
read (1) ethyl(triphenylphosphaniumyl)azanide
read (2) triphenylphosphane-N-ethylimide
For Azoxy compounds, have the general structure:
read Azoxy compounds have the general structure:
For Method 4 in P-74.2.2.1 gives preferred IUPAC names.
read Method (4) in P-74.2.2.1 gives preferred IUPAC names.
For R′ = H arenot included...
read R′ = H are not included... [add space]
For ... (see also P-66.5.3.1).
read ... (see also P-66.5.4.1).
For P-74.2.2.2.1. Nitrile ylides.
read P-74.2.2.2.1.3 Nitrile ylides.
For ...prefix azido (P-61.6);
read ...prefix azido (P-61.7);
For ... the compulsory prefix (P-61.4);
read ... the compulsory prefix diazo (P-61.4);
For ... nomenclature for radicals (P-44.6), priority...
read ... nomenclature for radicals (P-71.2), priority...
For P-75.1 Radical ions formed by the addition or subtraction of electrons
read P-75.1 Radical ions formed by the addition or removal of electrons
For ...used in presence of other suffixes.
read ...used in the presence of other suffixes.
For aminidyl (preselected name)
read aminidyl
read azanidyl (preselected name)
For 4,5-bis(trifluoromethyl)-1,2,3-trithiolan-5-ylium-4-yl
read 4,5-bis(trifluoromethyl)-1,2,3-trithiolan-5-ylium-4-yl (PIN)
For ...as given in P-72.1, P-72.2 and P-72.3, respectively...
read ...as given in P-71.1, P-72.1 and P-73.2, respectively...
For ... added to the name of the anionic parent hydride.
read ... added to the name of the cationic or anionic parent hydride.
For P-76.1 DELOCALIZATION IN NAMES INVOLVING ONE RADICAL OR IONIC CENTER IN AN OTHERWISE CONJUGATED DOUBLE BONDS STRUCTURE IS DENOTED BY THE APPROPRIATE SUFFIX WITHOUT LOCANTS.
read Delocalization in names involving one radical or ionic center in an otherwise conjugated double bonds structure is denoted by the appropriate suffix without locants.
Replace structure with:
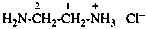
For (a) N,N-dimethyl-1,3-thiazolidin-2-amine—sulfuric acid (2/1) (PIN)
read (1) N,N-dimethyl-1,3-thiazolidin-2-amine—sulfuric acid (2/1)
read (2) bis(N,N-dimethyl-1,3-thiazolidin-2-amine) sulfate
For Example:
read Examples:
For ...that of the anion (see P-72.2.2.2.2).
read ...that of the anion (see P-72.2.2.2.1).
For Nomenclature in Inorganic Chemistry
read Nomenclature of Inorganic Chemistry
For ...in no other cases are lower-case letters used...
read ...in no other cases are only lower-case letters used...
For Identical isotopically modified atoms or groups that are not identically modified ...
read Isotopically modified atoms or groups that are not identically modified ...
For ...as the principle charactersitic group with...
read ...as the principle characteristic group with...
Replace the structure with:
CH3-CO-18O2H
For Example:
read Examples:
For stereosiomers.
read stereoisomers.
Replace the structures with:
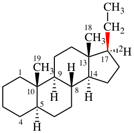
For (2R,3R)-3-chloro(2-2H1)butan-2-ol (PIN)
read (2R,3R)-3-chloro(2-2H)butan-2-ol (PIN)
For (not (2-13C)ethanol)
read [not (2-13C)ethanol]
For Examples:
read Example:
For Examples:
read Example:
For L-(amidino-14C,N′-15N)arginine
read (not L-(amidino-14C,N′-15N)arginine)
read L-(guanidino-14C,N′-15N)arginine (see Rule H-4.21, ref. 1)
Delete L-(amidino-14C,N′-15N)arginine
delete L-(guanidino-14C,N′-15N)arginine (see Rule H-4.21, ref. 1)
For (see Rule H-4.2.2. ref. 1)
read (see Rule H-4.22, ref. 1)
For (18O-2H)acetic acid
read (18O-2H)acetic acid (PIN)
For (18O,O-2H)acetic acid
read (18O,O-2H)acetic acid (PIN)
For C[3H3]-CO-C[2H2]-CH2-CH3
read C[2H3]-CO-C[2H2]-CH2-CH3
For (not benzene-1,3,5-[1,5-13C2,1,3-18O2]tricarboxylic acid)
read (not benzene-1,3,5-[1,3-13C2,1,5-18O2]tricarboxylic acid)
For 2-[15N]amino-3-hydroxy-[2,3-2H2 ,3-14C]propanoic acid
read 2-[15N]amino-3-hydroxy[2,3-2H2,3-14C]propanoic acid [delete space from name]
For Mixture of isotopically substituted
read Mixture of isotopically substituted compounds
For ...isotopically substituted is not modified at the indicated position.
read ...isotopically substituted compounds is not modified at the indicated position.
For [2-2H1;2]ethanol (PIN)
read [2-2H1;2]ethan-1-ol (PIN)
For [2-2H2;2]ethan[18O0;1]ol (PIN)
read [2-2H2;2]ethan-1-[18O0;1]ol (PIN)
For [G-14C]butanoic acid
read [G-14C]butanoic acid (PIN)
For ...in the same isotopic ration, the symbol ‘U’is used...
read ...in the same isotopic ratio, the symbol ‘U’ is used... [add space]
For [U-14C]butanoic acid
read [U-14C]butanoic acid (PIN)
For ethanol
read ethanol (PIN)
For [2-2H]ethan-1-[2H]ol
read [2-2H]ethan-1-[2H]ol (PIN)
For [2H]ethan-1-ol
read [2H]ethanol (PIN)
For [def13C]ethanol
read [def13C]ethanol (PIN)
For P-92 CIP priority and Sequence Rules
read P-92 The Cahn-Ingold-Prelog (CIP) priority system and Sequence Rules
For P-91.2.1.2 Non Cahn-Ingold-Prelog(CIP) stereodescriptors
read P-91.2.1.2 Other acceptable stereodescriptors
For ...products described in Chapter P-10.
read ...products (see Chapter P-10).
For Stereodescriptors used as preferred stereodescriptors and in general nomenclature
read Stereodescriptors used in substitutive nomenclature
For ...cumulenes R1R2C[=C=]nCR3R4, systems for example...
read ...cumulenes R1R2C=[C=]nCR3R4, systems for example...
For ‘A’ and ‘C’ to describe...
read ‘A’ and ‘C’ to describe...
For (c) Stereodescriptors no longer recommended in systematic substitutive nomenclature but used in the nomenclature of natural products (see Chapter P-10)
read P-91.2.1.2.2 Stereodescriptors used in the nomenclature of natural products (see Chapter P-10)
For ...optically inactive (see P-102.5.6.6.5);
For ...optically inactive (see P-102.5.6.5.2; P-102.5.6.6.5);
Move to after section (b).
For ...‘M’, ‘P’., and nonCIP stereodescriptors: ‘E’, ‘Z’, ‘seqCis’ and ‘seqTrans’. The Greek symbols ‘ξ’ or ‘Ξ’ may be used in general nomenclature.
read ...‘M’, ‘P’., ‘E’, ‘Z’, ‘seqCis’ and ‘seqTrans’.
For ...tetraene, i.e. ‘1,3,5,7-cyclooctatetraene’. From...
read ...tetraene, i.e. ‘cycloocta-1,3,5,7-tetraene’. From...
For ...ring systems (P-93.5.7)
read ...ring systems (P-93.5.7.3)
For ... introduction of theses affixes. This issue...
read ... introduction of these affixes. This issue...
For ...and illustrated in P-93.6.
read ...and illustrated in P-16.5.4.1 and P-93.6.
For (see P-92.2.1.2.1)
read (see P-92.2.1.2)
For ‘... is not is included in the name’
read ‘... is not included in the name’
For ...with an allene, ‘abC=C=Ccd’, the...
read ...with an allene, ‘abC=C=Cmn’, the...
Replace the structures with:
For ‘╒ ’ and ‘ ╕’ are enantiomorphic ligands)
read (‘╒ ’ and ‘ ╕’ are enantiomorphic ligands)
For The following ‘Sequence Rules’ are used (34, 35, 36) to...
read The following ‘Sequence Rules’ are used (refs. 34, 35, 36) to...
For like descriptor pairs are: ‘RR’, ‘SS ’, ‘MM ’, ‘PP ’, RM ’, ‘SP’, ‘seqCis/seqCis’, ‘seqTrans/seqTrans’, ‘RseqCis’, ‘SseqTrans’, ‘MseqCis’, ‘PseqTrans’...;
read like descriptor pairs are: ‘R-R’, ‘S-S ’, ‘M-M ’, ‘P-P ’, R-M ’, ‘S-P’, ‘seqCis-seqCis’, ‘seqTrans-seqTrans’, ‘R-seqCis’, ‘S-seqTrans’, ‘M-seqCis’, ‘P-seqTrans’...;
For unlike discriptor pairs are ‘RS’, ‘MP’, ‘RP’, ‘SM’, ‘seqCis/seqTrans’, ‘RseqTrans’, ‘SseqCis’, ‘PseqCis’, ‘MseqTrans’....
read unlike discriptor pairs are ‘R-S’, ‘M-P’, ‘R-P’, ‘S-M’, ‘seqCis-seqTrans’, ‘R-seqTrans’, ‘S-seqCis’, ‘P-seqCis’, ‘M-seqTrans’....
For ... and see also P-102.3.1)]
read ... and see also P-102.3.1]
Replace the structure with:
For ...as shown in Fig. 1. The first sphere...
read ...as shown in Fig. 9.1. The first sphere...
For Fig. 1 Ranking order for two ligands
read Fig. 9.1 Ranking order for two ligands
Replace structure with:
For ...over ‘C,H,H’ In sphere IV,...
read ...over ‘C,H,H’. In sphere IV,...
For ...ligands can be a parallel processes and frequently...
read ...ligands can be parallel processes and frequently...
For ...configuration of these chiral centers are shown below....
read ...configuration of these chirality centers are shown below....
For ...accordance with Sequence Rule (1). In sphere II,...
read ...accordance with Sequence Rule 1. In sphere II,...
For ... is senior to ‘C,(C),H)’ for the ...
read ... is senior to ‘C,(C),H’ for the ...
For ‘O,O,H’ for the –CH=O group...
read ‘O,(O),H’ for the –CH=O group...
For ...both carbons bonded to to ‘C-5 (C-6 and C-7)’...
read ...both carbons bonded to ‘C-5 (C-6 and C-7)’...
For ...and an ‘S’ configuration...
read ...and an ‘R’ configuration...
For ...further away duplicate atom node.
read ...further away duplicate atom node’.
For ...The following examples illustrate this sub-rule.
read ...The following examples illustrate this subrule.
For (1R)-1-(1-2H1)-ethan-1-ol
read (1R)-(1-2H1)ethan-1-ol (PIN)
For ‘seqcis’ = (Z) and ‘seqtrans’ = (E)
read ‘seqcis’ = ‘Z’ and ‘seqtrans’ = ‘E’
Delete Examples (cont’d)
For ... whose configuration is ‘seqcis’ (E) in one case ‘seqtrans’ (Z) in the other considering ...
read ... whose configuration is ‘seqcis’ (Z) in one case ‘seqtrans’ (E) in the other considering ...
For ... allow the rank ligands to be ranked...
read ... allow the ligands to be ranked...
For a first simplified digraph modified by introducing configurations at ‘C-2’, ‘C-5’, ‘C-6’, ‘C-8’, and ‘C-10’, as determined above.
read simplified digraph
For further simplified digraph to show the relevant information necessary to determine the configuration at ‘C-4’.
read a first simplified digraph modified by introducing configurations at ‘C-2’, ‘C-3’, ‘C-6’, ‘C-8’, and ‘C-10’, as determined above.
Add further simplified digraph to show the relevant information necessary to determine the configuration at ‘C-4’
For Final simplified digraph showing...
read Explanation: Final simplified digraph showing...
For (ii) Unlike discriptor pairs are: ‘RS’, ‘SR’
read (ii) Unlike discriptor pairs are: ‘RS’, ‘SR’
For ...descriptor for chiral centers, identified as R or S...
read ...descriptor for chirality centers, identified as R or S...
For ... any node of the digraph), is chosen...
read ... any node of the digraph and designated here with a bold font), is chosen...
For ...digraph for chiral centers at ‘C-2’...
read ...digraph for chirality centers at ‘C-2’...
For ...configuration for the chiral center ‘C-4’.
read ...configuration for the chirality center ‘C-4’.
New paragraph starting In...
for In the following digraph the configuration...
read In the following digraph (see example 1 in P-92.5.2.2) the configuration...
Delete The configuration at ‘C-4’ is determined by the four ligands ‘C1’, ‘H’ and the two branches ‘C-3,C-2,C-1’(right branch) and ‘C-5,C-6,C-7’ (left branch) showing the connectivity and the hierarchical order of nodes.
Forand the unlike pair ‘SR’ leads to the decision
readand the unlike pair ‘SR’ at ‘C-6’ leads to the decision
For ...the criterion in P-92.5.2.1 are applied...
read ...the criteria in P-92.5.2.1 are applied... >
For ...the configuration at ‘C-2’, ‘C-3’, ‘C-5’, and ‘C-6’ are determined...
read ...the configuration at ‘C-2’, ‘C-3’, ‘C-5’, and ‘C-6’ is determined...
For The seniority of B over A leads to the “R’ configuration for C-6.
read The seniority of B over A leads to the ‘R’ configuration for C-6.
For ...two of the ligands of chiral center ‘C-6’...
read ...two of the ligands of chirality center ‘C-6’...
For ...ranking of the chiral centers in both ligands...
read ...ranking of the chirality centers in both ligands...
For ...reference descriptor is ‘S’.
read ...reference descriptor is ‘S’.
For ...priority of f the branch...
read ...priority of the branch...
For In branch A, both descriptors (‘R’ and ‘S’) are used as reference descriptors...
read In branch A, both descriptors (‘R’ and ‘S’) are used as reference descriptors...
For Explanation:
read Note:
For The configuration at ‘C-2’ and ‘C-6’ is determined...
read Explanation: The configuration at ‘C-2’ and ‘C-6’ is determined...
For ...reflection-variant (see Example 6, below).
read ...reflection-variant (see Example 5, below).
For ... ‘S0’ ate used ...
read ... ‘S0’ are used ...
For ‘The configuration at ‘C-3’ and for...
read ‘The configuration at ‘C-4’ and for...
For ...a sterically unrelated set of chiral centers...
read ...a stereochemically unrelated set of chirality centers...
For rac-(2R,3R)-3-bromobutan-2-ol (PIN
read rac-(2R,3R)-3-bromobutan-2-ol (PIN)
For Examples:
read Example:
For 2-ambo-(2R,4′R,8′R)-α-tocopherol (refs. 27, 37, 44)
read 2-ambo-(2R,4′R,8′R)-α-tocopherol (refs. 37, 44)
read 2-ambo-(2R)-2,5,7,8-tetramethyl-2-[(4R,8R)-4,8,12-trimentltridecyl]-3,4-dihydro-2H-1-benzopyran-6-ol
For P-93.2.1 General methodogy
read P-93.2.1 General methodology
For P-93.2.2 Azanium (ammonium) and phosphanium (phosphonium) salts
read P-93.2.2 Azanium (ammonium) and phosphanium (phosphonium) compounds
For P-93.2.3 Amine oxides and phosphine oxides
read P-93.2.3 Amine oxides and phosphane oxides
For ...of any chiral center with four ligands...
read ...of any chirality center with four ligands...
Replace the structure with:
Replace the structure with:
Add [(S)-ethyl(methyl)(phenyl)azaniumyl]oxidanide
For Example:
read Examples:
For ...indicating how may ligands...
read ...indicating how many ligands...
For ...; the symbol (T-4)] is not used...
read ...; the symbol (T-4) is not used...
For The configurational index of a see-saw
read The configuration index of a see-saw
For ...bipyramid (see Rule IR-9.3.3.6) consists...
read ...bipyramid (see Rule IR-9.3.3.6, ref. 12) consists...
For ...(see SP-9.2, ref. 12)
read ...(see SP-9.2, ref. 8)
For ...of a octahedron (see Rule...
read of an octahedron (see Rule...
Exchange the two structures so that the name has locants and the explanation has priorities.
For ...the locant of the chiral center is included ..
read ...the locant of the chirality center is included ...
For ...and other chiral centers are specified..
read ...and other chirality centers are specified...
For ... as indicated in P-91.3; parentheses enclose the complete descriptor ...
read ... as indicated in P-91.3; brackets enclose the complete descriptor ...
For ...symbol (±) may be used in...
read ...symbol (+) or (–) may be used in...
For ...symbol (±) may be used...
read ...symbol (±), (+) or (–) may be used...
For ...amino acids peptides (P-103.2.1), and lipids...
read ...amino acids peptides (P-103.1.3), and lipids...
For ...of Sequence Rule (5) generates...
read ...of Sequence Rule 5 generates...
For ...of Sequence Rule (5) generates...
read ...of Sequence Rule 5 generates...
For ...configuration (see P-45.6.4);
read ...configuration (see P-45.6.3);
For P-93.4.2.3 Cumulenes havings an odd number of double bonds
read P-93.4.2.3 Cumulenes having an odd number of double bonds
For ...are ‘exo’ to the chain (see fourth example below)...
read ...are ‘exo’ to the chain (see fifth example below)...
For ..., but the name is placed in parentheses as indicated in P-93.2.1.
read ..., but the stereodescriptor is placed in parentheses as indicated in P-91.3.
For ... by one unit. Composite locants are used only when locants are not consecutive...
read ... by one unit. Compound locants are used only when locants are not consecutive...
For (1Ra )-1,3-dichloropropa-1,2-diene
read (1Ra)-1,3-dichloropropa-1,2-diene [delete space in name]
For ... by one unit. Composite locants are used only...
read ... by one unit. Compound locants are used only...
Delete amidinomycin
For ...chiral isomer, sequence rule 4 is applied exhaustively; then, sequence rule 5 (see P-92.6) is used...
read ...chiral isomer, Sequence Rule 4 is applied exhaustively; then, Sequence Rule 5 (see P-92.6) is used...
For ...center at 'C-1' s located on a reentrant angle.
read ...center at 'C-1' is located on a reentrant angle.
For ...‘R*’ stereodescrirptor]
read ...‘R*’ stereodescriptor]
For ...named as a suffix, then that the ligand of the pair of ligands having the lowest number and which is higher ranking...
read ...named as a suffix, then one of the ligands having the lowest locant and higher ranking...
For ... other isomers are described in P-92.5.2.1 and P-93.5.1.1.2(b).]
read ... other isomers are described in P-92.5.2.2 and P-93.5.1.1.2(b).]
For P-93.5.4.1 Specification of cyclic double bonds
read P-93.5.1.4.1 Specification of cyclic double bonds
read P-93.5.1.4.2 Specification of exo-cyclic double bonds
For ...‘cis’, is denoting the configuration of the cyclic double bonds (double bonds that are included in the ring) is permanently omitted to. From...
read ...‘cis’, denoting the configuration of the cyclic double bonds (double bonds that are included in the ring) is permanently omitted. From...
For (1Z,3Z,5Z,7Z,9Z)-cyclodeca- 1,3,5,7,9-pentaene (PIN)
read (1Z,3Z,5Z,7Z,9Z)-cyclodeca-1,3,5,7,9-pentaene (PIN) [delete space in name]
For [lowest locants are assigned to the ‘Z’ double bond; see P-14 (j)]
read [lowest locants are assigned to the ‘Z’ double bond; see P-14.4 (j)]
For The stereodescriptors ‘M’, ‘P’, ‘Ra’, or ‘Sa’ are used to denote ...
read The stereodescriptors ‘M’, ‘P’, ‘Rp’, or ‘Sp’ are used to denote ...
For ...corresponding prefix is then placed in parentheses, or any nesting symbol required, as discussed in P-93.2.1.
read ...corresponding prefix is then placed in enclosing marks.
For 1-chloro-2-[(2E)-ethylidene]-2H-indene
read 1-chloro-2-[(E)-ethylidene]-2H-indene
Replace This method is valid only when the double bonds and the ring form a linear system. Angular systems are specified by method (a).
by This method is only valid with a 2n-membered monocyclic ring substituted in opposite positions. Otherwise method (a) is used.
Add 1-[(Z)-ethylidene]-3-[(E)-ethylidene]cyclopentane
For simplified digraph for 2 and 3in the renumbered structure
read simplified digraph for 2 and 3 in the renumbered structure [insert a space after 3]
Add (4s,4′s)-4,4′-diethyl-1,1′-bi(cyclohexylidene)
add cis-4,4′-diethyl-1,1′-bi(cyclohexylidene)
For P-93.5.2.2 Specification of relative configuration: descriptors ‘endo’, ‘exo’, ‘syn’, ‘anti’, ‘cis’, and ‘trans’
read P-93.5.2.2 Relative configuration
For Explanation. The configuration of the double bond...
read Explanation: The configuration of the double bond...
For ...stereodescriptor 'seqCis0' and 'seqTrans0' for the double bonds 'C-1=C-1′'; priority being assigned to 'seqCis0' according...
read ...stereodescriptor 'seqCis' and 'seqTrans' for the double bonds 'C-1=C-1′'; priority being assigned to 'seqCis' according...
Add at the end of the explanation:
Note: While there is a cis arrangement of substituents, CIP descriptors include E which cannot be used alone to describe the configuration of the structure.
For ...as described in P-91.2.1.
read ...as described in P-93.1.2 and P-93.1.3.
For (1R,3s,5S)- 8-azabicyclo[3.2.1]octan-3-ol
read (1R,3s,5S)-8-azabicyclo[3.2.1]octan-3-ol. [Deleted space from name]
For Cumulene systems included in cyclic systems are treated as discussed in P-93.4.2 ...
read Cumulene systems included in cyclic systems are treated as discussed in P-93.4.2.2 ...
For ...Compound locants (see P-14.3 and P-31.1.1.1) are used...
read ...Compound locants (see P-14.3 and P-31.1.4.2) are used...
For ...‘Xabcd’, here ‘a’ > ‘b’ > ‘c’ > ‘d’
read ...‘Xabcd’, where ‘a’ > ‘b’ > ‘c’ > ‘d’ [corrected 2 September 2020]
For P-93 5.3.5 Axial chirality of spiro compounds
read P-93.5.3.5 Axial chirality of spiro compounds
Replace structure with:
Reorder part (a), (b) and (c) to part (b), (c) and (a) and change the letters accordingly.
For spiro[4.5]dec-2-ene (PIN
read spiro[4.5]dec-2-ene (PIN)
Replace with:
For P-93.5.5.2 Specification of chiral centers
read P-93.5.5.2 Specification of chirality centers
For ...with the methodogy described in P-92.1.2.1.3...
read ...with the methodology described in P-92.1.2.1.3...
For (11M )-1,4(1,4)-dibenzenacyclohexaphane-12-carboxylic acid (PIN)
read (11M)-1,4(1,4)-dibenzenacyclohexaphane-12-carboxylic acid (PIN) [delete space from name]
For (11M,44P)- 43-bromo-1,4(1,4)-dibenzenacyclohexaphane-12-carboxlic acid (PIN)
read (11M,44P)-43-bromo-1,4(1,4)-dibenzenacyclohexaphane-12-carboxlic acid (PIN) [remove space from name]
For P-93.5.5.2 Specification of chiral centers
read P-93.5.5.2 Specification of chirality centers
For Inherently chiral substitution pattern
read Type 2 Inherently chiral substitution pattern
For Is the original compound chiral
read Is the original compound chiral ?
For The two fullerenes molecules...
read The two fullerene molecules...
For Thus, the fullerene on the left hand side below...
read Thus, the fullerene on the right hand side below...
For ...The fullerene on the right hand side is (f,sA)-(C76-D2)[5,6]fullerene...
read ...The fullerene on the left hand side is (f,sA)-(C76-D2)[5,6]fullerene...
For ...used by Chemical Abstracts Service (ref. 21).
read ...used by Chemical Abstracts Service (ref. 22).
For (f,sA)-2H-5-aza -(C76-D2)[5,6]fullerene (PIN)
read (f,sA)-2H-5-aza-(C76-D2)[5,6]fullerene (PIN) [delete space in name]
For...fullerene is due to only to nonidentities...
read ...fullerene is due only to nonidentities...
For ...among the substituents are have a noninherently...
read ...among the substituents have a noninherently...
For ...indicated in P-93-5.6.2, in conformity...
read ...indicated in P-93.5.6.2, in conformity...
For ...to Sequence Rules 1 or 2 (see P-91.1.1). In the...
read ...to Sequence Rules 1 or 2 (see P-92.2 and P-92.3). In the...
For ...parent fullerene and it substitution pattern would...
read ...parent fullerene and its substitution pattern would...
For ...(C70-D5h(6))[5,6]fullerene-3′,3′,3′′,3′′-tetracarboxylate
read ...(C70-D5h(6))[5,6]fullerene-3′,3′,3′′,3′′-tetracarboxylate (PIN)
For ...(C70-D5h(6))[5,6]fullerene-3′,3′,3′′,3′′-tetracarboxylate
read ...(C70-D5h(6))[5,6]fullerene-3′,3′,3′′,3′′-tetracarboxylate (PIN)
For P-93.5.7.3 Specification of double bonds in unsaturated rings and ring systems
read P-93.5.7.3 Specification of double bonds in unsaturated alicyclic ring assemblies
For ...may be used as described in P-93.5.2.2.2.
read ...may be used as described in P-93.5.1.2.
For ...must be are specified...
read ...must be specified...
For P-94 CONFORMATION AND CONFOMATIONAL DESCRIPTORS
read P-94 CONFORMATION AND CONFOMATIONAL STEREODESCRIPTORS
For (a) if all atoms...
read (1) if all atoms...
read (2) if one of a set...
read (3) if all of a set...
For Two atoms or groups attached to two adjacent stoms are...
read Two atoms or groups attached to two adjacent atoms are...
For ... or ‘anti’ are not recommended in ...
read ... or ‘anti’ are not recommended in ...
For ...peptide (ref. 27), carbohydrate (ref. 26),...
read ...peptide (ref. 18), carbohydrate (ref. 27)...
For ...and lipid (ref. 8) nomenclature...
read ...and lipid (ref. 48) nomenclature...
For ...the structure of a new natural product has been...
read ...the structure of a simple new natural product has been...
For ...P-14.7, P-52 and P-58.2,...
read ...P-14.7, P-25.7 and P-58.2,...
For ...configuration of all chiral centers and the configuration...
read ...configuration of all chirality centers and the configuration...
For At chiral centers, the ‘α/β’ system is used...
read At chirality centers, the ‘α/β’ system is used...
For ...as described or in IUPAC-...
read ...as described in IUPAC-...
For ...configurations at brigeheads ‘C-9’ and ‘C-10’ are inverted...
read ...configurations at bridgeheads ‘C-9’ and ‘C-10’ are inverted...
For ...in configuration of a nonbrigeheaded side chain that...
read ...in configuration of a nonbridgeheaded side chain that...
For ...opened and two chiral centers are created...
read ...opened and two chirality centers are created...
For aspidofractidnine
read aspidofractinine
For oxyacanthan read 18-oxayohimban
For prostane read porphyrin
For P-101.3. SKELETAL MODIFICATIONS OF PARENT STRUCTURES
read P-101.3 SKELETAL MODIFICATIONS OF PARENT STRUCTURES
For P-101.3.1 Removal of skeletal atoms
read P-101.3.1 Removal of skeletal atoms without affecting the number of rings
For P-101.3.2 Addition of skeletal atoms
read P-101.3.2 Addition of skeletal atoms without affecting the number of rings
For P-101.3.6 Terminal ring removal
read P-101.3.6 Removal of a terminal ring
For 2,2′-dinor- β,β-carotene
read 2,2′-dinor-β,β-carotene [delete space in name]
For (not 19-methyl-5β-pregnane; extension of side chain is not allowed)
read (not 19-methyl-5β-pregnane; alkyl substitution of a side chain is not allowed)
For ...prescribed by P-101.3.2.2, even though...
read ...prescribed by P-101.3.2.2.2, even though...
For ...hydrogen atom below, ‘(α)’, or above, ‘(β)’, the plane...
read ...hydrogen atom below, ‘α’, or above, ‘β’, the plane...
For ...replaced by hydrogen atoms. A side-chain...
read ...replaced by a hydrogen atom. A side-chain...
For Example:
read Examples:>
For ...(Rule F-4.8, ref. 1;...
read ...(Rule F-4.9, ref. 1;...
Delete the locant 16.
For 10(11)a-homo-9-norergoline
read 10(11)a-homo-9-norergoline (preferred)
For ...the order of prefixes is cyclo/seco/homo/nor are...
read ...the order of prefixes is cyclo/seco/apo/homo/nor are...
For ...order apo/cyclo/homo/nor/seco for the four prefixes
read ...order apo/cyclo/homo/nor/seco for the five prefixes
For 6,7-seco-3a-homopimarane
read 6,7-seco-3a-homopimarane (preferred)
For fundamental parent structure)
read (fundamental parent structure)
For ...and P-51.3 to modify parent structures,...
read ...and P-51.4 to modify parent structures,...
For ...skeletal replacement (‘a’) replacement is also...
read ...skeletal replacement (‘a’) nomenclature is also...
For 8,9′-neolignane
read 8,9′-neolignane (fundamental parent structure)
For ...nomenclature (ref. 39, Carotenoid Rule...
read ...nomenclature (ref. 40, Carotenoid Rule...
For ...the prefixes ‘hydro’ (see P-31.2) and ‘dehydro’ (see P-31.3) are used...
read ...the prefixes ‘hydro’ and ‘dehydro’ (see P-31.2) are used...
For ...‘ene’ or ‘yne’ and by...
read ...‘ene’ or ‘yne’ and ‘anine’ to ‘enine’ or ‘ynine’ and by...
For Example:
read Examples:
For Example:
read Examples:
For ...is not recommended (see P-101-3.7.1).
read ...is not recommended (see P-101.3.7.1).
For Example:
read Examples:
For ...naming esters (see P-65.6.3.5.1). Names...
read ...naming esters (see P-65.6.3.5). Names...
For ...(see ref. 21).
read ...(see ref. 22).
For Example:
read Examples:
For ... has been recently revised (ref. 26). This...
read ... has been recently revised (ref. 27). This...
For Structures, with retained and systematic carbohydrate names, of the...
read Structures, and carbohydrate names, of the...>
For ...See ref. 25 for ...
read ...See ref. 26 for ...
For ...and P-66.1.4.1, respectively...
read ...and P-66.1.5, respectively...
For ethyl (methyl α-D-fructopyranosid)onate (PIN)
read ethyl (methyl α-D-fructopyranosid)onate
For ...drawn should be that one that shows...
read ...drawn should be the one that shows...
For ...(+)-rel- or (-)-rel-, where...
read ...(+)-rel- or (–)-rel-, where...
For ...configuration of sterogenic centers for a compound...
read ...configuration of stereogenic centers for a compound...
For H-[CHOH]m-CO[(CHOH]n-H
read H-[CHOH]m-CO-[CHOH]n-H
For ...atoms present (e.g. ‘aldopentose’, ketohexose’).
read ...atoms present (e.g. ‘aldopentose’, ‘ketohexose’).
For Structures, with retained and systematic carbohydrate names, of the 2-ketoses with three through six carbon atoms
read Structures, with carbohydrate names, of the 2-ketoses with three through six carbon atoms
For ...structure ‘a’ is a tridimensional representation; ...
read ...structure ‘a’ is a three-dimensional representation; ...
For ...the conformation of the...
read ...the configuration of the...
For ...The two stereosiomers are called ...
read ...The two stereoisomers are called ...
For ...The mode of cyclization must be defined completely ...
read ...The structure is defined completely ...
For Examples:
read Example:
For 2-O-acetyl-5-O-methyl-D-mannitoland; 5-O-acetyl-2-O-methyl-D-mannitol,
read 2-O-acetyl-5-O-methyl-D-mannitol; not 5-O-acetyl-2-O-methyl-D-mannitol.
For ...than four chiral centers are named...
read ...than four chirality centers are named...
For ...more than four chiral centers are named...
read ...more than four chirality centers are named...
For ...fewer than four chiral centers) is cited first.
read ...fewer than four chirality centers) is cited first.
For Examples:
read Example:
For D-glycero- D-gluco-heptose
read D-glycero-D-gluco-heptose
read D-gluco-D-glycero-heptose [Deleted spaces from names]
For When sequences of chiral centers are separated by nonchiral centers, the nonchiral centers are ignored, and the remaining set of chiral centers is assigned...
read When sequences of chirality centers are separated by nonchiral centers, the nonchiral centers are ignored, and the remaining set of chirality centers is assigned...
For ...numbered atom of the group of chiral centers next to the anomeric...
read ...numbered atom of the group of chirality centers next to the anomeric...
For ...ignored and the set of chiral centers is given the appropriate...
read ...ignored and the set of chirality centers is given the appropriate...
For ...also that of permanent prefixes described ...
read ...also the prefixes always cited as prefixes in substitutive nomenclature described ...
For (not 2-deoxy-D-allose
read (not 2-deoxy-D-allose)
For Amino sugars and thiosugars and other chalcogen analogues
read Amino sugars
Add 2-amino-2,6-dideoxy-D-glucose
For ...expressed by ‘a’ replacement prefixes...
read ...expressed by an ‘a’ replacement prefixes...
Replace the structure with:
For P-102.5.6.1 O-substitution
read P-102.5.6.1 O-Substitution
For P-102.5.6.4 N-substitution
read P-102.5.6.4 N-Substitution
For P-102.5.6.6 Carboxylic acids derived from monosaccharides
read P-102.5.6.6 Monosaccharide carboxylic acids
For methyl 5-deoxy- β-D-arabinofuranosid-5-yl hydrogen phosphonate
read methyl 5-deoxy-β-D-arabinofuranosid-5-yl hydrogen phosphonate [Deleted space from name]
For ...See ref. 25 for ...
read ...See ref. 27 for ...
For P-102.5.6.3 C-substitution
read P-102.5.6.3 C-Substitution
For P-102.5.6.3.2 Substitution replacing a hydroxy group
read P-102.5.6.3.2 Substitution replacing a nonterminal hydroxy group
For (2R,3R,4R,5S,6S)-6-[(acetyloxy)methyl]-6-bromooxane-2,3,4,5-tetrayl tetraacetate)
read (2R,3R,4R,5S,6S)-6-[(acetyloxy)methyl]-6-bromooxane-2,3,4,5-tetrayl tetraacetate
For Preferred IUPAC names are formed substitutively.
read Preferred names are formed substitutively.
For ...in 2-acetamido (or 2-butylamino)-2-deoxy-D-glucose.
read ...in 2-acetamido-2-deoxy-D-glucose or 2-(butylamino)-2-deoxy-D-glucose.
For 1-deoxy- L-mannitol
read 1-deoxy-L-mannitol [remove space from name]
For Example:
read Examples:
For meso- D-glycero-L-ido-heptitol
read meso-D-glycero-L-ido-heptitol [Deleted space from name]
For (3R,4R,5R)- 5-[(1R)-1,2-dihydroxyethyl]-3,4-dihydroxyoxolan-2-one
read (3R,4R,5R)-5-[(1R)-1,2-dihydroxyethyl]-3,4-dihydroxyoxolan-2-one [Deleted space from name]
For 5-amino-5-deoxy- D-galactono-1,5-lactam
read 5-amino-5-deoxy-D-galactono-1,5-lactam [Deleted space from name]
For Glycosides of glycosides of uronic acids are ...
read Glycosides of uronic acids are ...
Replace the structure with:
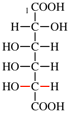
Replace the structure with:
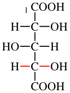
Replace the structure with:
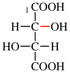
For (-)-tartaric acid
read (–)-tartaric acid
For ...described in P-102.5.6.6.2.1 and P-66.
read ...described in P-102.5.6.6.2.1, P-65 and P-66.
For 6-amino-6-deoxy-6-oxo- D-gluconic acid
read 6-amino-6-deoxy-6-oxo-D-gluconic acid [Deleted space from name]
For methyl 6-amino-6-deoxy-6-oxo- D-gluconate
read methyl 6-amino-6-deoxy-6-oxo-D-gluconate [Deleted space from name]
Delete, duplicate of it in P-102.6.1.2 page 1385
For ...; acetophenone cannot be substituted (see P-64.2.2.1).
read ...; acetophenone cannot be substituted (see P-64.2.1.2).
For ...acyclic amide, propanamide)
read ...acyclic amide, propanamide.
For Examples:
read Example:
For 6-(β- D-glucopyranosyl)-5,7-dihydroxy-2-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-4H-1-benzopyran-4-one
read 6-(β-D-glucopyranosyl)-5,7-dihydroxy-2-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-4H-1-benzopyran-4-one. [Deleted space from name]
For Example:
read Examples:
For ...P-102.6.1.2; a carbocylic acid is senior to...
read ...P-102.6.1.2; a carboxylic acid is senior to...
For ...of this type is name as a...
read ...of this type is named as a...
For ... ‘Nomenclature and Symbolism for Amino Acids and Peptides’ (ref. 27). A...
read ... ‘Nomenclature and Symbolism for Amino Acids and Peptides’ (ref. 18). A...
For (2S,3S)-2-amino-3-methylpentanoic acid (see P-103.1.3.2.2 for...
read rel-(2R,3R)-2-amino-3-methylpentanoic acid (see P-103.1.3.2.1 for...
For (2S,3R)-2-amino-3-hydroxybutanoic acid (see P-103.1.3.2.2 for...
read rel-(2R,3S)-2-amino-3-hydroxybutanoic acid (see P-103.1.3.2.1 for...
For ... peptides’ (ref. 27) must...
read ... peptides’ (ref. 18) must...
For 2-amino-3-methylpentanoic acid (see P-103.1.3.2.2 for...
read rel-(2R,3S)-2-amino-3-methylpentanoic acid (see P-103.1.3.2.1 for...
For 2-amino-3-hydroxybutanoic acid (see P-103.1.3.2.2 for...
read rel-(2R,3R)-2-amino-3-hydroxybutanoic acid (see P-103.1.3.2.1 for...
For 3,3 ′-disulfanediyldialanine
read 3,3′-disulfanediyldialanine [delete space from name]
For ...illustrated in CP-13 in ref. 27...
read ...illustrated in 3AA-15.2.3 in ref. 18...
For ...(see 3AA-15.2.3, ref.27).
read ...(see 3AA-15.2.3, ref. 18).
For The carbon atoms in proline are numbered as in pyrrolidine, the nitrogen atoms being numbered ‘1’, and the carboxy group ‘2’.
read The atoms in proline are numbered as in pyrrolidine, the nitrogen atom being numbered ‘1’, and the carbon atom bonded to the carboxy group is numbered ‘2’.
For ...compounds is termed ‘racemic’ and...
read ...compounds is termed a ‘racemate’ and...
For (3R)-3-hydroxy- L-proline (PIN)
read (3R)-3-hydroxy-L-proline
read cis-3-hydroxy-L-proline [delete spaces from names]
For (3S)-3-hydroxy- L-proline (PIN)
read (3S)-3-hydroxy-L-proline
read trans-3-hydroxy-L-proline [Deleted spaces from names]
For...‘Nα’, , ‘Nπ’ and ‘Nτ’ for histidine...
read ...‘Nα’, ‘Nπ’ and ‘Nτ’ for histidine...
For P-103.2.7 Amides and other nitrogeneous derivatives
read P-103.2.7 Amides, anilides, hydrazides, and other nitrogeneous analogues
For P-103.2.7 Aldehydes, ketones and alcohols
read P-103.2.8 Alcohols, aldehydes, ketones, and nitriles
Replace the structure with:
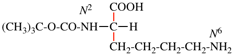
For ...a carbon atom carbon atom of an...
read ...a carbon atom
For Examples
read Example:
For (2S)-2-amino-β-alanine (see ref. 27)
read (2S)-2-amino-β-alanine (see ref. 18)
For 2-(3,5-dihydroxyphenyl)- L-glycine
read 2-(3,5-dihydroxyphenyl)-L-glycine [delete space in name]
For N-(1-deoxy- α -D-fructopyranos-1-yl)-L-alanine
read N-(1-deoxy-α-D-fructopyranos-1-yl)-L-alanine [ delete spaces in name]
For ...rather than as 2-ammoniumylpropanoate or 2-ammoniopropanoate as...
read ...rather than as 2-azaniumylpropanoate, 2-ammoniumylpropanoate or 2-ammoniopropanoate as...
For ...as in Chapter 7 (P-74.1.3)
read ...as in Chapter 7 (P-74.1.3).
For sodium glutamate(1–)
read sodium glutamate
For ...an anion the ending ‘ate; replaces...
read ...an anion the ending ‘ate’ replaces...
For P-103.2.3.3.2
read P-103.2.4.3.2
For ...(strictly each has one positive charge and two negative charges, but this...
read ...(strictly each has two positive charges and one negative charge, but this...
For ...refers to net charge) and may be ...
read ...refers to net charge) may be ...
For ... by the phrase ‘monocation, or by stating...
read ... by the phrase ‘monocation’, or by stating...
For P-103.2.3.4 Zwitterionic amino acids are named in two ways:
read P-103.2.4.4 Zwitterionic amino acids are named in two ways:
For S-methyl-l-cysteine zwitterion
read S-methyl-L-cysteine zwitterion
For ...derived from ‘cystine’ (see 103.1.1.2).
read ...derived from ‘cystine’ (see P-103.1.1.2).
For aspart-1- yl
read aspart-1-yl [delete space from name]
For Example:
read Examples:
For P-103.2.7 Amides, anilides, hydrazides, and other nitrogeneous analogues
read P-103.2.7 Amides, anilides, hydrazides, and other nitrogenous analogues
Add
The 1-amides of aspartic acid and glutamic acid are named as follows:
HO-CO-CH2-CH(NH2)-CO-NH2 HO-CO-CH2-CH2-CH(NH2)-CO-NH2
3,4-diamino-4-oxobutanoic acid 4,5-diamino-5-oxopentanoic acid
aspartic 1-amide glutamic 1-amide
For Alcohols, aldehydes and ketones corresponding...
read Alcohols, aldehydes, ketones, and nitriles corresponding...
For ...The endings ‘ol’, ‘al’, and ‘onitrile’...
read ...The endings ‘ol’, ‘al’, ‘one’, and ‘onitrile’...
For ...study by the IUPAC of Chemical Nomenclature and Structure Representation Division.
read ...study by the IUPAC Chemical Nomenclature and Structure Representation Division.
For ...found in natural amino acids (see Table 10.4):
read ...found in ‘common’ amino acids (see Table 10.4):
For Those formed between ‘C-1’ of one amino acid and a nitrogen atom ‘N-2’ of another amino acid are called ‘isopeptide bonds’.
read Those formed between an amino group of one amino acid and a carboxy group of another amino acid, which are not ‘eupeptide’ bonds, are called ‘isopeptide bonds’.
For [Lys2]bradykinin[2-
read [Lys2]bradykinin
Insert Examples:
For ...to describe configurations.. Other...
read ...to describe configurations. Other...
For 1L-5-O-ethyl-1,2-di-O-methyl-neo-inositol [(criterion (d)]
read 1L-5-O-ethyl-1,2-di-O-methyl-neo-inositol [criterion (d)]
Add at end of text Systematic names may have different numbering from the corresponding inositol name (see examples 2 and 5).
For P-106.2 Nucleotide diphosphates and triphosphates
read P-106.2 Nucleoside diphosphates and triphosphates
For (ref. 45)
read (ref. 47)
For P-106.2 NUCLEOTIDE DIPHOSPHATES AND TRIPHOSPHATES
read P-106.2 NUCLEOSIDE DIPHOSPHATES AND TRIPHOSPHATES
For ...(see P-102.5). 2- and 3-Deoxy modifications...
read ...(see P-102.5). The 2- and 3-deoxy modifications
For 2′,3′ -O-[(1S,2E)-3-phenylprop-2-ene-1,1-diyl]-5′-adenylic acid
read 2′,3′-O-[(1S,2E)-3-phenylprop-2-ene-1,1-diyl]-5′-adenylic acid [delete space in name]
For ...names for the nucleotide monophosphates by...
read ...names for the nucleoside monophosphates by...
For In general, the 3-sn-phosphatic acids are ...
read In general, the 3-sn-phosphatidic acids are ...
Replace the structure with:
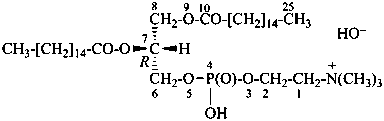
For ...as indicated in P-107.3.1.2]
read ...as indicated in P-107.3.2]
For (4E)- sphing-4-enine
read (4E)-sphing-4-enine [delete space in name]
For (4E)- N-hexadecanoylsphing-4-enine
read (4E)-N-hexadecanoylsphing-4-enine [remove space in name]
For ...Publications, 2005
read ...Publications, 2005.
For ...Steroids (Recommendations 1989)’, 192-246.
read ...Steroids (Recommendations 1989)’, 192-246, Pure Appl. Chem., 61, 1783-1822 (1989).
For ...Tetrapyrroles (Recommendations 1986)’, 278-329.
read ...Tetrapyrroles (Recommendations 1986)’, 278-329, Pure Appl. Chem., 59, 779-832 (1987).
For ...Peptides (Recommendations 1983)’, 39-69.
read ...Peptides (Recommendations 1983)’, 39-69, Pure Appl. Chem., 56, 595-624 (1984).
For ...(1995); Compendium of Chemical Technology, IUPAC Recommendations,...
read ...(1995); Compendium of Chemical Terminology, IUPAC Recommendations,...
For ...Makromoleculare Chem.1959: 29, 164-189 (sp. 169)
read ...Makromoleculare Chem. 29, 164-189 (1959) (particularly 169).
For 1919-008 (1996)
read 1919-2008 (1996)
For ...(1999)
read ...(1999).
For ...78(10), 1897-1970 (2006)
read ...78(10), 1897-1970 (2006).
For ...Cyclitols (Recommendations 1973)’, 149-155.
read ...Cyclitols (Recommendations 1973)’, 149-155, Pure Appl. Chem., 37, 283-297 (1974).
For ...Carotenoids (1970) and Amendments (1973)’, 226-238.
read ...Carotenoids (1970) and Amendments (1973)’, 226-238, Pure Appl. Chem., 41, 405-431 (1975).
For ...Compounds (Recommendations 1981), 239-241.
read ...Compounds (Recommendations 1981), 239-241, Pure Appl. Chem., 54, 1507-1510 (1982).
For ...Corrinoids (Recommendations 1973)’, 272-277.
read ...Corrinoids (Recommendations 1973)’, 272-277, Pure Appl. Chem., 48, 495-502 (1976).
For Applied chemistry and...
read Applied Chemistry and...
For ...2000’, Pure Appl. Chem, 72,1493-1523 (2000)
read ...2000’, Pure Appl. Chem., 72, 1493-1523 (2000).
For ...Constituents (Recommendations 1970)’, 109-114.
read ...Constituents (Recommendations 1970)’, 109-114, Pure Appl. Chem., 40, 277-290 (1974).
For ...Lipids’ (Recommendations 1976),, 180-190.
read ...Lipids’ (Recommendations 1976),, 180-190, Eur. J. Biochem., 79, 11-21 (1977).
For ...enclosing marks (for example chloryl* (not chloroxy).
read ...enclosing marks [for example chloryl* (not chloroxy)].
Add acetylazanylidene* = acetylimino CH3-CO-N= P-62.3.1.2
Add acetylimino = acetylazanylidene* (not acetylazanediyl) CH3-CO-N= P-62.3.1.2
For = tricyclo[3.3.1.13,7]decan-2-y
read = tricyclo[3.3.1.13,7]decan-2-yl
For (also 1- isomer)
read (also 1-isomer) [remove space before isomer]
Add (also 1-isomer)
For P-29.6.
read P-29.6.2.3
Add amidino: see carbamimidoyl*
For [not chlorido(amido)phosphoryl]
read (not chloroamidophosphoryl)
For [(4′-amino[1,1′-biphenyl]-4-yl)amino* = benzidino
read (4′-amino[1,1′-biphenyl]-4-yl)amino* = benzidino
For P-65.1.7.3.1
readP-65.1.7.3.1; P-65.1.7.4.1
For P-29.6.
read P-29.6.2.3; P-57.1.5.3
For P-65.1.7.3.1
read P-65.1.7.3.1; P-65.1.7.4.1
For C-aminocarbonimidoyl = carbamimidoyl* = amino(imino)methyl
read C-aminocarbonimidoyl = carbamimidoyl* = amino(imino)methyl (not amidino)
Add amino(hydrazinylidene)methyl = carbamohydrazonoyl* H2N-C(=N-NH2)– P-66.4.2.3.2
For amino(imino)methyl = carbamimidoyl* = C-aminocarbonimidoyl
read amino(imino)methyl = carbamimidoyl* = C-aminocarbonimidoyl (not amidino)
For (not guanidino)
read = guanidino
For aminooxalyl = oxamoyl* = amino(oxo)acetyl
read aminooxalyl = oxamoyl* = amino(oxo)acetyl (not carbamoylformyl; not carbamoycarbonyl)
For amino(oxo)acetamido = oxamoylamino*
read amino(oxo)acetamido = oxamoylamino* (not carbamoylformamido)
For amino(oxo)acetyl = oxamoyl* = aminooxalyl
read amino(oxo)acetyl = oxamoyl* = aminooxalyl (not carbamoylformyl; not carbamoycarbonyl)
For P-65.2.1.5: P-66.1.4.4
read P-65.2.1.5; P-66.1.4.4
For [(aminosulfanyl)methylidene]amino*
read [amino(sulfanyl)methylidene]amino*
read H2N-C(SH)=N–
For aminosulfonyl = sulfamoyl*
read aminosulfonyl = sulfamoyl* = sulfuramidoyl
For P-29.6.2.3
read P-29.6.2.3; P-57.1.5.3
Add 1-anthryl = anthracen-1-yl* (also 2-, 9-isomers)
For arsanylidene*
read arsanylidene* (not arsinidine)
Add arsinidine: see arsanylidene*
For azanetriyl = nitrilo*
read azanetriyl = nitrilo* (not azanylidyne; not azanylylidene) –N< P-35.2.1; P-62.2.5.1
For P-67.1.4.1.1.2
read P-67.1.4.1.1.2; P-67.1.4.1.2
Delete correction in column 1 and 2.
For benzenecarbohydroximoyl = N-hydroxybenzenecarboximidoyl* = N-hydroxybenzimidoyl
read benzenecarbohydroximoyl = N-hydroxybenzenecarboximidoyl* = N-hydroxybenzimidoyl = benzohydroximoyl
For P-67.1.4.1.1.2
read P-67.1.4.1.1.2; P-67.1.4.1.2
For P-68.3.1.3.2.2
read P-32.1.1; P-68.3.1.3.2.1; P-68.3.1.3.2.2
For P-67.1.4.1.1.1; P-.4.1.1.5
read P-67.1.4.1.1.1; P-67.1.4.1.1.5
For P-67.1.4.1.1.2
read P-67.1.4.1.1.2; P-67.1.4.1.2
For P-65.1.7.2.1
read P-34.2.1.1; P-34.2.2; P-65.1.7.2.1
For (not dithiophthaloyl)
read (not dithiophthaloyl) (also 1,3- and 1,4-isomers)
Add (also phthalimidoyl = 1,2-isomer; and isophthalimidoyl = 1,3-isomers)
For P-65.1.7.3.1
read P-65.1.7.3.1; P-65.1.7.4.2
For P-65.1.7.3.1
read P-65.1.7.3.1; P-65.1.7.4.3
For benzenesulfinamido* = benzenesulfinylamino
read benzenesulfinamido* = (benzenesulfinyl)amino
For benzenesulfinohydrazonamido* = benzenesulfinohydrazonoylamino
read benzenesulfinohydrazonamido* = (benzenesulfinohydrazonoyl)amino
For benzenesulfonylamino = benzenesulfinamido*
read (benzenesulfonyl)amino = benzenesulfinamido*
For benzenesulfonamido* = benzenesulfonylamino
read benzenesulfonamido* = (benzenesulfonyl)amino
For benzenesulfonylamino = benzenesulfonamido*
read (benzenesulfonylamino) = benzenesulfonamido*
For P-65.1.7.2.1
read P-34.2.1.1; P-34.2.2; P-65.1.7.2.1
For [1,1′-biphenyl]-4-yl* (not 4-phenylphenyl]
read [1,1′-biphenyl]-4-yl* (not 4-phenylphenyl)
add bismuthoniumyl = bismuthaniumyl* = bismuthonio H3Bi+– P-73.6
For 1,4-bis(sulfanylidene)butane-1,4-diyl: see butanebis(thioyl)*
read 1,4-bis(sulfanylidene)butane-1,4-diyl = butanebis(thioyl)* = 1,4-dithioxobutane-1,4-diyl (not dithiosuccinyl)
For boranediyl* (not borylene; not boranylidene)
read boranediyl* (not borylene; not boranylidene; not borylidene)
For boranetriyl*
read boranetriyl* (not borylidyne)
For butanebis(thioyl)* (not dithiosuccinyl)
read butanebis(thioyl)* = 1,4-bis(sulfanylidene)butane-1,4-diyl = 1,4-dithioxobutane-1,4-diyl (not dithiosuccinyl)
For butanethioyl* = thiobutyryl = 1-sulfanylidenebutyl
read butanethioyl* = thiobutyryl = 1-sulfanylidenebutyl = 1-thioxobutyl
For P-29.3.1; P-67.1.4.2; P-68.1.2
read P-29.3.1; P-67.1.4.2
For P-65.1.7.3.1
read P-65.1.7.3.1 P-65.1.7.4.1
For P-65.1.7.4.1
read P-65.1.7.3.2; P-65.1.7.4.1
For P-65.1.7.3.1
read P-65.1.7.3.1; P-65.1.7.4.1
For (not sec-butyl)
read (not sec-butyl; not but-2-yl)
For butan-2-yloxy* = 1-methylpropoxy (not sec-butoxy)
read (butan-2-yl)oxy* = 1-methylpropoxy (not sec-butoxy; not sec-butyloxy)
For P-65.1.7.3.1
read P-65.1.7.3.1 P-65.1.7.4.1
For P-65.1.7.3.1
read P-65.1.7.3.1 P-65.1.7.4.1
For but-2-enoyl*
read but-2-enoyl* (not crotonyl)
For sec-butyloxy: see butan-2-yloxy
read sec-butyloxy: see (butan-2-yl)oxy
Add but-2-yl: see butan-2-yl*
For tert-butyl (unsubstituted*) = 2-methylpropan-2-yl*
read tert-butyl* (unsubstituted) = 2-methylpropan-2-yl
Delete (not sec-butoxy)>
For tert-butyloxy: see tert-butoxy (unsubstituted*)
read tert-butyloxy: see tert-butoxy* (unsubstituted)
For (not guanidino)
read = guanidino
For (not guanidino)
read = guanidino
For carbamoylformamido = oxamoylamino* = amino(oxo)acetamide H2N-CO-CO-NH– P-66.1.1.4.5.1
read carbamoylformamido: see oxamoylamino*
For P-65.1.7.4.1
read P-65.1.7.3.2; P-65.1.7.4.1
For P-65.1.7.3.1
read P-65.1.7.3.1; P-65.1.7.4.1
For carbonimidoyl
read carbonimidoyl*
For carbonocyanidoyl* = cyanocarbonyl
read carbonocyanidoyl* = cyanocarbonyl = carbononitridoylcarbonyl
For (not hydrazinocarbonimidoyl)
read (not C-hydrazinocarbonimidoyl)
Add carbononitridoyl(disulfanyl) = cyanodisulfanyl* = carbononitridoyldithio (not thiocyanatosulfanyl) NC-SS– P-65.2.2
carbononitridoyldithio = cyanodisulfanyl* = carbononitridoyl(disulfanyl) (not thiocyanatosulfanyl) NC-SS– P-65.2.2
For carbononitridoylcarbonyl see carbonocyanidoyl*
read carbononitridoylcarbonyl = carbonocyanidoyl* NC-CO– P-65.2.1.5
Add carbononitridoyl(disulfanyl) = cyanodisulfanyl* NC-SS– P-65.2.2
For carbononitridoylselanyl’
read carbononitridoylselanyl
For carbononitridoyltellanyl = tellurocyanate*
read carbononitridoyltellanyl = tellurocyanato*
For carbononitridoylthio = thiocyanato* = carbononitridosulfanyl
read carbononitridoylthio = thiocyanato* = carbononitridoylsulfanyl
For P-65.2.2
read P-65.2.2; P-66.5.1.1.4
For carbonoperoxoyl* = hydroperoxycarbonyl
read carbonoperoxoyl* = (hydroperoxy)carbonyl (not peroxycarboxy)
For carboxycarbonyl = oxalo* = hydroxy(oxo)acetyl (not carboxyformyl)
read carboxycarbonyl = oxalo* [not carboxyformyl; not hydroxy(oxo)acetyl]
For (carboxycarbonyl)oxy = oxalooxy*
read (carboxycarbonyl)oxy = oxalooxy* [not (carboxyformyl)oxy]
For (carboxycarbonyl)sulfanyl = oxalosulfanyl*
read (carboxycarbonyl)sulfanyl = oxalosulfanyl* = (carboxycarbonyl)thio [not (carboxyformyl)sulfanyl; not (carboxyfomyl)thio]
For (carboxycarbonyl)thio = oxalosulfanyl*
read(carboxycarbonyl)thio = oxalosulfanyl* = (carboxycarbonyl)sulfanyl [not (carboxyformyl)sulfanyl; not (carboxyfomyl)thio]
For P-65.2.1.7
read P-65.1.5.3, P-65.2.1.7
For P-65.1.7.2.4
read P-65.1.7.2.4; P-65.2.1.5
For P-65.1.7.2.4
read P-65.1.7.2.4; P-65.2.1.5
For P-65.1.7.2.1
read P-65.1.2.2.3; P-65.1.7.2.1
For P-65.1.7.2.4
read P-65.1.7.2.4; P-65.2.1.5
For P-65.1.7.2.4
read P-65.1.7.2.4; P-65.2.1.5
Add P-65.1.2.2.3 [for 3-carboxy-3-oxopropyl*]
For chlorocarbonyl = carbonochloridoyl*
read chlorocarbonyl = carbonochloridoyl* (not chloroformyl)
For cyanodisulfanyl* = carbononitridoyl(disulfanyl) (not thiocyanatosulfanyl)
read cyanodisulfanyl* = carbononitridoyl(disulfanyl) = carbononitridoyldithio (not thiocyanatosulfanyl)
For cyano(isocyanato)(phosphorothioyl) = phosphorocyanidoisocyanatidothioyl* = cyano(isocyanato)(thiophosphoryl)
read cyano(isocyanato)phosphorothioyl = phosphorocyanidoisocyanatidothioyl* = cyano(isocyanato)(thiophosphoryl)
For cyano(isocyanato)(thiophosphoryl) = phosphorocyanidoisocyanatidothioyl* = cyano(isocyanato)(phosphorothioyl)
read cyano(isocyanato)(thiophosphoryl) = phosphorocyanidoisocyanatidothioyl* = cyano(isocyanato)phosphorothioyl
For P-67.1.4.4.2
read P-65.3.2.3; P-67.1.4.4.2
For P-65.1.7.3.1
read P-65.1.7.3.1 P-65.1.7.4.1
For P-66.5.1.1.4
read P-65.2.2; P-66.5.1.1.4
For cyclohexanecarboximidoyl* (not C-cyclohexylcarbonimidoyl)
read cyclohexanecarboximidoyl* = cyclohexylcarbonimidoyl = cyclohexyl(imino)methyl (not C-cyclohexylcarbonimidoyl)
For cyclohexanylidene = cyclohexylidene*
read cyclohexanylidene = cyclohexylidene* (see also: cyclohexane-1,1-diyl)
rAdd cyclohexylcarbonimidoyl = cyclohexanecarboximidoyl* = cyclohexyl(imino)methyl (not C-cyclohexylcarbonimidoyl) C6H11-C(=NH)– P-65.1.7.4.2
Add cyclohexylcarbonimidoyl = cyclohexanecarboximidoyl* C6H11-C(=NH)– P-65.1.7.4.2
For cyclohexylcarbonyl: see cyclohexanecarbonyl*
read cyclohexylcarbonyl = cyclohexanecarbonyl* = cyclohexyl(oxo)methyl
For cyclohexylidene* = cyclohexanylidene
read cyclohexylidene* = cyclohexanylidene (see also: cyclohexane-1,1-diyl) C6H10= P-29.3.3
Add cyclohexyl(oxo)methyl = cycohexanecarbonyl* = cyclohexylcarbonyl C6H11-CO– P-65.1.7.4.2
Add cyclopentanecarbohydrazonoyl* = cyclopentyl(hydrazinylidene)methyl C5H9-C(=NNH2)– P-65.1.7.4.2
For cyclopentanecarboximidoyl* = cyclopentyl(imino)methyl = C-cyclopentylcarbonimidoyl P-65.1.7.2.4
read cyclopentanecarboximidoyl* = cyclopentyl(imino)methyl = cyclopentylcarbonimidoyl (not C-cyclopentylcarbonimidoyl) P-65.1.7.4.2
Add: cyclopentylcarbonimidoyl = cyclopentanecarboximidoyl* = cyclopentyl(imino)methyl (not C-cyclopentylcarbonimidoyl) C5H9-C(=NH)– P-65.1.7.4.2
For cyclopentyl(hydrazinylidene)methyl: see cyclopentanecarbohydrazonoyl*
read cyclopentyl(hydrazinylidene)methyl = cyclopentanecarbohydrazonoyl* C5H9-C(=NNH2)– P-65.1.7.4.2
For cyclopentyl(imino)methyl: see cyclopentanecarboximidoyl*
read cyclopentyl(imino)methyl = cyclopentanecarboximidoyl* = cyclopentylcarbonimidoyl (not C-cyclopentylcarbonimidoyl) C5H9-C(=NH)– P-65.1.7.4.2
For cyclopropanyl = cyclopropyl*
read cyclopropanyl = cyclopropyl* C3H5– P-29.3.3
For cyclopropylidene* = cyclopropanylidene
read cyclopropylidene* = cyclopropanylidene C3H4= P-29.3.3
For P-29.3.3
read P-29.2; P-29.3.3
For decan-1-yl = see decyl*
read decan-1-yl = decyl*
For diacetylamino = N-acetylacetamido*
read diacetylamino = N-acetylacetamido* (not diacetylazanyl; not diacetamido)
For diazanylidenemethylidene = hydrazinylidenemethylidene*
read diazanylidenemethylidene = hydrazinylidenemethylidene* (not hydrazonomethylidene)
For P-29.3.2.2; P-3.2.1
read P-29.3.2.2; P-29.3.2.1
For dihydroarsoryl = arsinoyl*
read dihydroarsoryl = arsinoyl* (not arsinyl)
For dihydronitroryl = azinoyl*
read dihydronitroryl = azinoyl* (not azinyl)
For dihydrophosphorimidoyl = phosphinimidoyl*
read dihydrophosphorimidoyl = phosphinimidoyl* = imidophosphinoyl
For dihydrophosphorothioyl = phosphinothioyl*
read dihydrophosphorothioyl = phosphinothioyl* = thiophosphinoyl
For dihydrophosphoryl = phosphinoyl*
read dihydrophosphoryl = phosphinoyl* (not phosphinyl)
For dihydrostiborimidoyl = stibinimidoyl*
read dihydrostiborimidoyl = stibinimidoyl* = imidostibinoyl
Add dihydroxyarsoryl = arsono* (HO)2As(O)– P-67.1.4.1.1.1
For P-68.3.1.3.2.1; P-68.3.1.3.2.2
read P-32.1.1; P-68.3.1.3.2.1; P-68.3.1.3.2.2
For P-68.3.1.3.5.2
read P-34.2.1.3, P-68.3.1.3.5.2
For P-68.3.1.3.5.2
read P-34.2.1.3, P-68.3.1.3.5.2
For P-67.1.4.1.1.6
read P-67.1.4.1.1.6; P-68.3.2.3.2.2
For P-67.1.4.1.2
read P-67.1.4.1.1.2; P-67.1.4.1.2
For P-67.1.4.1.2
read P-67.1.4.1.1.2; P-67.1.4.1.2
For P-67.1.4.1.2
read P-67.1.4.1.1.4; P-67.1.4.1.2
For P-67.1.4.1.2
read P-67.1.4.1.1.4; P-67.1.4.1.2
For P-67.1.4.1.2
read P-67.1.4.1.1.2; P-67.1.4.1.2
For P-67.1.4.1.2
read P-67.1.4.1.1.4; P-67.1.4.1.2
For P-67.1.4.1.2
read P-67.1.4.1.1.4; P-67.1.4.1.2
For P-67.1.4.1.2
read P-67.1.4.1.1.2; P-67.1.4.1.2
For 1,2-diiminoethane-1,2-diyl
read diiminoethanediyl
For 1,1-dimethylethoxy = (2-methylpropan-2-yl)oxy* = tert-butoxy (unsubstituted*)
read 1,1-dimethylethoxy = (2-methylpropan-2-yl)oxy = tert-butoxy* (unsubstituted)
For 1,1-dimethylethyl = tert-butyl (unsubstituted*) = 2-methylpropan-2-yl*
read 1,1-dimethylethyl = tert-butyl* (unsubstituted) = 2-methylpropan-2-yl
For P-67.1.4.1.1.1
read P-67.1.4.1.1.1; P-67.1.4.1.1.5
For P-65.1.7.2
read P-65.1.7.2.2
Add 1,3-dioxo-1,3-dihydro-2H-isoindol-2-yl* = phthalimido  P-66.2.2
P-66.2.2
For P-29.4.1; P-29.6.3
read P-29.6.3; P-57.1.4
For P-65.1.7.3.1
read P-65.1.7.3.1 P-65.1.7.4.1
For P-65.1.7.3.1
read P-65.1.7.3.1 P-65.1.7.4.1
For P-65.1.7.3.1
read P-65.1.7.3.1 P-65.1.7.4.1
For P-67.1.7.2.1
read P-65.1.7.2.1
For P-65.1.7.3.1
read P-65.1.7.3.1; P-65.1.7.4.1
Add 2,5-dioxopyrrolidin-1-yl* = succinimido  P-66.2.2
P-66.2.2
For disilanyl*
read disilanyl* (not disilyl)
Add disilyl: see disilanyl*
For disulfanyl* = dithiohydroperoxy
read disulfanyl* = dithiohydroperoxy (not thiosulfeno)
For P-65.1.7.3.1
read P-65.1.7.3.1 P-65.1.7.4.1
For P-29.3.2.2; P-68.3.2.3.2.2
read P-29.3.2.2; P-45.3.1; P-68.3.2.3.2.2
For P-29.3.2.2; P-68.2.2
read P-29.3.2.2; P-46.1.3
For P-66.1.1.4.5..2
read P-66.1.1.4.5.2
For 1,2-dioxoethane-1,2-diyl = oxalyl*
read dioxoethanediyl = oxalyl*
For dithiocarboperoxoyl* (location of sulfur atoms unknown)
read dithiocarbonoperoxoyl* (location of sulfur atoms unknown)
For dithiohydroperoxy = disulfanyl*
read dithiohydroperoxy = disulfanyl* (not thiosulfeno)
For 1,2-dithiooxolo = hydroxy(sulfanylidene)ethanethioyl*
read 1,2-dithiooxolo: see hydroxy(sulfanylidene)ethanethioyl*
delete HO-CS-CS– P-65.1.7.2.4
For 1,4-dithioxobutane-1,4-diyl: see butanebis(thioyl)*
read 1,4-dithioxobutane-1,4-diyl = butanebis(thioyl)* = 1,4-bis(sulfanylidene)butane-1,4-diyl (not dithiosuccinyl) –CS-CH2-CH2-CS– P-65.1.7.4.1; P-65.1.7.4.3
For HS3O–
read HO-SS2– or HS-S(=S)(=O)–
For episeleno (ring formation*)
read episeleno = selano* (ring formation)
For epitelluro (ring formation*)
read epitelluro = tellano* (ring formation)
For epithio (ring formation*)
read epithio = sulfano* (ring formation)
For epoxy (ring formation*)
read epoxy* (ring formation) (not epoxidano)
Add epoxidano: see epoxy* (ring forming)
For ethanebis(thioyl)* = dithiooxalyl
read ethanebis(thioyl)* = dithiooxalyl = bis(sulfanylidene)ethanediyl
Delete this correction.
For ethanesulfinimidoyl* = ethylsulfinimidoyl
read ethanesulfinimidoyl* = S-ethylsulfinimidoyl
For P-63.5
read P-25.4.2.1.4; P-63.5
For P-63.5
read P-25.4.2.1.4; P-63.5
For P-63.5
read P-25.4.2.1.4; P-63.5
For P-63.5
read P-25.4.2.1.4; P-63.5
For P-66.1.1.4.5..2
read P-66.1.1.4.5.2
For ethoxy* = ethyloxy
read ethoxy* (not ethyloxy)
For (not o-phenetidino)
read (not o-phenetidino; also not m-, or p-)
For P-67.1.7.2.2
read P-65.1.7.2.2
For P-65.2.1.1.2
read P-62.2.1.1.2
For ethylene = ethane-1,2-diyl* (not vinylene)
read ethylene = ethane-1,2-diyl*
For ethylenebis(oxy) = ethane-1,2-diylbis(oxy)*
read ethylenebis(oxy) = ethane-1,2-diylbis(oxy)* (not ethylenedioxy; not ethane-1,2-diyldioxy)
For ethylthio = ethylsulfanyl*
read ethylthio = ethylsulfanyl* CH3-CH2-S– P-63.2.5.1
Add
formazan-1-yl* = (hydrazinylidenemethyl)diazenyl HC(=N-NH2)-N=N– P-34.2.1.3; P-68.3.1.3.5.2
formazan-3-yl* = diazenyl(hydrazinylidene)methyl HN=N-C(=N-NH2)– P-34.2.1.3; P-68.3.1.3.5.2
formazan-5-yl* = (diazenylmethylidene)hydrazinyl HN=N-CH=N-NH– P-34.2.1.3; P-68.3.1.3.5.2
For CH3-CH2-HSb(O)–
read CH3-CH2-SbH(O)–
For P-65.2.1.1.2
read P-62.2.1.1.2
For P-68.3.1.3.5.2
read P-34.2.1.3; P-68.3.1.3.5.2
For P-68.3.1.3.5.2
read P-34.2.1.3;
For formylazanylidene* (not formylimino)
read formylazanylidene = formylimino*
For formylimino: see formylazanylidene*
read formylimino* = formylazanylidene HCO-N= P-66.1.1.4.4
For P-65.1.7.2; P-66.6.3
read P-65.1.7.2; P-66.6.1.3
For P-66.1.1.4.3
read P-66.1.1.4.4
For P-66.1.1.4.3
read P-66.1.1.4.4
For P-65.1.7.3.1
read P-65.1.7.3.1 P-65.1.7.4.1
For P-65.1.7.4.2; P-65-1.7.3.1
read P-65.1.7.4.2; P-65.1.7.3.1
For P-29.6.2.3
read P-29.6.2.3; P-57.1.5.3
For P-29.3
read P-29.6.3
For P-65.1.7.4.2; P-65-1.7.3.1
read P-65.1.7.4.2; P-65.1.7.3.1
For P-29.6.2.3
read P-29.6.2.3; P-57.1.5.3
For P-65.1.7.4.2; P-65-1.7.3.1
read P-65.1.7.4.2; P-65.1.7.3.1
For guanidino: see carbamimidoylamino*
read guanidino = carbamimidoylamino* = carbamimidamido = [amino(imino)methyl]amino H2N-C(=NH)-NH– P-66.4.1.2.1.3
Replace structure with:
Replace structure with:
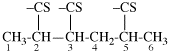
For P-65.1.7.3.1
read P-65.1.1.2.2; P-65.1.7.3.1
For CH3-[CH2]5 -CH=
read CH3-[CH2]5-CH=
For P-65.1.7.4.1
read P-65.1.7.3.1; P-65.1.7.4.1
Add
hydrazinecarbohydrazonoyl* = C-hydrazinylcarbonohydrazonoyl = hydrazinyl(hydrazinylidene)methyl H2N-NH-C(=N-NH2)– P-66.4.3.4.1
hydrazinecarbonyl* = hydrazinylcarbonyl = carbonohydrazidoyl (not carbazoyl; not hydrazinocarbonyl) H2N-NH-CO– P-66.3.2.1
(hydrazinecarbonyl)diazenyl* = (hydrazinylcarbonyl)diazenyl H2N-NH-CO-N=N– P-66.3.1.3.4
For hydrazinecarbonyl* = hydrazinylcarbonyl = carbonohydrazidoyl (not carbazoyl; not hydrazinocarbonyl) H2N-NH-CO— P-66.4.3.4.1
read hydrazinecarbonyl* = hydrazinylcarbonyl = carbonohydrazidoyl (not carbazoyl; not hydrazinocarbonyl) H2N-NH-CO— P-66.4.3.2.1
For P-66.3.5.3; P-68.3.1.2.6.1
read P-66.3.5.3; P-68.3.1.2.6
Add C-hydrazinylcarbonimidoyl = hydrazinecarboximidoyl* = hydrazinyl(imino)methyl = carbonohydrazidimidoyl (not carbazimidoyl; not C-hydrazinocarbonimidoyl) H2N-NH-C(=NH)– P-66.4.2.3.1
For (not hydrazinocarbonyl)
read (not cabazoyl; not hydrazinocarbonyl)
Correction deleted.
Add (hydrazinylcarbonyl)hydrazinylidene = (hydrazinecarbonyl)hydrazinylidene* H2N-NH-CO-NH-N= P-68.3.1.2.6
For hydrazinylidene(hydroxy)methyl = C-hydroxycarbonohydrazonoyl*
read hydrazinylidene(hydroxy)methyl = C-hydroxycarbonohydrazonoyl* [not hydrazono(hydroxy)methyl]
For P-66.3.5.3
read P-66.3.5.3; P-68.3.1.2.6
Add hydrazinylsulfinyl = hydrazinesulfinyl* H2N-NH-SO– P-66.3.2.1
Add hydrazo: see hydrazine-1,2-diyl*
Add hydrazono(hydroxy)methyl: see C-hydroxycarbonohydrazonoyl*
For hydrazonomethylidene = hydrazinylidenemethylidene* H2N=C= P-65.2.1.8
read hydrazonomethylidene: see hydrazinylidenemethylidene*
For hydroperoxycarbonyl = carbonoperoxoyl*
read (hydroperoxy)carbonyl = carbonoperoxoyl* (not peroxycarboxy)
For P-68.3.1.3.5.2
read P-34.2.1.3, P-68.3.1.3.5.2
For P-67.1.4.1.2
read P-67.1.4.1.1.2
For P-67.1.4.1.2
read P-67.1.4.1.1.2; P-67.1.4.1.2
For P-67.1.4.1.2
read P-67.1.4.1.1.2; P-67.1.4.1.2
For P-67.1.4.1.2
read P-67.1.4.1.1.2; P-67.1.4.1.2
For P-67.1.4.1.2
read P-67.1.4.1.1.2; P-67.1.4.1.2
Add hydrotrioxy = trioxidanyl* HO-O-O– P-68.4.1.3
hydrotriseleno = triselanyl* HSe-Se-Se– P-68.4.1.3
hydrotritelluro = tritellanyl* HTe-Te-Te– P-68.4.1.3
Add hydrotrithio = trisulfanyl* HS-S-S– P-68.4.1.3
For = acetohydroximoyl)
read = acetohydroximoyl
For N-hydroxybenzenecarboximidoyl* = N-hydroxybenzimidoyl = benzenecarbohydroximoyl
read N-hydroxybenzenecarboximidoyl* = N-hydroxybenzimidoyl = benzenecarbohydroximoyl = benzohydroximoyl
For N-hydroxybenzimidoyl = N-hydroxybenzenecarboximidoyl* = benzenecarbohydroximoyl
read N-hydroxybenzimidoyl = N-hydroxybenzenecarboximidoyl* = benzenecarbohydroximoyl = benzohydroximidoyl
For (hydroxycarbonothioyl)carbonyl* = hydroxy(thiocarbonyl)carbonyl (not 2-hydroxy-2-thiooxalyl)
read (hydroxycarbonothioyl)carbonyl = hydroxy(thiocarbonyl)carbonyl = hydroxy(sulfanylidene)acetyl* (not 2-thiooxalato; not 2-hydroxy-2-thiooxalyl)
Add hydroxy(imino)methyl = C-hydroxycarbonimidoyl* HO-C(=NH)– P-35.3.2; P-65.1.3.1.2
For P-65.1.3.1.1
read P-35.3.2; P-65.1.3.1.2
For hydroxyselanyl* (not seleneno)
read hydroxyselanyl* = OSe-selenohydroperoxy (not seleneno)
For hydroxy(sulfanylidene)acetyl* (not 2-hydroxy-2-thiooxalo)
read hydroxy(sulfanylidene)aceyl* = (hydroxycarbonothioyl)carbonyl = hydroxy(thiocarbonyl)carbonyl (not 2-thiooxalato; not 2-hydroxy-2-thiooxalyl)
For hydroxy(sulfanylidene)ethanethioyl = hydroxybis(sulfanylidene)ethyl*
read hydroxy(sulfanylidene)ethanethioyl* = hydroxybis(sulfanylidene)ethyl
For hydroxytellanyl = OTe-tellurohydroperoxy = tellureno
read hydroxytellanyl = OTe-tellurohydroperoxy (not tellureno)
For P-61.5.4; P-67.1.4.1.1.6; P-67.1.6
read P-61.5.3; P-67.1.4.1.1.6; P-67.1.6
For P-67.1.4.1.1.5
read P-67.1.4.1.1.5; P-67.1.4.1.1.6
For hydroxy(thiocarbonyl)carbonyl = hydroxy(sulfanylidene)acetyl*
read hydroxy(thiocarbonyl)carbonyl = hydroxy(sulfanylidene)acetyl* = (hydroxycarbonothioyl)carbonyl (not 2-thiooxalato; not 2-hydroxy-2-thiooxalyl)
For 2-hydroxy-2-thiooxalyl = see: hydroxy(carbonothioyl)carbonyl*
read 2-hydroxy-2-thiooxalyl: see hydroxy(sulfanylidene)acetyl*
For imidophosphinoyl = phosphinimidoyl*
read imidophosphinoyl = phosphinimidoyl* = dihydrophosphorimidoyl
Add imidostibinoyl = stibinimidoyl* = dihydrostiborimidoyl H2Sb(=NH)– P-67.1.4.1.1.4; P-67.1.4.1.2
Delete isocyanatosulfonyl* = sulfuroisothiocyanatidoyl (SCN)-SO2– P-67.1.4.4.1
For P-67.1.4.1.1.4
read P-67.1.4.1.1.4; P-67.1.4.1.2
For P-62.3.1.2
read P-35.2.1; P-62.3.1.2
For P-65.1.7.4.1
read P-65.1.7.3.2; P-65.1.7.4.1
For isonicotinoyl = pyridine-4-carbonyl* = 4-pyridylcarbonyl
read isonicotinoyl = pyridine-4-carbonyl* = 4-pyridylcarbonyl = oxo(pyridin-4-yl)methyl
For isopropoxy = (propan-2-yl)oxy* = 1-methylethoxy
read isopropoxy = propan-2-yloxy* = 1-methylethoxy
For P-29.6.2.2
read P-29.3.2.2; P-29.4.1; P-29.6.2.2
For P-29.3.4
read P-29.3.4.1; P-57.1.5.3
For P-67.1.4.4.1
read P-61.8
For 7- isoquinolyl
read 7-isoquinolyl
For = (2Z)-1,4-dioxobut-2-en-1,4-diyl
read= (2Z)-1,4-dioxobut-2-ene-1,4-diyl
For methanehydrazonohydrazido* = 2-methanehydrazonoylhydrazine-1-yl = 2-(hydrazinylidenemethyl)hydrazin-1-yl
read methanehydrazonohydrazido* = 2-(methanehydrazonoyl)hydrazine-1-yl = 2-(hydrazinylidenemethyl)hydrazin-1-yl
For CH(=NH-NH2)-NH–
read CH(=N-NH2)-NH-
For P-67.1.4.1.1
read P-67.1.4.4.1
For P-65.1.7.3.1
read P-65.1.7.3.1 P-65.1.7.4.1
For P-65.1.7.3.1
read P-65.1.7.3.1 P-65.1.7.4.1
For P-65.1.7.3.1
read P-65.1.7.3.1 P-65.1.7.4.1
For 2-methanehydrazonoylhydrazine-1-yl = methanehydrazonohydrazido* = 2-(hydrazinylidenemethyl)hydrazin-1-yl
read 2-(methanehydrazonoyl)hydrazin-1-yl = methanehydrazonohydrazido* = 2-(hydrazinylidenemethyl)hydrazin-1-yl
For methanesulfinamido* = methanesulfinylamino
read methanesulfinamido* = (methanesulfinyl)amino
For methanesulfinylamino = methanesulfinamido*
read (methanesulfinyl)amino = methanesulfinamido*
For methanesulfonamido* = methanesulfonylamino
read methanesulfonamido* = (methanesulfonyl)amino
For methanesulfonylamino = methanesulfonamido*
read (methanesulfonyl)amino = methanesulfonamido*
For methanesulfonylazanylidene: see methanesulfonylimino*
read (methanesulfonyl)azanylidene = (methanesulfonyl)imino* = (methylsulfonyl)imino CH3-SO2-N= P-66.1.1.4.4
For methanesulfonylimino* = (methylsulfonyl)imino (not methanesulfonylazanylidene)
read (methanesulfonyl)imino* = (methylsulfonyl)imino = (methanesulfonyl)azanylidene
Add methanethioamido* = (methanethioyl)amino = thioformamido HCS-NH– P-66.1.4.4
For methanethioylamino
read (methanethioyl)amino
For P-65.6.3.2.2.2
read P-65.3.2.2.2
For P-65.1.7.2.3
read P-65.1.7.2.3; P-66.6.3
For methoxy* = methyloxy
read methoxy* (not methyloxy)
For 2-methoxyanilino* = (2-methoxyphenyl)amino (also 3- and 4-methoxy isomers) (not 2-anisidino)
read 2-methoxyanilino* = (2-methoxyphenyl)amino (also m = 3- and p = 4-methoxy isomers) (not 2-anisidino; not o-anisidino)
For methoxycarbonothioyl*
read methoxycarbonothioyl* = methoxythiocarbonyl
Add (2-methoxyphenyl)amino = 2-methoxyanilino* (also 3- and 4-isomers) (not 2-anisidino; not o-anisidino) 2-(CH3-O)-C6H4-NH– P-62.2.1.1.2
Add methoxythiocarbonyl = methoxycarbonothioyl* CH3-O-CS– P-65.2.1.5
For CH3O-SO-O–
read CH3-O-SO-O–
For CH3O-SO2-O–
read CH3-O-SO2-O–
For P-65.1.7.2.1
read P-65.1.7.2.1; P-66.6.1.3
Delete this correction.
For methyldiselanyl*
read methyldiselanyl* = methyldiseleno
Add methyldiseleno = methyldiselanyl* CH3-Se-Se– P-63.3.1
For methylditellanyl*
read methylditellanyl* = methylditelluro
Add methylditelluro = methylditellanyl* CH3-Te-Te– P-63.3.1
For 1-methylethenyl = prop-1-en-2-yl* (not isopropenyl)
read 1-methylethen-1-yl = prop-1-en-2-yl* = isopropenyl
For P-29.4.1; P-29.6.3
read P-29.4.1; P-29.6.3; P-57.1.4
For P-29.4.1
read P-29.4.1; P-29.6.3
For P-29.6.2.2
read P-29.3.2.2; P-29.4.1; P-29.6.2.2
Add 1-methylethoxy = propan-2-yloxy* = isopropoxy (CH3)2CH-O– P-63.2.2.2
For (also 3- and 4-isomers)
read (also m- = 3- and p- = 4-isomers)
Delete this correction.
For 2-methylpropan-2-yl* = tert-butyl (unsubstituted*)
read 2-methylpropan-2-yl = tert-butyl* (unsubstituted)
For (2-methylpropan-2-yl)oxy* = tert-butyl (unsubstituted*)
read (2-methylpropan-2-yl)oxy = tert-butoxy* (unsubstituted)
For 1-methylpropoxy = butan-2-yloxy*
read 1-methylpropoxy = (butan-2-yl)oxy*
For (not sec-butoxy)
read (not sec-butoxy; not sec-butyloxy)
For (not sec-butyl)
read (not sec-butyl; not but-2-yl)
For P-65.1.7.3.1
read P-65.1.7.3.1 P-65.1.7.4.1
For P-29.6.2.3 [corrected 24 March 2021]
read P-29.6.2.3; P-57.1.5.3
For P-67.1.4.1.1.5
read P-67.1.4.1.1.3
For P-65.1.7.3.1
read P-65.1.7.3.1 P-65.1.7.4.1
For P-29.6.3
read P-29.6.3; P-57.1.4
For (methylsulfanyl)oxy*
read (methylsulfanyl)oxy* [not (methylthio)oxy]
For S-methylsulfinimidoyl = see methanesulfinimidoyl*
read S-methylsulfinimidoyl = methanesulfinimidoyl*
For (methylsulfonyl)imino = (methanesulfonyl)imino*
read (methylsulfonyl)imino = (methanesulfonyl)imino* = (methanesulfonyl)azanylidene
Move (methylsulfanyl)sulfonyl* = (methylthio)sulfonyl CH3-S-SO2– P-65.3.2.3
For methyltellanyl* (not methyltelluro) CH3-Te– P-63.2.5
read methyltellanyl* = methyltelluro CH3-Te– P-63.2.5
For methyltelluro: see methyltellanyl*
read methyltelluro = methyltellanyl* CH3-Te– P-63.2.5
For methylthio = see methylsulfanyl*
read methylthio = methylsulfanyl*
For CH3-SO2–
read CH3-SeO2–
For P-63.2.5.1
read P-63.2.2.1.2, P-63.2.5
For P-63.2.5.1
read P-63.2.2.1.2, P-63.2.5
For P-63.2.2.1.2; P-63.2.5,1
read P-63.2.2.1.2; P-63.2.5
For P-65.3.2.3
read P-65.3.2.3; P-65.6.3.2.3
For P-63.2.2.1.2; P-63.2.5,1
read P-63.2.2.1.2; P-63.2.5
For P-65.6.3.3.1
read P-65.3.2.3; P-65.6.3.2.3
For P-29.3.3
read P-29.3.3; P-29.6.2.3; P-64.7.1
Move naphthalene-2,3-diylidene* 2,3-C10H6(=)2 P-29.3.4.1
Add naphthalen-1-yl(oxo)methyl = 1-naphthoyl = naphthalene-1-carbonyl* = 1-naphthylcarbonyl (also 2-isomer) 1-C10H7-CO– P-65.1.7.3.1; P-65.1.7.4.2
For 1-naphthylcarbonyl: see naphthalene-1-carbonyl*
read 1-naphthylcarbonyl = 1-naphthoyl = naphthalene-1-carbonyl* = naphthalen-1-yl(oxo)methyl (also 2-isomer) 1-C10H7-CO– P-65.1.7.3.1; P-65.1.7.4.2
For P-29.3.4.1;P-29.6.2.3 [corrected 24 March 2021]
read P-29.3.4.1; P-29.6.2.3; P-57.1.5.3
For nitramido* (not nitroamino)
read nitramido* = nitroamino
Add nitridostiboryl = stiboronitridoyl* N≡Sb< P-67.1.4.1.1.4
For aci-nitro: see hydroxy(oxo)-λ5-azanylidene*
read aci-nitro = hydroxy(oxo)-λ5-azanylidene* HO-N(O)= P-61.5.3; P-67.1.4.1.1.6; P-67.1.6
For P-29.3.4.1;P-29.6.2.3 [corrected 24 March 2021]
read P-29.3.4.1; P-29.6.2.3; P-57.1.5.3
For P-65.1.7.3.1; P-65.1.7.4.2
read P-65.1.7.3.1; P-65.6.3.2.3
For P-65.1.7.3.1
read P-65.1.7.3.1 ; P-65.1.7.4.1
For P-29.3.3.2; P-29.3.2.1
read P-29.3.2.2; P-29.3.2.1
For P-65.1.7.3.1
read P-65.1.7.3.1, P-65.1.7.4.1
For P-65.1.7.3.1
read P-65.1.7.3.1, P-65.1.7.4.1
For oxalimidoyl = ethanediimidoyl* = 1,2-diiminoethane-1,2-diyl
read oxalimidoyl = ethanediimidoyl* = diiminoethanediyl
For oxalosulfanyl* = (carboxycarbonyl)sulfanyl
read oxalosulfanyl* = (carboxycarbonyl)sulfanyl = (carboxycarbonyl)thio [not (carboxyformyl)sulfanyl; not (carboxyformyl)thio]
For oxalyl* = ethanedioyl
read oxalyl* = ethanedioyl = dioxoethanediyl
For oxalyldinitrilo* = oxalyldioylbis(azanetriyl) = ethanedioyldinitrilo = ethanedioylbis(azanetriyl)
read oxalyldinitrilo* = oxalylbis(azanetriyl) = ethanedioyldinitrilo = ethanedioylbis(azanetriyl)
For oxamoyl* = aminooxalyl = amino(oxo)acetyl (not carbamoylformyl)
read oxamoyl* = aminooxalyl = amino(oxo)acetyl (not carbamoylformyl; not carbamoylcarbonyl)
For H2NO–
read H2N(O)–
For P-65.1.7.2.1
read P-65.1.2.2.3; P-65.1.7.2.1
For P-65.1.7.2.4
read P-65.1.6.3; P-65.1.7.2.4
For oxooctadecyl = octadecanoyl* = stearoyl
read 1-oxooctadecyl = octadecanoyl* = stearoyl
For oxo(phenyl)methyl: see benzoyl*
read oxo(phenyl)methyl = benzoyl* = benzenecarbonyl= phenylcarbonyl
For P-65.1.7.3.1
read P-65.1.7.3.1; P-65.1.7.4.1
For P-65.1.7.3.1
read P-65.1.7.3.1, P-65.1.7.4.1
For P-65.1.7.2.1; P-66.6.3
read P-65.1.7.2.1; P-66.6.1.3
For P-65.1.7.3.1
read P-65.1.7.3.1, P-65.1.7.4.1
For P-65.1.7.3.1
read P-65.1.7.3.1; P-65.1.7.4.1
For P-65.1.7.2.1
read P-34.2.1.1; P-34.2.2; P-65.1.7.2.1
Add 1-oxopropyl = propanoyl* = propionyl CH3-CH2-CO– P-65.1.7.3.1; P-65.1.7.4.1
For 2-oxopropyl*
read 2-oxopropyl* = acetonyl
Add 2-oxopropylidyne* CH3-CO-C≡ P-64.5
For oxyl* = ylooxidanyl
read oxyl* = ylooxidanyl (not ylohydroxy)
For tert-pentyl = 2-methylbutan-2-yl* = 1,1-dimethylpropyl CH3-CH2-C(CH3)2– P-29.4.1; P-29.6.1
read tert-pentyl: see 2-methylbutan-2-yl*
For CH3-CO-CH3&ndash
read CH3-CO-CH2–
For P-65.1.1.2.3
read P-65.1.1.2.3; P-65.1.7.4.1
For P-65.1.7.3.1
read P-65.1.7.3.1 P-65.1.7.4.1
For P-63.2.2.1.1
read P-15.3.1.2.1.1; P-63.2.2.1.1
For P-65.1.7.3.1
read P-65.1.7.3.1 P-65.1.7.4.1
For P-65.1.7.3.1
read P-65.1.7.3.1, P-65.1.7.4.1
For pentylidyne* = pentan-1-ylidyne
read pentylidyne* = pentanylidyne
For 9-phenanthryl = see phenanthren-9-yl* (also 1-, 2-, 3-, and 4- isomer)
read 9-phenanthryl = phenanthren-9-yl* (also 1-, 2-, 3-, and 4- isomer) 9-C14H9– P-29.3.4.1, P-29.6.2.3, P-57.1.5.3
Add phenethyl: see 2-phenylethyl*
For P-29.3.4.1; P-29.6.2.3
read P-29.3.4.1; P-29.6.2.3; P-57.1.5.3
For phenoxy* = phenyloxy)
read phenoxy* (not phenyloxy)
For 1,4-phenylenebis(iminomethylene) = benzene-1,4-dicarboximidoyl* = terephthalimidoyl
read 1,4-phenylenebis(iminomethylene) = benzene-1,4-dicarboximidoyl* = terephthalimidoyl = 1,4-phenylenedicarbonimidoyl
For 1,2-phenylenebis(oxomethylene) = benzene-1,2-dicarbonyl*
read 1,2-phenylenebis(oxomethylene) = benzene-1,2-dicarbonyl* = phthaloyl = 1,2-phenylenedicarbonyl
For 1,3-phenylenebis(oxomethylene) = benzene-1,3-dicarbonyl*
read 1,3-phenylenebis(oxomethylene) = benzene-1,3-dicarbonyl* = isophthaloyl = 1,3-phenylenedicarbonyl
For 1,4-phenylenebis(oxomethylene) = benzene-1,4-dicarbonyl*
read 1,4-phenylenebis(oxomethylene) = benzene-1,4-dicarbonyl* = terephthaloyl = 1,4-phenylenedicarbonyl
Add 1,2-phenylenebis(sulfanylidenemethylene) = benzene-1,2-dicarbothioyl* 1,2-C6H4(CS–)2 P-65.1.7.4.3
For 1,4-phenylenebis(thioxomethylene): see benzene-1,2-dicarbothioyl*
read 1,2-phenylenebis(thioxomethylene) = benzene-1,2-dicarbothioyl* = 1,2-phenylenebis(sulfanylidenemethylene) (not dithiophthaloyl) (also 1,3- and 1,4-isomers) 1,2-C6H4(CS–)2 P-65.1.7.3.1; P-65.1.7.4.3
Add 1,4-phenylenedicarbonimidoyl = benzene-1,4-dicarboximidoyl* = terephthalimidoyl = 1,4-phenylenebis(iminomethylene) 1,4-C6H4(C=NH)2– P-65.1.7.3.2
For phenylethyl* (not phenethyl)
read 2-phenylethyl* (not phenethyl)
For phenylmethoxy = benzyloxy*
read phenylmethoxy = benzyloxy* C6H5-CH2-O– P-63.2.2.1.1
For phenylmethylidene = benzylidene*
read phenylmethylidene = benzylidene* (not benzal)
For phenyloxy : see phenoxy* C6H5-O– P-63.2.2.2
read phenyloxy : see phenoxy*
Add 4-phenylphenyl: see [1,1′-biphenyl]-4-yl*
For phenyl(sulfanylidene)methyl:: see benzenecarbothioyl*
read phenyl(sulfanylidene)methyl = benzenecarbothioyl* = thiobenzoyl = phenyl(thioxo)methyl
For (phenylsulfinyl)amino = benzenesulfinamido*
read (phenylsulfinyl)amino = benzenesulfinamido* = (benzenesulfinyl)amino
For (phenylsulfonyl)amino = benzenesulfonamido*
read (phenylsulfonyl)amino = benzenesulfonamido* = (benzenesulfonyl)amino
For P-67.1.7.3.1
read P-65.1.7.3.1
For phenylthio = see phenylsulfanyl*
read phenylthio = phenylsulfanyl*
For phenyl(thioxo)methyl: see benzenecarbothioyl*
read phenyl(thioxo)methyl = benzenecarbothioyl*= thiobenzoyl = phenyl(sulfanylidene)methyl
For phosphinimidoyl* = imidophosphinoyl
read phosphinimidoyl* = imidophosphinoyl = dihydrophosphorimidoyl
For phosphinothioyl* = thophosphinoyl
read phosphinothioyl* = thophosphinoyl = dihydrophosphorothioyl
For P-73.6
read P-73.6; P-74.1.3
For P-67.1.4.1.1.2
read P-67.1.4.1.1.4; P-67.1.4.1.2
For P-67.1.4.1.1.4
read P-67.1.4.1.1.2; P-67.1.4.1.2
For phosphoramidochloridyl* = amido(chlorido)phosphoryl
read phosphoramidochloridyl* = amidochlorophosphoryl (not chloroamidophosphoryl)
For phosphorocyanidoisocyanatidothioyl* = cyano(isocyanato)phosphorothioyl = cyano(isocyanato)(thiophosphoryl)
read phosphorocyanidoisocyanatidothioyl* = cyano(isocyanato)phosphorothioyl = cyano(isocyanato)thiophosphoryl
For piperidino = piperidin-1-yl*
read piperidino = piperidin-1-yl* = 1-piperidyl C5H19N– P-29.6.2.3, P-57.1.5.3
For phosphoroperoxoyl* = peroxyphosphoryl = hydroperoxyphosphoryl
read phosphoroperoxoyl* = peroxyphosphoryl = (hydroperoxy)phosphoryl
For phosphoro(thioperoxoyl)* = (thioperoxy)phosphoryl
read phosphoro(thioperoxoyl)* = (thioperoxy)phosphoryl = (thiohydroperoxy)phosphoryl
Add phthalimido = 1,3-dioxo-1,3-dihydro-2H-isoindol-2-yl*  P-66.2.2
P-66.2.2
For piperidino = piperidin-1-yl*
read piperidino = piperidin-1-yl* = 1-piperidyl C5H19N– P-29.6.2.3
For P-73.6
read P-73.6; ; P-74.1.3
For P-73.6
read P-73.6; ; P-74.1.3
For P-67.1.4.1.1.4
read P-67.1.4.1.1.4; P-67.1.5.2
Add 4-piperidyl = piperidin-4-yl*
For 1-piperidyl: see piperidin-1-yl*
read 1-piperidyl = piperidin-1-yl* = piperidino C5H19N– P-29.6.2.3; P-57.1.5.3
For plumbylidene* = plumbanylidene)
read plumbylidene* = plumbanylidene
For plumbylidyne* = plumbanylidyne)
read plumbylidyne* = plumbanylidyne
For propanediimidoyl* = malonimidoyl = 1,3-diiminopropan-1,3-diyl
read propanediimidoyl* = malonimidoyl = 1,3-diiminopropane-1,3-diyl
For P-29.6.2.3
read P-29.6.2.3; P-57.1.5.3
For P-29.6.2.3
read P-29.6.2.3; P-57.1.5.3
For P-65.1.7.3.1
read P-65.1.7.3.1 P-65.1.7.4.1
For propanethioyl* = thiopropionyl = 1-sulfanylidenepropyl
read propanethioyl* = thiopropionyl = 1-sulfanylidenepropyl = 1-thioxopropyl
Delete propan-1-ylidyne = propyidyne* CH3-CH2-C≡ P-29.3.2.2; P-29.3.2.1
For propan-2-yloxy* = isopropoxy = 1-methylethoxy
read (propan-2-yl)oxy* = isopropoxy = 1-methylethoxy
For P-65.1.7.3.1
read P-65.1.7.3.1; P-65.1.7.4.1
For P-29.2
read P-29.3.2.1; P-29.3.2.2
Add:
propylene: see propane-1,2-diyl*
For propyloxy = propoxy CH3-CH2-CH2-O– P-63.2.2.2
read propyloxy: see propoxy*
For CH3-CH2-C=
read CH3-CH2-CH=
For P-65.1.7.3.1
read P-65.1.7.3.1; P-65.1.7.4.1
For P-65.1.7.3.2
read P-65.1.7.3.2; P-65.1.7.4.1
For P-65.1.7.3.1
read P-65.1.7.3.1; P-65.1.7.4.1
For P-65.1.7.3.1; P-65.1.7.4.2
read P-65.1.7.3.1; P-65.6.3.2.3
Add
pyridinio = pyridin-1-ium-1-yl*
pyridin-1-ium-1-yl* = pyridinio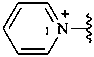
P-73.6
For pyruvoyl: see 2-oxopropanoyl* CH3-CO-CO– P-65.1.1.2.3
read pyruvoyl: see 2-oxopropanoyl*
For P-29.3.4.1, P-29.6.2.3
read P-29.3.4.1, P-29.6.2.3, P-57.1.5.3
For P-29.6.2.3
read P-29.6.2.3; P-57.1.5.3
For selaniumyl* = selenonio* = selenoniumyl
read selaniumyl* = selenonio = selenoniumyl
Add selano* = episeleno (ring formation) –Se– P-25.4.2.1.4; P-63.5
Add OSe-selenohydroperoxy = hydroxyselanyl* (not seleneno) HOSe– P-63.4.2.2
Add (OSe-selenohydroperoxy)methyl = (hydroxyselanyl)methyl* (HOSe)-CH2– P-63.4.2.2
For = selenonio’
read = selenonio
For P-63.2.5.1
read P-63.2.5
For P-65.3.2.1
read P-65.3.0; P-65.3.2.1
For P-65.3.2.1
read P-65.3.0; P-65.3.2.1
Add selenonyl –SeO2– P-65.3.2.3
Add semicarbazido = 2-carbamoylhydrazin-1-yl* = 2-(aminocarbonyl)hydrazin-1-yl H2N-CO-NH-NH– P-68.3.1.2.4
Add stannylene: see stannanediyl
For P-64.6.1
read P-29.3.1; P-64.6.1
For stibanylidene*
read stibanylidene* (not stibinylidene)
For stibinimidoyl* = imidostibinoyl
read stibinimidoyl* = imidostibinoyl = dihydrostiborimidoyl
Add stibinylidene: see stibanylidene*
For stiboronitridoyl*
read stiboronitridoyl* = nitridostiboryl
For H2Sb(O)
read H2Sb(O)–
For P-65.1.7.3.1
read P-65.1.7.3.1; P-65.1.7.4.1
For P-68.3.2.3.2.2
read P-56.4; P-68.3.2.3.2.2
For P-29.3.1; P-68.3.2.3.2.2
read P-29.3.1; P-56.4; P-68.3.2.3.2.2
For P-67.1.4.1.1.4
read P-67.1.4.1.1.4; P-67.1.4.1.2
For P-67.1.4.1.1.2
read P-67.1.4.1.1.2; P-67.1.4.1.2
For P-67.1.4.1.1.2
read P-67.1.4.1.1.2; P-67.1.4.1.2
Add succinimido = 2,5-dioxopyrrolidin-1-yl*  P-66.2.2
P-66.2.2
For P-65.1.7.3.1
read P-65.1.7.3.1 P-65.1.7.4.1
For sulfanediyl* (not thio)
read sulfanediyl* (not thio; not sulfenyl)
For sulfanediylbis(methylene)* (not sulfanediyldimethylene)
read sulfanediylbis(methylene)* (not sulfanediyldimethylene; not thiodimethylene)
For sulfanediyldimethylene: see sulfanediylbis(methylene)* –CH2-S-CH2– P-63.2.2.1.3
read sulfanediyldimethylene: see sulfanediylbis(methylene)*
Add sulfano* = epithio (ring formation) –S– P-25.4.2.1.4; P-63.5
For P-65.3.2.3:P-66.1.1.4.2
read P-65.3.2.3; P-66.1.1.4.2
For P-63.2.5.1
read P-63.2.5
Move left to align with line 6 and 8.
For sulfanylideneamino = thionitroso* = thioxoamino
read sulfanylideneamino* = thionitroso = thioxoamino
Add (sulfanylideneamino)sulfanyl* = (thionitroso)sulfanyl = (thioxoamino)sulfanyl S=N-S– P-67.1.4.3.2
For 1-sulfanylidenebutyl = butanethioyl* = thiobutyryl
read 1-sulfanylidenebutyl = butanethioyl* = thiobutyryl = 1-thioxobutyl
For 1-sulfanylidenepropyl = propanethioyl* = thiopropionyl
read 1-sulfanylidenepropyl = propanethioyl* = thiopropionyl = 1-thioxopropyl
Add sulfenyl: see sulfanediyl*
For CS=
read S=C=
For sulfinyldioxy = sulfinylbis(oxy)* –O-SO-O– P-65.3.2.3
read sulfinyldioxy: see sulfinylbis(oxy)*
For sulfuramidoyl = sulfamoyl* = aminosufonyl
read ulfuramidoyl = sulfamoyl* = aminosulfonyl
For P-65.3.2.1
read P-65.3.0; P-65.3.2.1
For P-65.3.2.1
read P-65.3.0; P-65.3.2.1
For P-67.1.4.4.1
read P-65.3.2.3, P-67.1.4.4.1
For P-67.1.4.4.1
read P-65.3.2.3, P-67.1.4.4.1
Delete this correction.
Delete this correction.
For sulfurodithioyl = sulfonodithioyl*
read sulfurodithioyl = sulfonodithioyl* –S(=S)2– P-65.3.2.3; P-67.1.4.4.1
Delete sulfuro(isothiocyanatido)thioyl = isothiocyanatosulfonothioyl* SCN-S(O)(S)– P-67.1.4.4.1
Add tellano* = epitelluro (ring formation) –Te– P-25.4.2.1.4; P-63.5
For tellureno = hydroxytellanyl*
read tellureno: see hydroxytellanyl*
Add OTe-tellurohydroperoxy = hydroxytellanyl* (not tellureno) HO-Te– P-63.4.2.2
Move here lines 2, 3, 4, 5, 6 and 7 from page 1509 including the corresponding formulae and rules.
For –(=NH)2–
read –S(=NH)2–
For P-67.1.4.4.1
read P-65.3.2.3; P-67.1.4.4.1
For P-67.1.4.4.1
read P-65.3.2.3, P-67.1.4.4.1
For P-63.2.5.1
read P-63.2.2.1.2; P-63.2.5
For P-65.3.2.1
read P-65.3.0; P-65.3.2.1
For P-65.3.2.1
read P-65.3.0; P-65.3.2.1
For P-29.3.1; P-64.6.1
read P-29.3.1; P-64.6.1; P-66.6.3
Add tetrathio = tetrasulfanediyl* –S-S-S-S– P-68.4.1.2
For = 1,4-phenylenebis(iminomethylene)
read = 1,4-phenylenedicarbonimidoyl
Move to below line 27 of page 1508.
For thenyl (2- isomer only) = thiophen-2-ylmethyl C4H3S-CH2– P-29.6.3
read thenyl (2- isomer only): see (thiophen-2-yl)methyl
For thio: see sulfanediyl* (not sulfenyl)
read thio: see sulfanediyl*
For thiobenzoyl = benzenecarbohioyl* = phenyl(sulfanylidene)methyl
read thiobenzoyl = benzenecarbohioyl* = phenyl(sulfanylidene)methyl = phenyl(thioxo)methyl
For HNS<
read HN(S)<
For P-65.1.7.3.1
read P-65.1.7.3.1; P-65.1.7.4.2
For P-29.6.2.3
read P-29.6.2.3; P-57.1.5.3
For thiobutyryl = butanethioyl* = 1-sulfanylidenebutyl
read thiobutyryl = butanethioyl* = 1-sulfanylidenebutyl = 1-thioxobutyl
For thioformamido: see methanethioamido*
read thioformamido = methanethioamido* = (methanethioyl)amino HCS-NH– P-66.1.4.4
For H{O/S)C-CO–
read H{S/O}C-CO–
For P-67.1.4.1.1.5
read P-67.1.4.1.1.4; P-67.1.4.1.1.5
For (not seleneno)
read (not hydroxythio; not sulfeno)
For SO-thiohydroperoxy = sulfanyloxy*
read SO-thiohydroperoxy = sulfanyloxy* (not mercaptooxy)
For (thiohydroperoxy)phosphoryl = phosphoro(thioperoxoyl)*
read (thiohydroperoxy)phosphoryl = phosphoro(thioperoxoyl)* = (thioperoxy)phosphoryl
Add P-67.1.4.1.1.4
For thionitroso* = sulfanylideneamino = thioxoamino
read thionitroso = sulfanylideneamino* = thioxoamino
For (thionitroso)sulfanyl*
read (thionitroso)sulfanyl = (sulfanylideneamino)sulfanyl* = (thioxoamino)sulfanyl
For 2-thiooxalo (position of sulfur not specified*) HO-CS-CO– or HS-CO-CO– P-65.1.7.2.4
read 2-thiooxalo: see hydroxy(sulfanylidene)acetyl
For thiophosphinoyl = phosphinothioyl*
read thiophosphinoyl = phosphinothioyl* = dihydrophosphorothioyl
For thiopropionyl = propanethioyl* = 1-sulfanilydenepropyl
read thiopropionyl = propanethioyl* = 1-sulfanilydenepropyl = 1-thioxopropyl
For thiosulfino (unspecified*)
read thiosulfino* (unspecified)
For thiosulfo* (unspecified*)
read thiosulfo* (unspecified)
For thioxoamino = thionitroso* = sulfanylideneamino
read thioxoamino = thionitroso = sulfanylideneamino*
Add (thioxoamino)sulfanyl = (sulfanylideneamino)sulfanyl* = (thionitroso)sulfanyl S=N-S– P-67.1.4.3.2
Add 1-thioxobutyl = butanethioyl* = 1-sulfanylidenebutyl = thiobutyryl CH3-CH2-CH2-CS– P-65.1.7.4.1
For 1-thioxopropyl: see propanethioyl*
read 1-thioxopropyl = propanethioyl* = thiopropionyl = 1-sulfanylidenepropyl CH3-CH2-CS– P-65.1.7.4.1
For S=N-SH–
read S=N-S–
read P-67.1.4.3.2
For P-29.6.2.3
read P-29.6.2.3; P-57.1.5.3
For H2{O2S}P–
read (HO)(HS)P(O)– or (HO)2P(S)–
For H{O/S}S
read H{S/O}S–
For P-67.1.4.1.1.4
read P-67.1.4.1.1.4; P-67.1.4.1.2
For P-64.6.1
read P-29.3.1; P-64.6.1
For (also m- and p-isomers)
read (also m- = 3- and p- = 4-isomers)
For (also m and p-isomers)
read (also m = 3- and p = 4-isomers)
For triaz-2-en-1-ium-1 -yl* = triaz-2-en-1-io
read triaz-2-en-1-ium-1-yl* = triaz-2-en-1-io [delete space in name]
For 2-triazeno: see triaz-2-en-1-yl* HN=N-NH– P-68.3.1.5.2
read triaz-2-eno: see triaz-2-en-1-yl*
For triaz-2-en-1-yl* (not 2-triazeno)
read triaz-2-en-1-yl* (not triaz-2-eno)
For trioxidanediyl*
read trioxidanediyl* = trioxy
Add trioxy = trioxidanediyl* –O-O-O– P-68.4.1.2
For triphenylmethyl* = trityl (unsubstituted*)
read triphenylmethyl* = trityl (unsubstituted)
For triselanediyl*
read triselanediyl* = triseleno
For triselanyl*
read triselanyl* = hydrotriseleno
Replace the structure with:
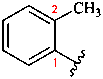
For –N=N-N–
read –N=N-NH–
For P-29.6.2.3
read P-29.6.2.3; P-57.1.5.3
Add triseleno = triselanediyl* –Se-Se-Se– P-68.4.1.2
For trisulfanediyl* = trithio)
read trisulfanediyl* = trithio
Add trisulfanyl* = hydrotrithio HS-S-S– P-68.4.1.3
For tritellanediyl*
read tritellanediyl* = tritelluro
For tritellanyl*
read tritellanyl* = hydrotritelluro
Add tritelluro = tritellanediyl* –Te-Te-Te– P-68.4.1.2-
For trithio = see trisulfanediyl*
read trithio = trisulfanediyl*
For trityl (unsubstituted*) = triphenylmethyl*
read trityl (unsubstituted) = triphenylmethyl*
For vinyl: see ethenyl*
read vinyl = ethenyl*
For vinylidene: see ethenylidene*
read vinylidene = ethenylidene*
For P-65.1.7.3.3
read P-65.1.7.2.4; P-65.1.7.3.3
Add ylooxy = ylooxidanyl* (not ylohydroxy) •O– P-71.5
For Alkaloids
read 1. Alkaloids
Replace the structure with:
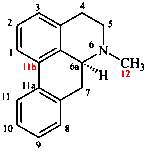
Replace the structure with:
Replace the structure with:
For cinchonan**
read cinchonan
Replace the structure with:
Replace structure with:
Replace the structure with:

Replace the structure with:

Replace the structure with:

For veratraman
read veratraman**
Replace the structure with:
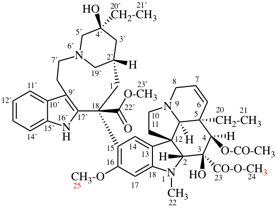
For vincane**
read vincane††
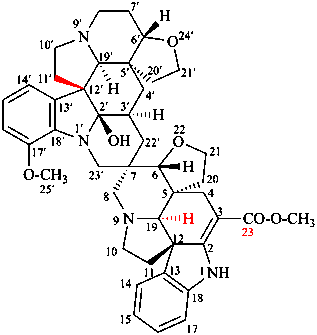

For spirostan
read spirostan††
For **These natural structures are named systematically by CAS.
read **These structures are named systematically by CAS.
For aristolane
read aristolane**
For beyerane**
read beyerane††
For **These natural structures are named systematically by CAS.
read **These structures are named systematically by CAS.
Replace the structure with:
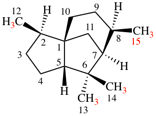

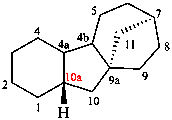
For steroids, 1511–1138
read steroids 1527–1531
For lignane
read lignane**
For 3,3′-neolignane
read 3,3′-neolignane**
For porphyrin††
read 21H,23H-porphyrin††
9 April 2025
Return to:
Bibliographic lists home page.
IUPAC Books