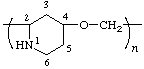
poly(piperidine-2,4-diyloxymethylene)
(heterocycle is senior to heteroatom; shorter path between them; Rules 1, 12)
Continued with 9. Examples of Polymer Names 61-79
Example 41

poly(piperidine-2,4-diyloxymethylene)
(heterocycle is senior to heteroatom; shorter path between them; Rules 1, 12)
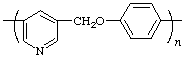
poly(pyridine-3,5-diylmethyleneoxy-1,4-phenylene)
(pyridine is senior to O; shorter path between them; Rules 1, 11, 12)
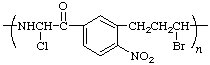
poly[imino(1-chloro-2-oxoethylene)(4-nitro-1,3-phenylene)(3-bromopropane-1,3-diyl)]
(heteroatom is senior to carbocycle; shorter path between them; Rules 1, 11)
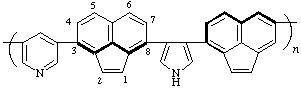
poly(pyridine-3,5-diylacenaphthylene-3,8-diylpyrrole-3,4-diylacenaphthylene-3,7-diyl)
(pyridine is senior to pyrrole; shorter path between them; heavy line denotes path followed; Rules 2d, 12)
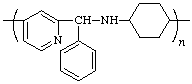
poly[pyridine-4,2-diyl(phenylmethylene)iminocyclohexane-1,4-diyl]
(heterocycle is senior to heteroatom; shorter path between them; Rules 1, 11, 12)
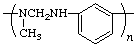
poly[(methylimino)methyleneimino-1,3-phenylene]
(heteroatoms are senior to carbocycle; shorter path through both N; substituted heteroatom is senior to the same unsubstituted heteroatom; Rules 1, 5, 11, 15)
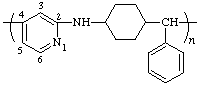
poly[pyridine-4,2-diyliminocyclohexane-1,4-diyl(phenylmethylene)]
(heterocycle is senior to heteroatom; shorter path between them; Rules 1, 11, 12)
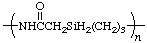
poly[imino(1-oxoethylene)silanediylpropane-1,3-diyl]
(N is senior to Si; shorter path; Rule 4)
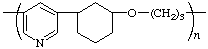
poly(pyridine-3,5-diylcyclohexane-1,3-diyloxypropane-1,3-diyl)
(of two equal paths of three atoms between heterocycle and heteroatom,the path through carbocycle is preferred; Rules 11, 12, 14)
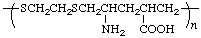
poly[sulfanediylethylenesulfanediyl(2-amino-4-carboxypentane-1,5-diyl)]
(shorter path from S to S; direction determined by lower locant for the substituent earlier in the alphabetical order; Rules 10e, 15)
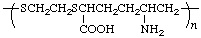
poly[sulfanediylethylenesulfanediyl(4-amino-1-carboxypentane-1,5-diyl)]
(shorter path through both S; lowest locants for substituents; Rules 10d, 15)
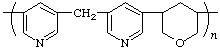
poly[pyridine-3,5-diylmethylenepyridine-3,5-diyl(tetrahydropyran-3,5-diyl)]
(shorter path between pyridine subunits; Rules 12, 15)

poly[sulfanediyl(2-chloropropane-1,3-diyl)sulfanediylpropane-1,3-diyl]
(substituted acyclic carbon chain is senior to unsubstituted; Rules 10c, 15)
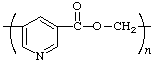
poly(pyridine-3,5-diylcarbonyloxymethylene)
(heterocycle is senior to heteroatom; substituted acyclic carbon chain is senior to unsubstituted one; Rules 1, 10c, 12)
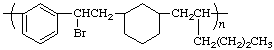
poly[1,3-phenylene(1-bromoethylene)cyclohexane-1,3-diyl(2-butylethylene)]
(least hydrogenated ring is senior; the direction is determined by the alphabetical order of the substituents in the carbon chain; Rules 9a, 10e, 11)
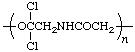
poly[oxy(1,1-dichloroethylene)imino(1-oxoethylene)]
(O is senior to N; of the two two-carbon chains the one with the larger number of substituents is senior; Rules 4, 10c)
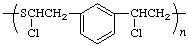
poly[sulfanediyl(1-chloroethylene)-1,3-phenylene(1-chloroethylene)]
(heteroatom is senior to carbocycle; of equal chains with the same substituents that with lower locant is senior; Rules 1, 10d)
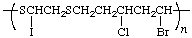
poly[sulfanediyl(1-iodoethylene)sulfanediyl(5-bromo-3-chloropentane-1,5-diyl)]
(shorter path through both S; direction determined by the lower locant of the iodo substituent; Rules 10d, 15)
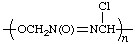
poly[oxymethylene-ONN-azoxy(chloromethylene)]
(O is senior to N; direction in the group -N(O)=N- is indicated by the prefix ONN; Rules 4, 7d)
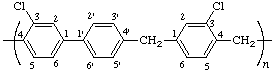
poly[(3-chlorobiphenyl-4,4'-diyl)methylene(3-chloro-1,4-phenylene)methylene]
(direction determined by the lower locant for the chloro substituent in biphenyl; Rules 9c, 9f, 11)