Nomenclature of Carbohydrates (Recommendations 1996)
2-Carb-24
Continued from 2-Carb-23
Contents
2-Carb-24. O-Substitution
2-Carb-24.1. Acyl (alkyl) names
Substituents replacing the hydrogen atom of an alcoholic hydroxy group of a saccharide or saccharide derivative are denoted as O-substituents. The 'O-' locant is not repeated for multiple replacements by the same atom or group. Number locants are used as necessary to specify the positions of substituents; they are not required for compounds fully substituted by identical groups. Alternative periphrase names for esters, ethers, etc. may be useful for indexing purposes. For cyclic acetals see 2-Carb-28.
Examples:
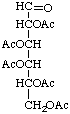
Penta-O-acetyl-aldehydo-D-glucose
or aldehydo-D-glucose pentaacetate
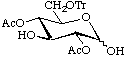
2,4-Di-O-acetyl-6-O-trityl-D-glucopyranose
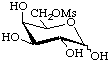
6-O-Methanesulfonyl-D-galactopyranose
or D-galactopyranose 6-methanesulfonate
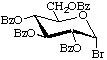
Tetra-O-benzoyl-α-D-glucopyranosyl bromide
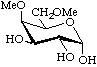
4,6-Di-O-methyl-α-D-galactopyranose
Note. Acyl substituents on anomeric OH are designated (as above) by O-acyl prefixes. However, anomeric O-alkyl derivatives are named as glycosides (see 2-Carb-33).
2-Carb-24.2. Phosphorus oxoacid esters
2-Carb-24.2.1. Phosphates
Of special biochemical importance are the esters of monosaccharides with phosphoric acid. They are generally termed phosphates (e.g. glucose 6-phosphate). In biochemical use, the term 'phosphate' indicates the phosphate residue regardless of the state of ionization or the counter ions.
The prefix terms used for phosphate esters in organic nomenclature ([14], p.65) are 'O-phosphono-' and 'O-phosphonato-' for the groups (HO)2P(O)- and (O-)2P(O)- respectively, bonded to oxygen.
The term 'phospho-' is used for (HO)2P(O)- or ionized forms in a biochemical context (see recommendations for the nomenclature of phosphorus-containing compounds [24]).
If a sugar is esterified with two or more phosphate groups, the compound is termed bisphosphate, trisphosphate etc. (e.g. fructofuranose 1,6-bisphosphate). The term diphosphate denotes an ester with diphosphoric acid, e.g. adenosine 5'-diphosphate.
Note. In abbreviations, a capital P is used to indicate a terminal -PO3H2 group or a non-terminal -PO2H- group (or dehydronated forms).
Examples:
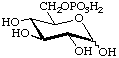
D-Glucopyranose 6-(dihydrogen phosphate)
or 6-O-phosphono-D-glucopyranose
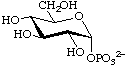
α-D-Glucopyranosyl phosphate
(biochemical usage: glucose 1-phosphate) (Glc1P)
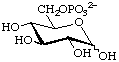
D-Glucopyranose 6-phosphate (often shortened to glucose 6-phosphate)
or 6-O-phosphonato-D-glucopyranose
or 6-phospho-D-glucose (Glc6P) (in a biochemical context)
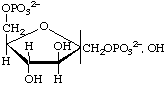
D-Fructofuranose 1,6-bisphosphate
(often shortened to fructose 1,6-bisphosphate)
or 1,6-di-O-phosphonato-D-fructofuranose
or 1,6-bisphospho-D-fructofuranose
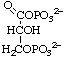
3-O-Phosphonato-D-glyceroyl phosphate
or 3-phospho-D-glyceroyl phosphate
or 1,3-bisphospho-D-glycerate (for biochemical usage)
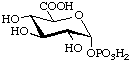
α-D-Glucopyranuronic acid
1-(dihydrogen phosphate)
(biochemical usage: glucuronate 1-phosphate) (GlcA1P)
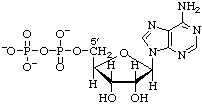
Adenosine 5'-diphosphate (ADP) or 5'-diphosphoadenosine
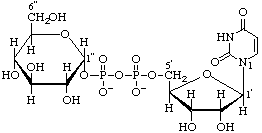
Uridine 5'-(α-D-glucopyranosyl diphosphate)
(trivial name uridinediphosphoglucose) (UDP-Glc)
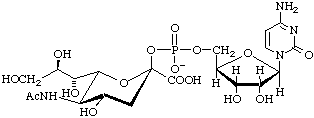
Cytidine 5'-(5-acetamido-3,5-dideoxy-D-glycero-β-D-galacto-non-2-ulopyranosylonic acid monophosphate) (CMP-β-Neu5Ac)
2-Carb-24.2.2. Phosphonates
The following examples illustrate the use of phosphonate terminology for esters of phosphonic acid, HP(O)(OH)2. For formation of the alternative (substitutive) names, see 2-Carb-31.2.
Examples:
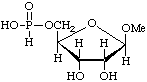
Methyl β-D-ribofuranoside 5-(hydrogen phosphonate)
or methyl 5-deoxy-β-D-ribofuranosid-5-yl hydrogen phosphonate
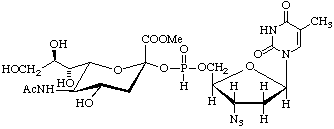
3'-Azido-3'-deoxythymidine5'-[(methyl 5-acetamido-3,5-dideoxy-
L-glycero-α-D-galacto-on-2-ulopyranosylonate) phosphonate]
Derivatives substituted on phosphorus are named by standard procedures [13, 14]; e.g. P-methyl derivatives are named as methylphosphonates.
Compounds with a phosphonate group linked by a P-C bond to a carbohydrate residue may be named as glycos-n-ylphosphonates (cf. 2-Carb-31.2) or as C-substituted carbohydrates (cf. amino sugars, 2-Carb-14).
Example:
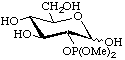
2-Deoxy-2-dimethoxyphosphoryl-D-glucopyranose
(this usage of 'phosphoryl' is given in [13], Section D, Rule 5.68, and [14], p. 65)
or dimethyl 2-deoxy-D-glucopyranos-2-ylphosphonate
2-Carb-24.2.3. Phosphinates
Esters of phosphinic acid, H2P(O)(OH), are named by the same methods as used for phosphonates. For examples with two P-C bonds see 2-Carb-31.3.
2-Carb-24.3. Sulfates
The prefix terms used for sulfuric esters are 'O-sulfo-' and 'O-sulfonato-', for the groups (HO)S(O)2- and (O-)S(O)2- respectively, bonded to oxygen. Sulfates may also be named by citing the word 'sulfate', preceded by the appropriate locant, after the carbohydrate name.
Example:
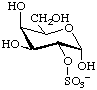
α-D-Galactopyranose 2-sulfate
or 2-O-sulfonato-α-D-galactopyranose
The mixed sulfuric phosphoric anhydride (PAdoPS or PAPS) of 3'-phospho-5'-adenylic acid is named as an acyl sulfate:
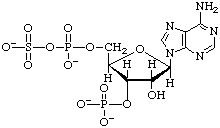
3'-Phospho-5'-adenylyl sulfate (PAPS)
References
13. IUPAC Nomenclature of Organic Chemistry, Sections A, B, C, D, E, F and H, 1979 Edition, Pergamon Press, Oxford, U.K. Sections E and F are reprinted in ref. 2, pp. 1-18 and 19-26, respectively.
14. Guide to IUPAC Nomenclature of Organic Compounds, Recommendations 1993, Blackwell Scientific Publications, Oxford (1993).
24. IUPAC-IUB Commission on Biochemical Nomenclature (CBN), Nomenclature of phosphorus-containing compounds of biochemical importance (Recommendations 1976), Hoppe-Seylers Z. Physiol. Chem., 358, 599-616 (1977); Eur. J. Biochem., 79, 1-9 (1977); Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 74, 2222-2230 (1977); Biochem. J., 171, 1-19 (1978); ref. 2. pp. 256-265.
Continue to the next section with 2-Carb-25 and 2-Carb-26 of Nomenclature of Carbohydrates.
Return to Carbohydrates home page.