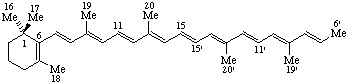Revised Section F: Natural Products and Related Compounds (IUPAC Recommendations 1999)
RF-4.3 and RF-4.4
Continued from RF-4.2 Addition of Skeletal Atoms without affecting the Number of Rings
Contents of this section
RF-4.3. Bond Formation
The creation of an additional ring by means of a direct link between any two atoms of a fundamental parent structure is described by the prefix cyclo preceded by the locants of the skeletal atoms so connected. Where necessary, the stereochemical configurations created by the new bond are denoted by α, β, or ξ as described under RF-10.
Examples:
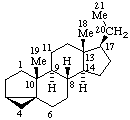 | 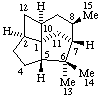 |
3α,5-Cyclo-5α-pregnane
(note that the cyclo bond in this drawing
is α relative to the other three bonds) | 10β,12-Cyclocedrane
(note that the locants for the methyl groups at position 6 were reversed in the
provisional Section F Rules (ref 1, 2)) |
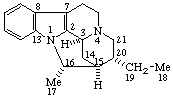 | 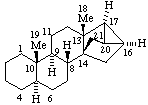 |
(16βH)-1,16-Cyclocorynan
(see RF-4.5.1 for the use of βH) 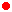 | (20S)-14,21:16β,20-Dicyclo-5α,14β-pregnane
(see RF-10.2.1 for the use of β at position 14) |
RF-4.4. Bond Cleavage
RF-4.4.1. Cleavage of a ring bond (saturated or unsaturated) with addition of the appropriate number of hydrogen atoms at each new terminal group thus created, is indicated by the prefix "seco-" and the locants of the cleaved bond. The original numbering is retained.
Examples:
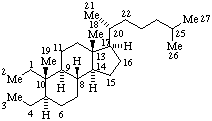 |  |
| 2,3-Seco-5α-cholestane | 13,14-Secopodocarpane  |
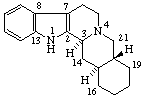 |  |
Yohimban
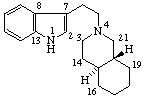
(fundamental parent structure) | 2,3-Secoyohimban |
Note: The configurations at positions 15 and 20 of the secoyohimban, above, are the same as those of yohimban. Reorientation of this portion of the molecule, as shown below, results in the hydrogen atoms at positions 15 and 20 apparently changing sides even though the configuration is unchanged. It is recommended that the configuration of substituents of such a seco-system is indicated by the R/S system. 
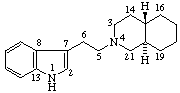 This situation has been recognized in the recommendations for naming Vitamin D compounds [9,10-seco steroids (ref 6)] where sequence rule descriptors (R/S) are recommended for describing all configurations in ring A, since these compounds are often drawn in an alternative orientation.
This situation has been recognized in the recommendations for naming Vitamin D compounds [9,10-seco steroids (ref 6)] where sequence rule descriptors (R/S) are recommended for describing all configurations in ring A, since these compounds are often drawn in an alternative orientation.
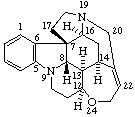 | 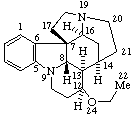 |
Strychnidine
(fundamental parent structure) | 21,22-Secostrychnidine |
RF-4.4.2. The unitalicized prefix "apo-" preceded by a locant is used to indicate removal of all of a side chain of a fundamental parent structure beyond the skeletal atom corresponding to that locant. Removal of two or more side chains is indicated by the prefixes "diapo-", "triapo-", etc., preceded by appropriate locants. Numbering of the skeletal atoms in the parent structure is retained in the resulting fragment.
Note: This procedure is used only in carotenoid nomenclature (ref 5). 
Example:
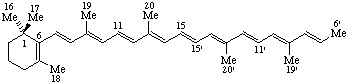
6'-Apo-β-carotene
References for this section
1. International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry, "Nomenclature of Organic Chemistry: Section F - Natural Products and Related Compounds, Recommendations 1976", IUPAC Information Bulletin Appendices on Tentative Nomenclature, Symbols, Units, and Standards, No. 53, December, 1976. [also in: Eur. J. Biochem. 86, 1-8 (1978)].
2. International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry, Nomenclature of Organic Chemistry, Sections A, B, C, D, E, F, and H, l979 edition, Pergamon Press, Oxford, 1979.
5. International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry and International Union of Biochemistry, Commission on Biochemical Nomenclature, "Nomenclature of Carotenoids", Pure Appl. Chem., 41, 405-431 (1975).
6. International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry and International Union of Biochemistry, Joint Commission on Biochemical Nomenclature, "Nomenclature of Vitamin D", Pure Appl. Chem. 54, 1511-1516, (1982). [also in: Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 218, 342-346 (1982), Endokrinol. Inf. No.2, 53-64 (1982), Eur. J. Biochem. 124, 223-227 (1982), and Mol. Cell. Biochem. 49, 177-181 (1982)].
Continue with RF-4.5 Bond Migration
Return to Section F: Natural Products home page.
Return to IUPAC chemical nomenclature home page.