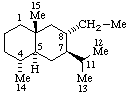 | 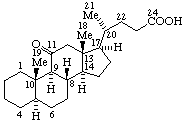 |
| 8α-Ethyleudesmane | 11-oxo-5α-cholan-24-oic acid |
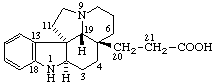 | 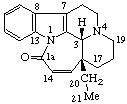 |
| Aspidospermidine-21-carboxylic acid | 1(14)a-Homoeburnamenin-1a-one |
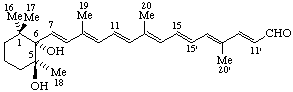
(5S,6S)-5,6-Dihydroxy-5,6-dihydro-10'-apo-β-caroten-10'-al
Contents of this section
Derivatives of parent structures are named according to the usual methods of systematic organic nomenclature (ref 2, 3) as far as possible.
The prefixes and suffixes of organic nomenclature are used in the prescribed manner to name atoms and groups that are considered to substitute for hydrogen atoms of parent structures. In naming derived acids and related characteristic groups, unmodified parent structures are used as far as possible.
Examples:
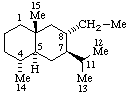 |  |
| 8α-Ethyleudesmane | 11-oxo-5α-cholan-24-oic acid |
 |  |
| Aspidospermidine-21-carboxylic acid | 1(14)a-Homoeburnamenin-1a-one |

(5S,6S)-5,6-Dihydroxy-5,6-dihydro-10'-apo-β-caroten-10'-al
RF-9.2. Modifications to Principal Characteristic Groups
Modifications to principal characteristic groups, such as esters, acetals, etc., are named by the usual methods of organic nomenclature. Cyclic modifications, such as lactones, cyclic acetals, etc., are named preferably as such rather than as fused ring, bridged, or spiro modified parent structures (see also RF-6.1).
Examples:
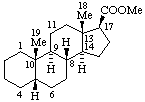 | 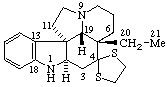 |
| Methyl 5β-androstane-17β-carboxylate | Aspidospermidin-4-one ethylene dithioketal |
RF-9.3. Substituent Prefix Names
Substituent prefix names for natural product parent structures may be formed in the usual way by adding a suffix, such as "-yl", "-diyl", "-ylidene", to the name of the parent structure with elision of the final "e", if any, of the parent structure name before "y".
Examples:
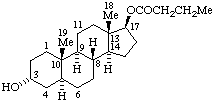
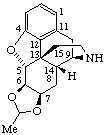 | 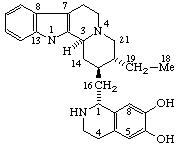 |
| Acetaldehyde 4,5α-epoxy morphinan-6β,7β-diyl acetal | (1R)-1-(17-Norcorynan-16-yl)-1,2,3,4-tetrahydroisoquinoline-6,7-diol |
RF-9.4. Ring Assemblies and Spiro Derivatives
Ring assemblies and spiro derivatives of parent structures are named in the usual manner (ref 2, 3).
Examples:
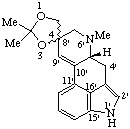 | 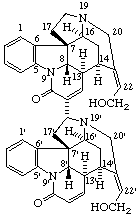 |
| (4ξ)-2,2,6'-Trimethyl-9',10'-didehydrospiro[1,3-dioxolane-4,8'-ergoline] | 11,11',12,12'-Tetradehydro- [11,18'α-bi-12,24-secostrychnidine]-10,10'-dione |
Note: In the ring assembly name (dione) above the hydroxy group is created by the seco operation. To provide for the explicit citation of the hydroxy group as a substituent, the oxygen atom could be removed first using the nor operation; this would be followed by the seco operation and the addition of the prefix "hydroxy-".
2. International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry, Nomenclature of Organic Chemistry, Sections A, B, C, D, E, F, and H, l979 edition, Pergamon Press, Oxford, 1979.
3. International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry, A Guide to IUPAC Nomenclature of Organic Compounds, Blackwell Scientific Publications, Oxford, 1993. [Corrections see Pure Appl. Chem., 71, 1327-1330 (1999).]