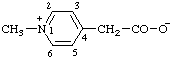
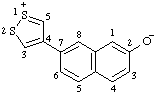
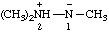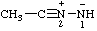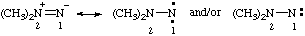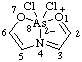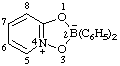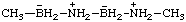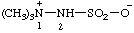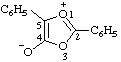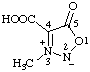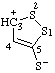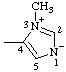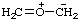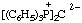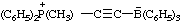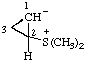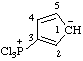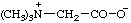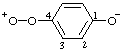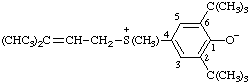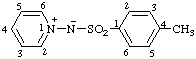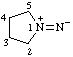Revised Nomenclature for Radicals, Ions, Radical Ions and Related Species
(IUPAC Recommendations 1993)
Rule RC-84. Cationic and anionic centers in a single structure
Continued from RC-83.4. Multiple Anionic Centers
Contents of this section
- Rule RC-84. Cationic and anionic centers in a single structure
- RC-84.1. Zwitterionic compounds having equal numbers of cationic and anionic centers in the same parent compound
- RC-84.1.1. Zwitterionic parent hydrides
- RC-84.1.2. Zwitterionic parent compounds with at least one ionic center on a characteristic group expressible an a suffix
- RC-84.2. Prefixes for zwitterionic parent hydrides as substituents
- RC-84.3. Ionic centers not in the same parent structure
RC-84. Cationic and anionic centers in a single structure (replaces C-871)
RC-84.1. Zwitterionic compounds having equal numbers of cationic and anionic centers in the same parent compound (including ionic centers on characteristic groups expressible as suffixes).
RC-84.1.1. Zwitterionic parent hydrides are named by combining appropriate operational suffixes (see RC-82.1.1.2, RC-82.2.2.1, RC-82.2.2.2, RC-83.1.2.1, and RC-83.2) at the end of the name of a neutral parent hydride, in the order "-ium", "-ylium", "-ide", and "-uide" or by citing ionic replacement prefixes (see C-82.4 and RC-83.3) in front of the name of the neutral parent hydride. In either case, anionic affixes are cited after cationic affixes in the name, and are given preference for low locants. An ionic or neutral characteristic group suffix, if present, may be added, if desired. The final "e" of the name of the parent hydride, or of an "-ide" or "-uide" suffix, is elided before "i" or "y", or before a functional suffix beginning with a vowel. Numerical prefixes, appropriate for each type of affix, are added to specify the number of each kind of ionic center. Where there is a choice, lowest locants are given to the ionic centers in the following order, listed in decreasing order of priority: "-uide" ("uida-"), "-ide" ("ida-"), "-ylium" ("ylia-") , and "-ium" ("onia-") .
Examples:
Note: Several trivial names for this compound have appeared in the literature, of which dimethylisodiazene and dimethylazamine are the least objectionable. The name 1,1-dimethyldiazene does not correspond to the structure and the name (dimethylamino)nitrene is considered to break a traditional principle of systematic substitutive nomenclature long established for naming acyclic hydrocarbons, i.e., that a homogeneous chain of atoms should not be broken. However, the effect of this principle in noncarbon systems is under study by the Commission.
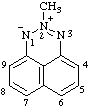
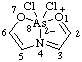 | 8,8-dichloro-1λ4,4λ5-[1,3,2]oxazarsolo[2,3-b][1,3,2]oxazarsole-1,4-bis(ylium)-8,8-diuide
[RC-82.3.1 and RC-83.2(a)] |
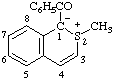 | 1-benzoyl-2-methyl-1H-isothiochromen-2-ium-1-ide
(RC-82.1.1.2 and RC-83.1.2.1)
1-benzoyl-2-methyl-1,2-dihydroisothiochromenylium-1-ide
(RC-82.3.2 and RC-83.1.2.1) |
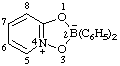 | 2,2-diphenyl-4λ5-[1,3,4,2]dioxazaborolo[4,5-a]pyridin-4-ylium-2-uide
[RC-82.3.1 and RC-83.2(a)]
2,2-diphenyl-4λ5,2λ5-[1,3,4,2]dioxazaborolo[4,5-a]pridin-4-ylium-2-ide
[RC-82.3.1 and RC-83.2(b)]
2,2-diphenyl-1,3-dioxa-3a-azonia-2-boranuidaindene
(RC-82.4 and RC-83.3)
[formerly 2,2-diphenyl-1,3-dioxa-3a-azonia-2-borataindene (ref 4s)] |
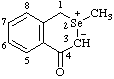 | 2-methylisoselenochroman-2-ium-3-id-4-one
(RC-82.1.1.2 and RC-83.1.2.1)
2-methyl-4-oxoisoselenochroman-2-ium-3-ide  |
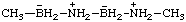 | 2,4-diaza-3,5-diborahexane-2,4-diium-3,5-diuide
[RC-82.1.1.2 and RC-83.2(a)]
2,4-diaza-3λ5,5λ5-diborahexane-2,4-diium-3,5-diide
(RC-82.1.1.2 and RC-83.1.2.1)
3,5-diazonia-2,4-diboranuidahexane
(RC-82.4 and RC-83.3)
[formerly 3,5-diazonia-2,4-diboratahexane (ref 4s)] |
(Note: In the third name, the ionic replacement name, the anionic centers are given preference for lowest locants, but in the first two names, in which neutral replacement prefixes and ionic suffixes are used, the neutral heteroatoms have priority for lowest locants.)
RC-84.1.2. Zwitterionic parent compounds with at least one ionic center on a characteristic group expressible as a suffix (see RC-82.1.2.1, RC-82.2.3.2, RC-82.2.3.3, RC-83.1.3.1, RC-83.1.3.3, RC-83.1.4, and RC-83.1.5) may be named by adding the appropriate ionic suffix to the name of an ionic parent hydride. Ionic centers on skeletal atoms of the ionic parent hydride are preferred to the position of attachment of ionic suffixes for assignment of lowest locants.
Examples:
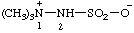 | 1,1,1-trimethyldiazan-1-ium-2-sulfonate
(RC-82.1.1.2 and RC-83.1.3.1)
1,1,1-trimethylhydrazin-1-ium-2-sulfonate
[traditional parent hydride name (ref 14)] (RC-82.1.1.2 and RC-83.1.3.1) |
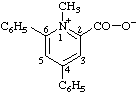 | 1-methyl-4,6-diphenylpyridin-1-ium-2-carboxylate
(RC-82.1.1.2 and RC-83.1.3.1) |
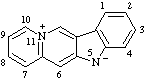
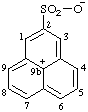 | 9bH-phenalen-9b-ylium-2-sulfonate (RC-82.2.2.2 and RC-83.1.3.1) |
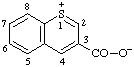 | 1λ4-thiochromen-1-ylium-3-carboxylate (RC-82.3.1 and RC-83.1.3.1)
thiochromenylium-3-carboxylate (RC-82.3.2 and RC-83.1.3.1) |
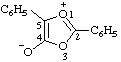 | 2,5-diphenyl-1λ4,3-dioxol-1-ylium-4-olate
(RC-82.3.1 and RC-83.1.4.2)
2,5-diphenyl-3-oxa-1-oxoniacyclopenta-1,4-dien-4-olate
(RC-82.4 and RC-83.1.4.2) |
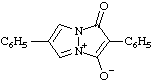
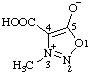 | 4-carboxy-3-methyl-1,2,3-oxadiazol-3-ium-5-olate
(RC-82.1.1.2 and RC-83.1.4.2) |
Note: This is one of the canonical forms of a sydnone. Other canonical forms can also be treated by these methods as shown by the following example:
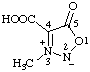 | 3-methyl-5-oxo-2,5-dihydro-1,2,3-oxadiazol-3-ium-2-ide-4-carboxylic acid
(RC-82.1.1.2, RC-83.1.2.1, and RC-83.1.2.2)
3-methyl-5-oxo-1,2,3-oxadiazol-3-ium-2(5H)-ide-4-carboxylic acid
(RC-82.1.1.2, RC-83.1.2.1, and RC-83.1.2.2) |
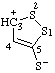 | 3H-1,2-dithiol-3-ylium-5-thiolate (RC-82.2.2.2 and RC-83.1.4.2) |
RC-84.2. Prefixes for zwitterionic parent hydrides as substituents are formed by replacing the final "e" of the name of the zwitterionic parent hydride (see RC-84.1.1), if present, by an operational suffix "-yl" or "-ylidene", or by adding a suffix such as "-diyl" to the name of the zwitterion. Where there is a choice, the free valence of the zwitterionic substituent prefix has preference for assignment of lowest locants.
Example:
RC-84.3. Ionic centers not in the same parent structure. A zwitterionic compound or an ionic compound in which all ionic centers are not in a single parent structure, or when it is not desired to include all ionic centers in one parent structure, is named by expressing the cationic centers or the parts of the structure containing the cationic centers as substituent prefixes to the name of an anionic parent compound (see RC-83).
Examples:
Note: The name "betaine" is also used as a class name for such zwitterionic compounds.
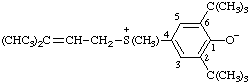
2,6-di-tert-butyl-4-[methyl(3-methylbut-2-en-1-yl)sulfonio]phenoxide
(RC-82.5.8.1, RC-83.1.4.1, and RC-80.8)
4-[methyl(3-methylbut-2-en-1-yl)-2,6-bis(2-methylpropan-2-yl)sulfoniumyl]phenoxide
(RC-82.5.8.3, RC-83.1.4.1, and RC-80.8)
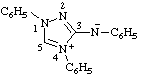 | N,1,4-triphenyl-1H-1,2,4-triazol-4-ium-3-aminide
(RC-82.1.1.2 and RC-83.1.5)
(1,4-diphenyl-1H-1,2,4-triazol-4-ium-3-yl)phenylamide
(RC-82.5.8.3 and RC-83.1.5)
(1,4-diphenyl-1H-1,2,4-triazol-4-ium-3-yl)phenylazanide
(RC-82.5.8.3 and RC-83.1.5) |
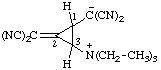
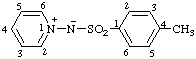 | N-(4-methylbenzenesulfonyl)pyridin-1-ium-1-aminide
(RC-82.1.1.2 and RC-83.1.5)
(4-methylbenzenesulfonyl)(pyridinio)amide
(RC-82.5.8.2 and RC-83.1.5)
(4-methylbenzenesuifonyl)(pyridin-1-ium-1-yl)azanide
(RC-82.5.8.3 and RC-83.1.5) |
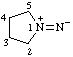 | pyrrolidin-1-ium-1-ylideneamide
(RC-82.5.8.3 and RC-83.1.6)
pyrrolidin-1-ium-1-ylideneazanide
(RC-82.5.8.3 and RC-83.1.6) |
References for this section
1. International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry. Organic Chemistry Division. Commission on Nomenclature of Organic Chemistry, Nomenclature of Organic Chemistry, Sections A, B, C, D, E, F and H, 1979 ed., Pergamon Press, Oxford, 1979, 559 p.
4. Reference 1, Section D, pp. 323-471: [s] Rule D-7.63, pp. 449-50.
14. International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry. Inorganic Chemistry Division. Commission on Nomenclature of Inorganic Chemistry, "Nomenclature of Inorganic Chemistry: II.2. The Nomenclature of Hydrides of Nitrogen and Derived Cations, Anions, and Ligands (Recommmendations 1981)" Pure Appl. Chem. 54, 2545-52 (1982), Rule II.2.1, p. 2546.
Continue with Rule RC-85. Radical ions
Return to ions and radicals home page.
Return to chemical nomenclature home page.