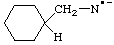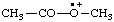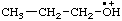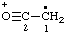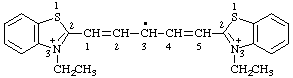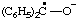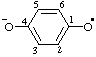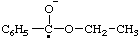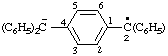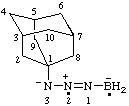Revised Nomenclature for Radicals, Ions, Radical Ions and Related Species
(IUPAC Recommendations 1993)
RC-85. Radical Ions
Continued from Rule RC-84. Cationic and anionic centers in a single structure
Contents of this section
- Rule RC-85. Radical ions
- RC-85.0. Introduction
- RC-85.1. Descriptive names
- RC-85.2. Radical ions derived from parent hydrides
- RC-85.3. Radical ions on characteristic groups
- RC-85.3.1. Radical ions on ionic suffix groups
- RC-85.3.2. Radical ions on characteristic groups other than those described by RC-85.3.1
- RC-85.4. Ionic and radical centers in different parent structures
RC-85. Radical ions [replaces C-83.3 and C-84.4 (ref 1)]
RC-85.0. Introduction. For the purposes of organic nomenclature, a radical ion is a molecular entity having at least one radical center (see RC-81.0) and one cationic center (see RC-82.0) or anionic center (see RC-83.0) or both (see RC-84.0), which may be on the same or on different atoms.
RC-85.1. Descriptive names. Radical ions derived formally from a neutral parent hydride, parent compound, or hydro derivative of either by the addition or removal of electrons may be named by adding the phrase "radical cation" or "radical anion" as separate words following the name of the neutral parent hydride or parent compound with the same molecular formula. The numerical prefixes "di-", "tri-", etc., are added to each term to indicate indicate multiple radical or ionic sites.
Alternatively, the phrase "radical ion" may be used with the type and amount of charge given by an appended parenthetical arabic number and appropriate charge sign (often called a Ewens-Bassett number (ref 21c) or a charge number (ref 6m), for example, radical ion(2-). Numerical prefixes are used to denote the number of radical centers, when more than one are present.
Note 1: These names are most useful when the positions of the radical and/or ionic sites are unknown, or when it is not necessary or desirable to indicate specific positions for such sites.
Note 2: It should be noted that, since the suffix denoting a radical center is cited last in systematic structural names, the phrase following the name of the neutral parent hydride or parent compound perhaps should be "cation radical", "anion radical", or "ion radical". This format is being used in the literature and, although not used in these recommendations, may be considered as an acceptable alternative.
Examples:
Note: In this document, a radical ion in an empirical formula is denoted by a superscript dot followed by the appropriate charge sign (ref 7). It is recognized that in mass spectroscopy the opposite sequence is used (ref 8), following well established tradition in that field.
| [C2H6]•+ | ethane radical cation
ethane radical ion(1+) |
| [C4H6]•+ | butadiene radical cation
butadiene radical ion(1+) |
| [(CH3)2Se=Se(CH3)]•+ | tetramethyl-1λ4,2λ4-diselene radical cation (ref 16)
tetramethyl-1λ4,2λ4-diselene radical ion(1+) (ref 16) |
| [CH3-SF5]•+ | pentafluoro(methyl)-λ6-sulfane radical anion (ref 16)
pentafluoro(methyl)-λ6-sulfane radical ion(1-) (ref 16) |
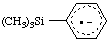 | (trimethylsilyl)benzene radical anion
(trimethylsilyl)benzene radical ion(1-) |
 | bicyclo[5.3.1]undeca-1,3,5,7,9-pentaene radical anion
bicyclo[5.3.1]undeca-1,3,5,7,9-pentaene radical ion(1-) |
| [C6H5-C6H5](2•)(2-) | biphenyl diradical dianion biphenyl diradical ion(2-) |
| [C14H10](•)(3-) | phenanthrene radical trianion phenanthrene radical ion(3-) |
RC-85.2. Radical ions derived from parent hydrides. A radical ion derived formally by the removal of one or more hydrogen atoms from a single skeletal atom or from different skeletal atoms of an ionic or zwitterionic parent hydride is named by replacing the final "e" of its name, if present, or by adding to its name, operational suffixes, such as "-yl", "-ylidene", "-diyl", etc. The λ-convention (ref 16) may offer a considerable advantage for naming such radical ions. However, the use of names in which the skeletal atoms are in standard valency states is preferred (see also Note 5 to RC-82.2.2.2 and the Notes to RC-82.4 and RC-83.3). Skeletal positions with radical centers have preference over skeletal positions with ionic centers for assignment of lowest locants.
Note: Added hydrogen (see RC-81.1.4, RC-82.2.2.4, and RC-83.1.2.2) is not considered necessary where the radical center is derived from a position at which a hydron or hydride ion has been added, i.e., at an "-ium" or "-uide" center.
Examples of radical cations:
| H2C•+ | methyliumyl
λ2-methaniumyl (ref 16) (see also RC-81.1.3.3)
carbynium (see also RC-81.1.3.1) |
| H4Si•+ | silaniumyl |
| [CH3-CH2](•)(2+) | ethaniumyliumyl |
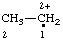 | ethan-1-ium-1-ylium-1-yl |
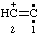 and/or and/or 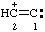 | ethen-2-ylium-1-ylidene 1λ2-ethen-2-ylium
(ref 16) (see also RC-81.1.3.3) |
 and/or [C6H6]•+ and/or [C6H6]•+ | benzeniumyl |
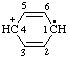 | cyclohexa-2,5-dien-4-ylium-1-yl |
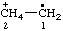 | ethan-2-ium-1-yl |
| (CH3)3N•+ | trimethylammoniumyl
trimethylazaniumyl |
| C6H5-N•+ | phenylazanyliumyl |
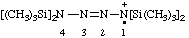 | 1,1,4,4-tetrakis(trimethylsilyl)tetraaz-2-en-1-ium-1-yl |
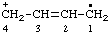 | but-2-en-4-ylium-1-yl |
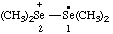 | tetramethyl-1λ4-diselan-2-ium-1-yl (ref 16) |
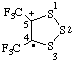 | 4,5-bis(trifluoromethyl)-1,2,3-trithiolan-5-ylium-4-yl |
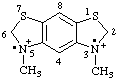 | 3,5-dimethyl-2,3,5,6-tetrahydrobenzo[1,2-d:5,4-d']bisthiazole-3,5-iium-3,5-diyl |
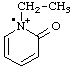 | 1-ethyl-2-oxo-1,2-dihydropyridin-1-ium-1-yl |
Examples of radical anions:
| HN•- | amidyl
azanidyl |
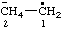 | ethan-2-id-1-yl |
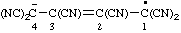 | hexacyanobut-2-en-4-id-1-yl |
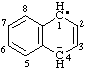 | 1,4-dihydronaphthalen-4-id-1-yl |
| (CH3)3B•- | trimethylboranuidyl [see also RC-83.2(a)]
trimethyl-λ5-boranidyl (ref 16) [see also RC-83.2(b)] |
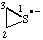 | 1λ4-thiiran-1-id-1-yl (ref 16) |
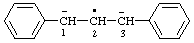 | 1,3-diphenylpropane-1,3-diid-2-yl |
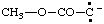 and/or and/or 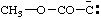 | (methoxycarbonyl)methanidylidene |
Examples of zwitterionic radical ions:
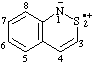 | 1H-benzo[c][1,2]thiazin-2-ium-1-id-2-yl
1H-2,1-benzothiazin-2-ium-1-id-2-yl (ref 3h) |
 | (triethylammonio)boranuidyl [see also RC-83.2(a)]
(triethylammonio)-λ5-boranidyl (ref 16) [see also RC-83.2(b)] |
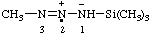 | 3-methyl-1-(trimethylsilyl)triaz-2-en-2-ium-1-id-2-yl |
RC-85.3. Radical ions on characteristic groups.
RC-85.3.1. Radical ions on ionic suffix groups. A radical ion derived formally by the removal of one or more hydrogen atoms from a cationic characteristic group given by Table 4 in RC-82.1.2.1 (except for acid suffixes), or the anionic characteristic group "-aminide" (RC-83.1.5), is named by adding an operational suffix, such as "-yl", "-ylidene" and "-diyl" to the ionic suffix, or by replacing the final "e" of the ionic suffix, if present, by an operational suffix.
Examples:
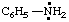 | aniliniumyl
benzenaminiumyl |
| CH3-N•- | methanaminidyl (see RC-83.1.5)
methylamidyl (see RC-83.1.5)
methylazanidyl (see RC-83.1.5) |
| CH3-CO-N•+ | acetamidyliumyl |
C6H5-C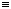 N•+ N•+ | benzonitriliumyl |
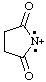 and/or and/or 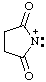 | succinimidiumylidene |
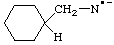 | cyclohexylmethanaminidyl
(cyclohexylmethyl)amidyl
(cyclohexylmethyl)azanidyl (see RC-83.1.5) |
RC-85.3.2. Radical ions on characteristic groups other than those described by RC-85.3.1. A radical ion derived formally by the removal of a hydrogen atom from an ionic characteristic group other than those in RC-85.3.1 above is named on the basis of a parent radical ion, named according to RC-85.2.
Examples:
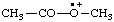 | acetyl(methyl)oxoniumyl |
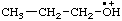 | propyloxoniumyl |
| CH2=C=O•+ | vinylideneoxoniumyl |
| CH3-CO-N•- | acetylamidyl
acetylazanidyl |
| C6H5-SO2-NH-N•- | 2-benzenesulfonyldiazan-1-id-1-yl |
RC-85.4. Ionic and radical centers in different parent structures. A radical ion derived formally by the removal of one or more hydrogen atom(s) from an ionic or zwitterionic compound in which the ionic centers and the radical positions cannot be included in the same parent structure is named by expressing the ionic center(s), or the part of the structure containing the ionic center(s), by means of substituent prefixes attached to the name of a parent radical the name of which is derived according to RC-81.1 or RC-81.2.
Examples:
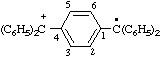 | [4-(diphenylmethyliumyl)phenyl]diphenylmethyl |
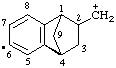 | 2-methyliumyl-1,2,3,4-tetrahydro-1,4-methanonaphthalene-2,6-diyl |
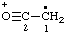 | 2-oxoniumylidyneethyl |
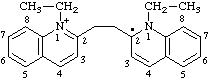
1-ethyl-2-[2-(1-ethylquinolin-1-ium-2-yl)ethyl]-1,2-dihydroquinolin-2-yl
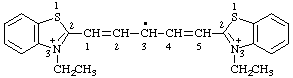
1,5-bis(3-ethylbenzo[d][1,3]thiazol-3-ium-2-yl)penta-1,4-dien-3-yl
1,5-bis(3-ethyl-1,3-benzothiazol-3-ium-2-yl)penta-1,4-dien-3-yl (ref 3h) 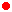
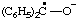 | oxidodiphenylmethyl |
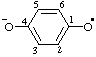 | 4-oxidophenoxyl |
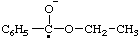 | ethoxy(oxido)phenylmethyl |
Note: The trivial name "benzyl" is not used as a substituent prefix when a-substituted (see footnote to item 17 in the Appendix, List A).
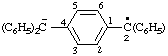 | [4-(diphenylmethanidyl)phenyl]diphenylmethyl |
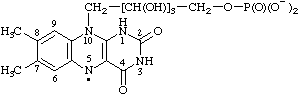
7,8-dimethyl-2,4-dioxo-10-[2,3,4-trihydroxy-5-(phosphonatooxy)pentyl]-1,2,3,4,5,10-hexahydrobenzo[g]pteridin-5-yl
(RC-81.1.4)
7,8-dimethyl-2,4-dioxo-10-[2,3,4-trihydroxy-5-(phosphonatooxy)pentyl]-2,3,4,10-tetrahydrobenzo[g]pteridin-5(1H)-yl
(RC-81.1.4)
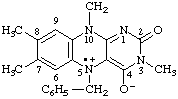
5-benzyl-3,7,8,10-tetramethyl-4-oxido-2-oxo-2,3,5,10-tetrahydrobenzo[g]pteridin-5-ium-5-yl 
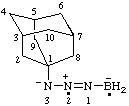
[3-(1-adamantyl)-2-ylotriaz-1-en-2-ium-3-id-1-yl]boranuidyl [RC-83.2(a)]
[3-(1-adamantyl)-2-ylotriaz-1-en-2-ium-3-id-1-yl]-λ5-boranidyl (ref 16) [RC-83.2(b)]
References for this section
1. International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry. Organic Chemistry Division. Commission on Nomenclature of Organic Chemistry, Nomenclature of Organic Chemistry, Sections A, B, C, D, E, F and H, 1979 ed., Pergamon Press, Oxford, 1979, 559 p.
3. Reference 1, Section B, pp. 53-76: [h] Rule B3.5, pp. 67-8.
6. International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry. Inorganic Chemistry Division. Commission on Nomenclature of Inorganic Chemistry, Nomenclature of Inorganic Chemistry, Recommendations 1990, G. J. Leigh, ed., Blackwell Scientific Publications, Oxford, England, 1990, 289 p. [m] Introduction, p. 11.
7. International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry, Compendium of Chemical Terminology (IUPAC Recommendations), V. Gold, K. L. Loening, A. D. McNaught, P. Sehmi, compilers, Blackwell Scientific Publications, Oxford, 1987, 456 p.
8. International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry. Physical Chemistry Division. Commission on Molecular Structure and Spectroscopy, "Recommendations for Nomenclature and Symbolism for Mass Spectroscopy, Recommendations 1991", Pure Appl. Chem. 63, 1541-66 (1991).
16. International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry. Organic Chemistry Division. Commission on Nomenclature of Organic Chemistry, Treatment of Variable Valence in Organic Nomenclature (Lambda Convention), Recommendations 1983, Pure Appl. Chem. 56, 769-78 (1984).
21. B. P. Block, W. H. Powell, and W. C. Fernelius, Inorganic Chemical Nomenclature: Principles and Practice, American Chemical Society, Washington, D. C., 1990, 210 pp., [c] Subsection 2.3.3, p. 15.
Continue with References (full list)
Return to ions and radicals home page.
Return to chemical nomenclature home page.
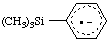

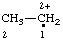
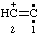 and/or
and/or 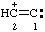
 and/or [C6H6]•+
and/or [C6H6]•+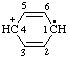
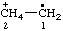
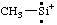 and/or
and/or 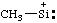
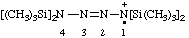
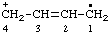
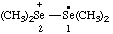
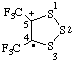

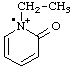
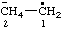
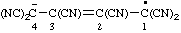

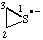
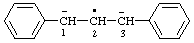
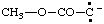 and/or
and/or 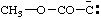


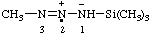
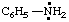
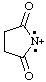 and/or
and/or